ICSE Class 10 Biology Transpiration Questions and Answers
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 4 Transpiration for ICSE Board Examinations. We provide step by step Solutions for ICSE Biology Class 10 Solutions Pdf. You can download the Class 10 Biology ICSE Textbook Solutions with Free PDF download option.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
Short Questions
Question 1: Define transpiration.
Answer: Transpiration is a process in which excess of water is lost in the form of vapours from the aerial parts of the plant.
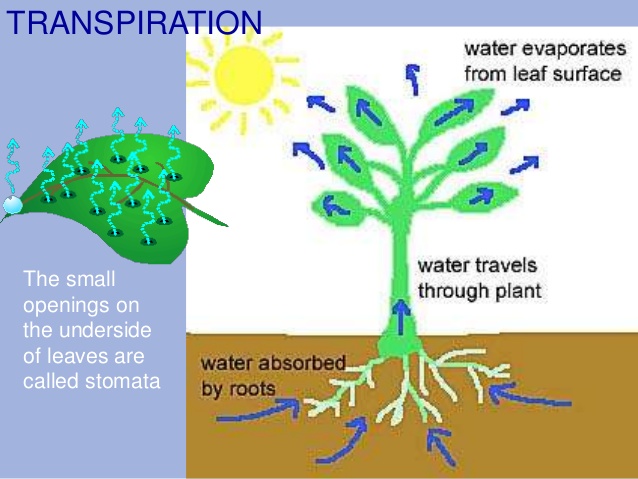
Question 2: Name the three types of transpiration.
Answer: (i) Stomatal transpiration.
(ii) Lenticular transpiration.
(iii) Cuticular transpiration.
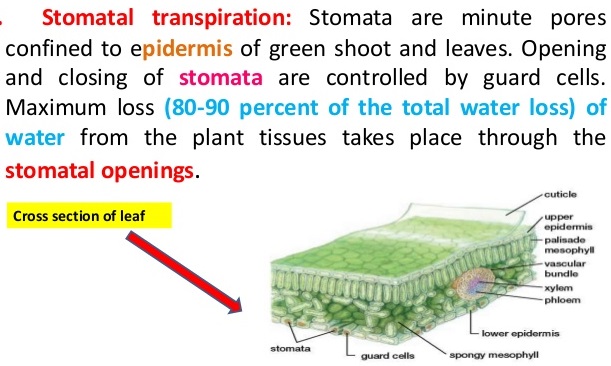


Question 3: What is meant by the term transpiration stream ?
Answer: A pulling force called suction, caused by the evaporation of water in a leaf draws a long, continuous column of water through the xylem from the root to the leaf. This is called the transpiration stream.
Question 4: Where are stomata generally found ?
Answer: Stomata are generally found on the epidermis of the leaf.
Question 5: State the functions of guard cells.
Answer: Guard cells regulate opening and closing of stomata thus, control gas exchange and transpiration.
Question 6: How does a stomata differ from a lenticel ?
Answer: Stomata present, on the leaf and open only during the day while lenticel present on the stem of woody plants and open at all the times.
Question 7: What are lenticels ? Where are they found ?
Answer: Lenticels are minute, permanent openings which may develop in the young stems of woody plants. Some water is lost continuously through the lenticular openings in the form of water vapour.
Question 8: (i) Name the organ in which guard cells are located and mention the main functions of these.
(ii) Give the function of thick cuticle layer in desert plants.
Answer: (i) The guard cells are located in the leaves. These regulate the stomatal opening for transpiration and diffusion of gases and close in order to reduce water transpiration.
(ii) It lowers the rate of transpiration thus conserving water.
Question 9: What is the advantage of wilting to a plant ?
Answer: The stomata close and there is a general reduction in the loss of water by the leaves due to transpiration.
Question 10: Briefly explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by:
(a) Intensity of light.
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere.
Answer: (a) Light intensity: It increases or decreases the rate of transpiration. In strong light, the rate of transpiration is more because stomata are wide open. In dim light or on a cloudy day the stomata are partially closed reducing the rate of transpiration.
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere: If the air outside is humid the rate of transpiration is reduced, since the outward diffusion of internal water vapour is affected.
Question 11: Describe any three conditions which affect transpiration.
Answer: The three conditions which affect transpiration are the following :
- Sunlight: In bright sunlight, the stomata remains fully open and transpiration takes place through the stomatal pores. At night stomata remains closed, so transpiration is reduced.
- Wind: If the Wind velocity is high, transpiration becomes rapid because the water vapour is carried away before the air around the leaf becomes saturated.
- Available water: If available water in the soil is low, the transpiration is low and the leaves may even begin to wilt.
