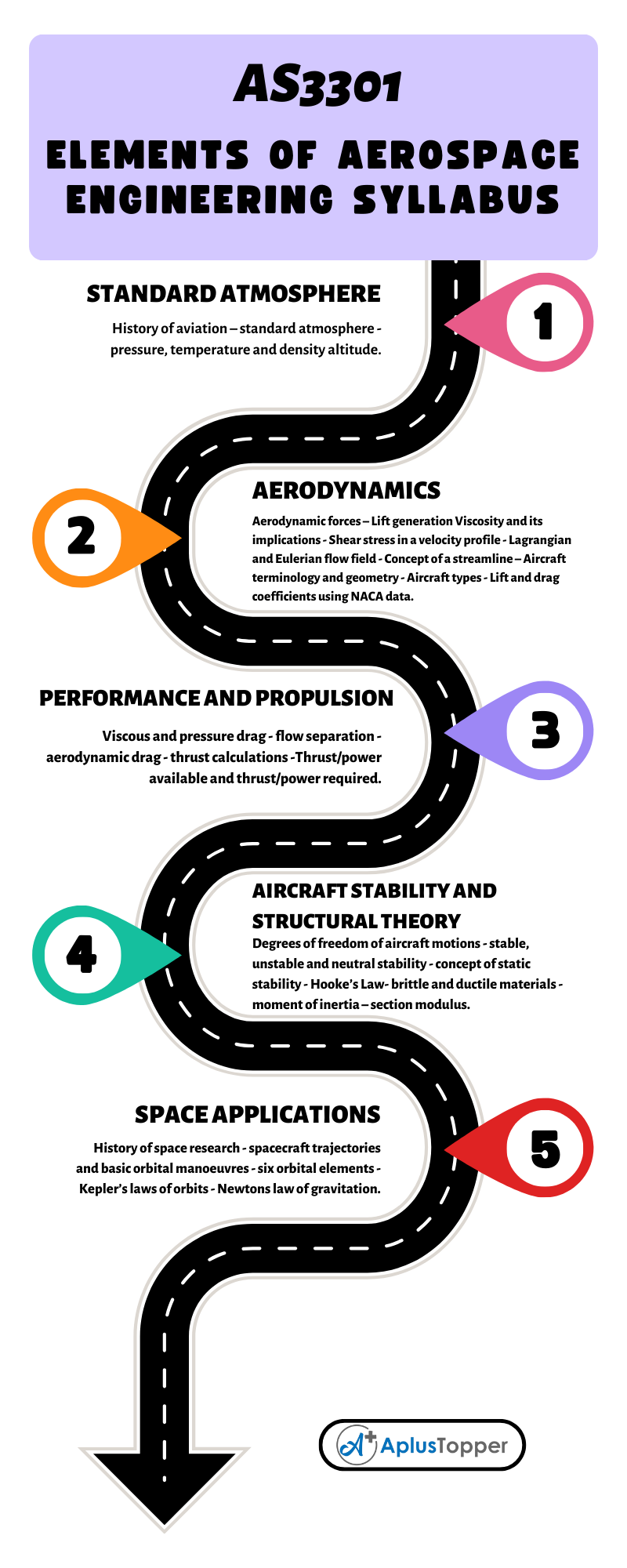
What is a Locus
What is a LocusLocusA locus is a set of points which satisfies a certain condition.As seen by the headlights (and taillights) in the picture below, a locus of points (the headlights or taillights) is the path traced out by the moving points under given …
Theorems Dealing with Parallelograms
Theorems Dealing with ParallelogramsDefinition: A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. Properties2 sets of parallel sides2 sets of congruent sidesopposite angles congruentconsecutive angles supplementarydiagonals …
Notation
NotationWhat’s the story on this notation between things that are congruent and those that are equal? The notation used in geometry can often be confusing. The major problems seem to develop when working with segments and angles. Let’s see if we can cla…
Converse
ConverseThe converse of a conditional statement is formed by interchanging the hypothesis and conclusion of the original statement. In other words, the parts of the sentence change places. The words “if” and “then” do not move.Example: Conditional: “If …
Concurrence
ConcurrenceLines that contain the same point are called concurrent. Concurrence is the concept of three or more lines intersecting in a single (common) point, having a single point of intersection.MediansA median of a triangle is a segment joining any ve…
Compound Locus
Compound LocusA compound locus problem involves two, or possibly more, locus conditions occurring at the same time. The different conditions in a compound locus problem are generally separated by the word “AND” or the words “AND ALSO”.Strategy for Solvi…
Theoretical vs Empirical Probability
Theoretical vs Empirical ProbabilityProbability describes the chance that an uncertain event will occur.Empirical Probability of an event is an “estimate” that the event will happen based on how often the event occurs after collecting data or running an…
Complement of an Event
Complement of an EventIf A is an event within the sample space S of an activity or experiment, the complement of A (denoted A’) consists of all outcomes in S that are not in A. The complement of A is everything else in the problem that is NOT in A.Consid…
Proofs with Similar Triangles
Proofs with Similar TrianglesDefinition: Two triangles are similar if and only if the corresponding sides are in proportion and the corresponding angles are congruent. There are three accepted methods of proving triangles similar: AATo show two triangle…
Mutually Exclusive Events
Mutually Exclusive Events An event is a set of outcomes. It is a subset of the sample space for an activity or experiment. Event: Drawing a black card from a deck of standard cards. Probability of this event = 26/52 = 1/2When an event corresponds to a s…