Univariate vs Bivariate Data
Univariate and Bivariate distribution
“If it is proved true that in a large number of instances two variables tend always to fluctuate in the same or in opposite directions, we consider that the fact is established and that a relationship exists. This relationship is called correlation.”
- Univariate distribution: These are the distributions in which there is only one variable such as the heights of the students of a class.
- Bivariate distribution: Distribution involving two discrete variable is called a bivariate distribution. For example, the heights and the weights of the students of a class in a school.
- Bivariate frequency distribution: Let x and y be two variables. Suppose x takes the values x1, x2, …., xn and y takes the values y1, y2, ….., yn then we record our observations in the form of ordered pairs (x1, y1), where 1 ≤ i ≤ n, 1 ≤ j ≤ n. If a certain pair occurs fij times, we say that its frequency is fij.
The function which assigns the frequencies fij’s to the pairs (xi, yj) is known as a bivariate frequency distribution.
Difference between Univariate and Bivariate Data
Univariate data means “one variable” (one type of data).
Bivariate data means “two variables” (two types of data).
| Univariate Data | Bivariate Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sample question: How many of the students in the freshman class are female? | Sample question: Is there a relationship between the number of females in Computer Programming and their scores in Mathematics? |
Covariance
Let (xi, yj); i = 1, 2, …., n be a bivariate distribution, where x1, x2, …., xn are the values of variable x and y1, y2, ….., yn those of y. Then the covariance Cov (x, y) between x and y is given by
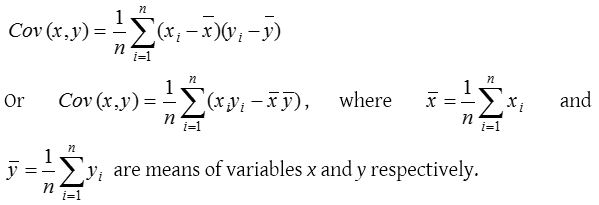
Covariance is not affected by the change of origin, but it is affected by the change of scale.