Question 12: What are the advantages of transpiration to the plant ?
Answer: (i) It results in ascent of sap by creating a suction force.
(ii) It results in cooling of the plant in summer.
(iii) It helps in distribution of water to all parts of the plants.
(iv) It helps in elimination of excess of water absorbed by the roots.
Question 13: What are the disadvantages of transpiration ?
Answer: (i) Some plants will die due to excessive water loss by transpiration.
(ii) Due to high rate of transpiration plant suffer from loss of turgidity.
Question 14: “A higher rate of transpiration is recorded on a windy day rather than on a calm day.” Explain.
Answer: Wind causes faster movement of air and remove the moist air and faster evaporation of water and therefore higher rate of transpiration.
Question 15: Explain the relationship between transpiration through the aerial parts and absorption by the root hairs.
Answer: The loss of water due to transpiration tends to lower the concentration of water in the cell sap. Thus, the root hair with its semi-permeable membrane and hypertonic cell sap establish an osmotic system with the water available in the soil surrounding the root hair. This is how the two processes are interrelated.
Question 16: Describe an experiment to prove that transpiration occurs more from the under surface of dorsiventral leaves.
Answer: Two equal pieces of cobalt chloride paper are dried and placed one on the upper surface and the other on the lower surface of dorsiventral leaves. They are firmly held in place by pieces of cellotapes or glass slides. After a few minutes the cohalt chloride paper shows change in colour from blue to pink. The time taken for the cobalt chloride paper on the upper surface of the leaf to turn pink is much longer than for the under surface. Thus, it proves that the rate of transpiration is greater from the under surface of dorsiventral leaves.
Give Reasons
Question 1: Transplanting of seedlings to flowerbed in the evening is better than doing so in the morning.
Answer: During day time transpiration rate is very high. As a result to excessive transpiration and the seedling will wilt and ultimately die. However in the evening, transpiration rate is very slow and the seedling will be able to retain the water absorbed from the soil and as a result of this they will remain transplanted.
Question 2: Land plants die if their foots remain water logged.
Answer: Older portions of the root do not have root hairs. They are covered with a protective layer of dead calls having tiny openings called lenticels. Through these lenticels, gaseous exchange occurs between the soil and inner living cells. If the roots of land plants remain waterlogged, then lenticels will not be able to do gaseous exchange and as a result of this plants will die.
Question 3: Young plants will an a hot sunny day.
Answer: On a hot sunny day, the rate of transpiration exceeds the rate of water absorption by roots. As a result of this leaves collapse and plant wilts.
Question 4: Plants absorb more water than their requirement.
Answer: The plants absorb much more water than their requirement because:
(a) They require more mineral salts for their growth and minerals are present in very small quantity in water
(b) Most of the water is lost through transpiration. Therefore, to prevent wilting they require excess of water.
Question 5: Balsam plants wilt during midday even if the soil is well watered.
Answer: Transpiration rate in such plants is very high during mid day and exceeds the water absorption rate of the roots. So more water is lost than absorbed. This water deficiency in cells cause them to loose turgidity and the plants wilt.
Question 6: Why do plants absorb more water than what is required by them ?
Answer: Plants absorb more water than required because minerals are present in extremely small quantity in absorbed water. To obtain a continuous supply of minerals it has to absorb large quantity of water.
Question 7: Forest bring in the rain, transpiration is the cause. Explain why.
Answer: When water is lost by evaporation (transpiration) heat energy is taken up from the plant body to vapourize the water, here the water is rapidly taken up by the roots and again released through the leaves by transpiration. In the air above, the moisture forms clouds and soon falls as rain.
Question 8: Why do some herbaceous plants show wilting of leaves during mid-day which again recover in the evening ?
Answer: During mid-day the rate of transpiration is maximum. During this time, in some herbaceous plants, the rate of transpiration exceeds the amount of water absorbed. Thus, the leaves loss its turgid state and show wilting.
Question 9: Guard cells are small in size and are kidney shaped in outline.
Answer: Because of their small size, guard cells are rapidly influenced by turgor changes. Because of their kidney shaped outline, they remain joined at their ends. This concave-convex curvature of the two guard cells can be varied easily and this further facilitates the stomatal pore to open and close easily.
Differentiate
Question 1: Transpiration and Guttation.
Answer:
| Transpiration | Guttation |
| (i) It is regulated by guard cells | It is due to root pressure. |
| (ii) It occurs at day time. | It occurs at night. |
| (iii) Water escapes through stomata and lenticels. | Water escapes through hydathodes only. |
| (iv) Water escapes in the form of water vapour. | Water escapes from the hydathodes on the margin of the leaves in the form of water droplets. |
Question 2: Transpiration and Evaporation.
