What Is An Electrical Fuse
What will happen if a large amount of electric current passes through an appliance? It causes
the wires to get overheated, and the appliance gets damaged. This situation arises as a result of some fault in the circuit and can be extremely dangerous as it can lead to a fire.

To prevent electric appliances from getting damaged from an excessive flow of current, a safety device called a fuse is used. A fuse is a safety device used in an electric circuit. An electric fuse prevents a large amount of current from flowing into any appliance or device as it cuts off the supply of electric current, thus preventing further damage.
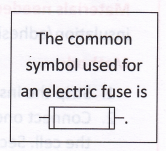
The common symbol used for an electric fuse is shown below.
Principle of an Electric Fuse
The electric fuse works on the principle of heating effect of current. The amount of heating caused depends on the amount of current flowing through the wire. The greater the current, the more is the heating caused.
An electric fuse consists of a thin wire usually placed inside a glass or ceramic cartridge. The wire is made of a material that melts easily when heated. It is designed such that only a certain amount of current can flow through it. If the current exceeds this amount, the heating in the wire causes it to melt. We say that the fuse ‘blows’. This breaks the circuit and stops the flow of current in the circuit.
