Which Type of Image is Formed by a Plane Mirror?
When you look into a plane mirror, you will see an image of yourself which has the following characteristics:
- Your image is upright.
- Your image is the same size as you are.
- Your image is at the same distance as you are from the mirror.
(Object distance = Image distance) - Your left and right sides are interchanged in your image. So, your left hand becomes the right hand of your image. When this happens, your image is said to be laterally inverted.
- Your image is behind the mirror and cannot be seen on the screen. Your image is known as a virtual image.
People also ask
- What is Reflection of Light?
- Analysing Reflection of Waves
- What is the Law of Reflection of Light?
- Application of Reflection of Light in Daily Life
- What do you mean by Total Internal Reflection?
- Applications of Total Internal Reflection
- Image Reflection by a Plane Mirror
- Is an Image formed by Reflection Real or Virtual
- Reflection of Light from Spherical Mirror
- What are Concave and Convex Mirrors?
- How is Focal Length related to Radius of Curvature?
- How is the Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror?
Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors
The characteristics and the position of the image formed by a plane mirror can be determined by drawing a ray diagram.
The following are the steps to draw a ray diagram when viewing an object in a plane mirror.
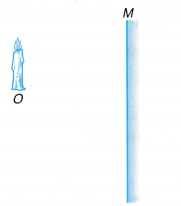
- The object, O (the candle) is placed in front of a mirror, M.
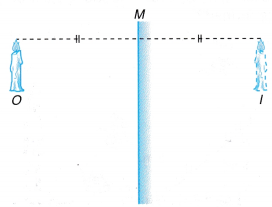
- The position of its image, I is located. The image distance is equal to the object distance, OM = IM. The image size is same as the object size. The line joining the object, O and the image, I is perpendicular to the mirror, M.
- The reflected rays are drawn as if they are from the image, I. The image is virtual. Therefore, the rays behind the mirror do not exist. They are virtual rays and are represented by dotted lines. The continuous lines from the mirror to the eye indicate the reflected rays.
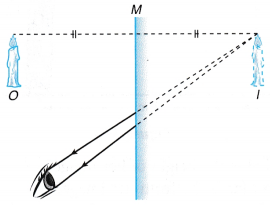
- The incident rays are drawn from the object, O to the mirror, M. Lines joining the object to the positions of the reflected rays on the mirror represent the incident rays.
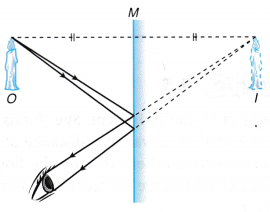
Image is Formed by a Plane Mirror Example Problems with Solutions
- A woman of height 1.5 m stands 3 m in front of a plane mirror as shown in Figure.
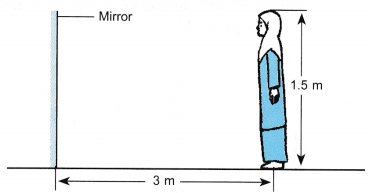
(a) What is the height of her image?
(b) How far is she from her image?
(c) If she walks 2 m towards the mirror, how far is she from her image now?
Solution:
(a) Height of image = 1.5 m
(b) Distance from image
= 3 + 3
= 6 m
(c) Distance from mirror
= 3 – 2
= 1 m
Distance from image
= 1 + 1
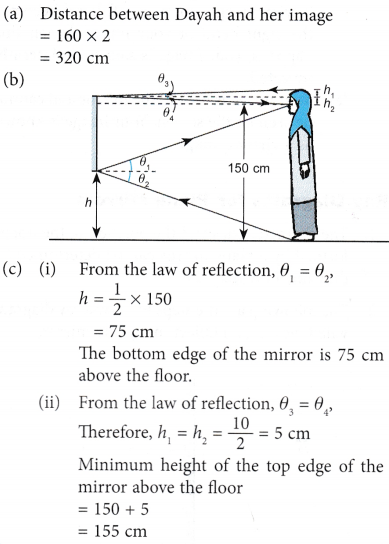
= 2 m - The height of Dayah is 160 cm. She stands facing a mirror mounted on a wall at a distance of 160 cm. The distance between her eyes and the floor is 150 cm and she could just see her feet at the bottom edge of the mirror.
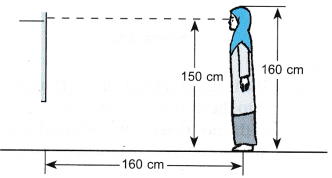
(a) What is the distance between Dayah and her image in the mirror?
(b) Draw light rays to show how she could see her head and her feet.
(c) (i) How high above the floor is the bottom edge of the mirror?
(ii) What is the minimum height of the top edge of the mirror from the floor if she is able to see the top of her head?
Solution:
- Diagram shows a student standing 5 m in front of a mirror.
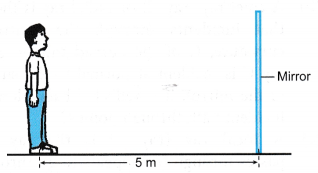
If the mirror is moved towards the student by a distance of 1 m, what is the distance between the student and his image?
Solution:
The distance between the student and the mirror is now (5 – 1) = 4 m.
Therefore, the distance between the student and his image is (4 m + 4 m) = 8 m.
