Some Common Measuring Instruments
- The measuring tape is used to measure lengths of several meters. Measurements are accurate up to 0.01 m. It is suitable for measuring the distance jumped by a long jumper, the distance of the throw of a javelin and the height of a jump by a high jumper.
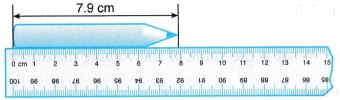
- The meter rule is used to measure lengths of a few centimeters to a meter. Measurements are accurate up to 0.1 cm. It can be used to measure the length of a pencil, the width of a book and the height of a school bag.
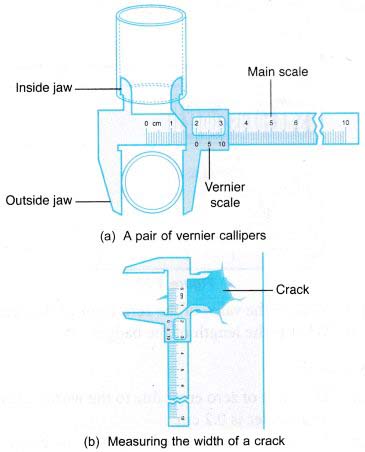
- The vernier callipers is used to measure lengths of less than 10 cm. Measurements are accurate up to 0.01 cm. It can be used to measure the external and internal diameters of round objects like pipes and cylindrical containers. It can also measure the thickness of a book, a piece of glass pane and even the width of a crack.
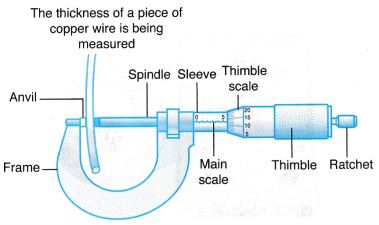
- The micrometer screw gauge is used for very small readings. Measurements are accurate up to 0.01 mm. It can be used to measure the thickness of a cardboard, a coin or a key and the diameter of a piece of wire.
Reading the Vernier Callipers
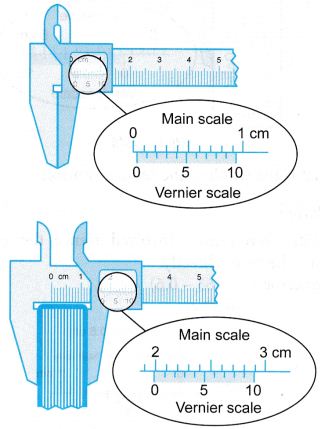
Example 1. Figure shows a pair of vernier callipers being used to measure the diameter of a metal pipe.
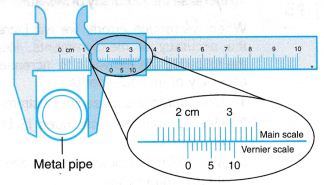 Solution:
Solution:
Reading on main scale = 2.1 cm
Reading on the vernier scale = 0.07 cm
Therefore, the diameter of the metal pipe = 2.1 + 0.07
= 2.17 cm
Example 2. A boy uses a pair of vernier callipers to measure the width of a handphone as shown in Figure.
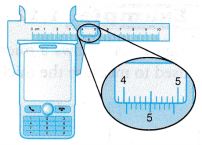 What is the reading of the vernier callipers?
What is the reading of the vernier callipers?
Solution:
Reading on main scale = 4.0 cm
Reading on the vernier scale = 0.04 cm
Therefore, the width of the handphone = 4.0 + 0.04 = 4.04 cm
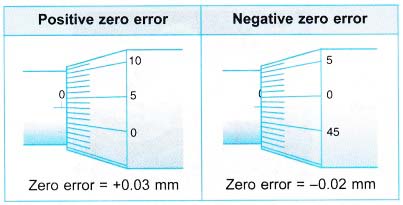
Zero Errors in Vernier Callipers
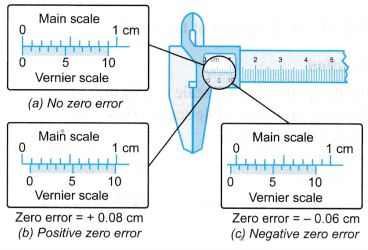 Above Figure shows three possible situations when using a pair of vernier callipers, that is,
Above Figure shows three possible situations when using a pair of vernier callipers, that is,
(a) no zero error,
(b) positive zero error,
(c) negative zero error.
