What are the Types of Epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue :
Epithelial tissue is a simplest as a protective covering.
Function of epithelial tissue:
- Epithelial cover the body surface as an outer layer of skin and provide protection to the underlying tissues from mechanical injury, drying up, entry of germs (viral or bacterial pathogens), and harmful chemicals.
- Epithelia forms inner lining of mouth, alimentary canal and other internal organs inside the body and protect these organs.
- Epithelial lining of the intestine absorbs water and digested food.
- Epithelial tissues help in the elimination of nitrogenous and other waste products.
- Epithelial lining of the cavities give rise to glands that provide valuable secretions such as mucus, gastric juice, etc.
Types of epithelial tissue :
1. Squamous epithelium :
- Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered with squamous epithelium.
- The skin, which protects the body, is also made of squamous epithelium.
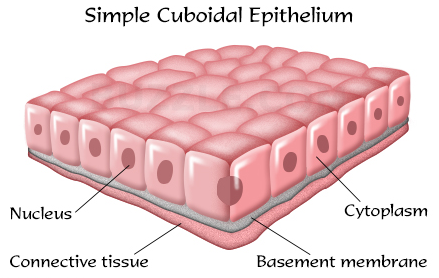
2. Cuboidal epithelium :
- Structure. This epithelium consists of cube-like cells which are about as tall as wide. The outline of cells is polygonal in surface view and square in section.
- Occurrence. The cuboidal epithelium lines the small salivary ducts, pancreatic ducts, sweat glands, salivary glands and thyrid glands. It also covers the ovaries and lines the sperm-producing tubules.
- Function. It helps in protection , secretion, absorption, excretion and gamete formation.
- Cuboidal epithelium (with cube-shaped cells) forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support.
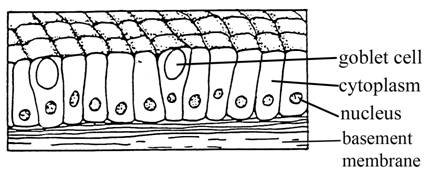
3. Columnar epithelium
- This epithelium consists of tall or pillar-like cells that are much taller than wide. The nuclei are generally elongated along the long axis of cells.
- Occurrence. The columnar epithelium lines the stomach, intestine and gall bladder. It also lines mammary gland ducts and parts of urethra.
- Function. It helps in protection, absorption and secretion. Columnar epithelium of intestine is specialized for the absorption of water and digested food.
Columnar epithelium
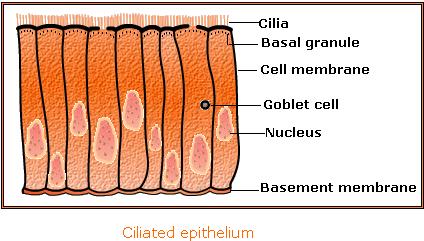
4. Cilliated epithelium :
- Structure. This epithelium consists of cuboidal or columnar cells that bear cilia on their free surfaces. A cilium is fine, vibratile cytoplasmic outgrowth that arises from a minute basal granule.
- Occurrence. Cuboidal ciliated epithelium lines certain parts of urinary tubules of the kidney and sperm ducts. Columnar ciliated epithelium lines the nasal passages, oviducts (fallopian tubes), terminal bronchioles and ventricles of the brain.
- Function. This epithelium helps in the movement of mucus, urine, eggs, sperms and cerebrospinal fluid in a particular direction.
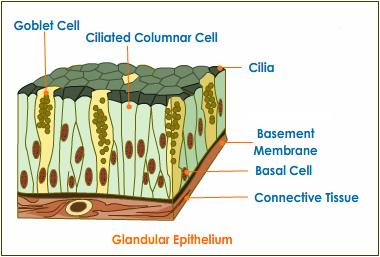
5. Glandular epithelium :
- This epithelium consists of columnar cells modified to secrete chemicals. It lines the glands such as gastric glands, pancreatic lobules, intestinal glands, etc.