Hence,
Correct reading = Reading obtained – Zero error
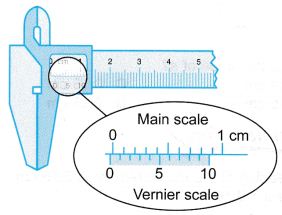
Example 3. Figure shows a pair of vernier callipers with zero error being used to measure the thickness of a book.
 What is the thickness of the book?
What is the thickness of the book?
Solution:
Zero error = +0.03 cm
Reading with zero error = 1.99 cm
Therefore, the thickness of the book
= 1.99 – 0.03
= 1.96 cm
Example 4. Figure shows a pair of vernier callipers with zero error being used to measure the width of a remote control.
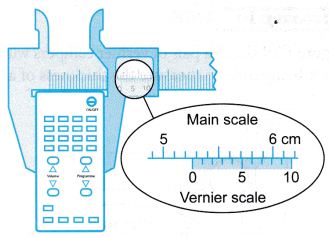 What is the width of the remote control?
What is the width of the remote control?
Solution:
Negative zero error is involved. Hence, the reading cannot be made directly.
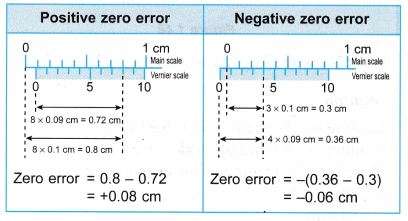
Zero error = -(0.63 – 0.6)
= -0.03 cm
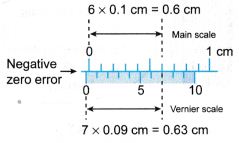
Reading with zero error = 5.26 cm
Therefore, the width of the remote control = 5.26 – (-0.03)
= 5.29 cm
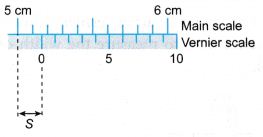
Example 5. The diagram shows the position of a vernier scale at the main scale of a vernier calipers. What is the value of s?
 Solution:
Solution:
The reading of the measurement is 5.16 cm.
Hence s = 0.16 cm.
Reading the Micrometer Screw Gauge
Example 6. Figure shows a micrometer screw gauge being used to measure the thickness of a coin.
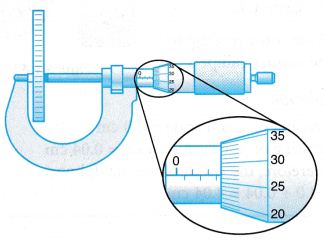 What is the thickness of the coin?
What is the thickness of the coin?
Solution:
Reading on the main scale = 2.50 mm
Reading on the thimble scale = 0.27 mm
Thickness of the coin = (2.50 + 0.27) mm
= 2.77 mm
Example 7. Figure shows the scale of a micrometer screw gauge.
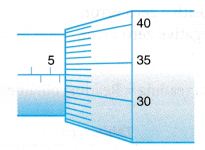 What is the reading of the micrometer?
What is the reading of the micrometer?
Solution:
Reading on the main scale = 5.50 mm
Reading on the thimble scale = 0.33 mm
Therefore, the reading of the micrometer = 5.50 + 0.33
= 5.83 mm
Zero Errors in Micrometer Screw Gauge
There are two possible types of zero errors in using the micrometer screw gauge, that is the positive zero error and the negative zero error.
Example 8. Figure (a) shows the zero error of a micrometer screw gauge and Figure (b) shows its subsequent reading of a measurement.
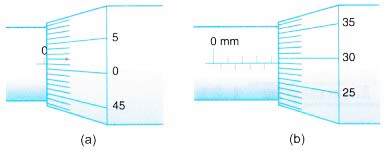 What is the actual value of the measurement?
What is the actual value of the measurement?
Solution:
Zero error = +0.01 mm Reading = 4.29 mm
Actual value of measurement = 4.29 – 0.01
= 4.28 mm
Example 9. Figure (a) shows the zero error of a micrometer screw gauge and Figure (b) shows its subsequent reading of a measurement.
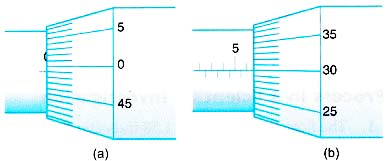 What is the actual value of the measurement?
What is the actual value of the measurement?
Solution:
Zero error = -0.01 mm
Reading = 6.30 mm
Actual value of measurement = 6.30 – (-0.01)
= 6.31 mm