Answer:
| Transpiration | Evaporation |
| Loss of water in the form of vapour from aerial parts of the plant. | Loss of water from the surface of the water bodies in the form of vapour. |
| It is a vital and partly a physical process controlled by both internal and external factors. | It is a physical change controlled by the temperature and humidity of the atmosphere. |
| It is a slow process. | It is a fast process. |
Question 3: Stomata and Lenticels.
Answer:
| Stomata | Lenticels |
| (i) These are located on the lower surface of dicot leaves and both upper and lower surfaces of monocot leaves. | These are located on the stems of woody plants. |
| (ii) They lose water vapour and process is termed stomatal transpiration. | They lose water vapour and process is called lenticular transpiration. |
Question 4: Cuticular and Lenticular transpiration.
Answer:
| Cuticular Transpiration | Lenticular Transpiration |
| It takes place through the thin cuticle covering the leaves of the plant. | It takes place through the opening on the stems of woody plants, called lenticels. |
Question 5: Transpiration and Translocation.
Answer:
| Transpiration | Translocation |
| It is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial organs of the plant. | It is the transfer of prepared food to the different parts of the plant, including the storage organs. |
| It occurs through stomata. | It occurs through vascular tissues. |
Question 6: Transpiration and Perspiration.
Answer:
| Transpiration | Perspiration |
| (i) It takes place in plants. | It takes place in animals. |
| (ii) Only water vapour is removed. | Sweat containing urea, uric add and salts are removed with water. |
| (iii) It takes place through the leaves and stem and through the stomata and lenticels. | It takes place through the skin. It takes place through the sweat pores of the sweat glands. |
Question 7: Stomata and Hydathodes.
Answer:
| Stomata | Hydathodes |
| Stomata pass out water in the form of vapours. | Hydathodes send out water in the form of droplets. |
Question 8: Guttation and Bleeding.
Answer:
| Guttation | Bleeding |
| It is the process in which water droplets oozes out from the hydathodes present at the tip and margins of leaves. | It is the process in which plant sap oozes out through injured or cut ends of the plant. |
Question 9: Cobalt chloride paper and Goat’s bladder.
Answer:
| Cobalt Chloride Paper | Goat’s Bladder |
| It is used for the process of transpiration to check the presence of water. | It is used for the process of osmosis as semi- permeable membrane. |
Diagram Based Questions
Question 1: The diagram below represents a structure found in a leaf.
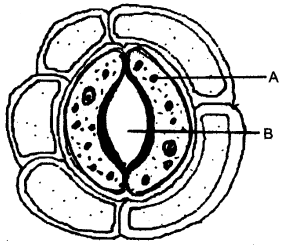
Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the pis labeled A and B.
(ii) What is the biological term for the above structure?
(iii) What is the function of the part labeled A?
(iv) Mention two structural features of A, which help in the function mentioned in (iii) above.
(v) Where is this structure likely to be found in a leaf?
(vi) The above structure helps in the process of transpiration. Explain the term transpiration.
(vii) How many other cells are found surrounding this structure as seen in the diagram?
Answer: (1) A—Guard cell B—Stoma.
(ii) Stomatal apparatus.
(iii) Regulates opening & dosing of Stomata.
(iv) Gives rigidity and protection to the cell.
(v) On the epidermis of leaf.
(vi) Transpiration is the loss of water as water vapours from the aerial parts of the plant.
(vii) Five.
Question 2: The figure below represents the vertical section of a leaf:
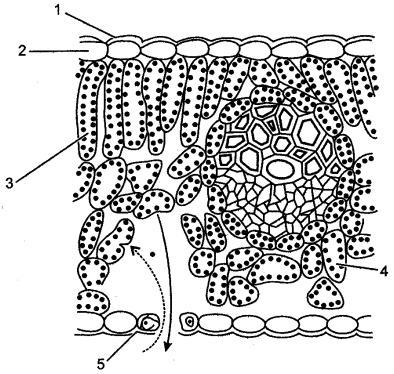
(i) Name the parts labeled 1 to 5.
(ii) What do the two arrows (dotted and solid) indicate in the day time and at night ?
(iii) Could you add one more arrow in the figure ? If yes, what for ?
(iv) How many leaf veins have been shown in this section ?
Answer: (i) 1. Cuticle, 2. Upper epidermis, 3. Palisade tissue, 4. Spongy parenchyma, 5. Guard cell of stoma.
(ii) In the day time dotted arrow shows the path of CO2 while solid arrow shows the path of oxygen. A night dotted arrow shows the path of oxygen while solid arrow shows the path of CO2:
(iii) Yes, we can add one more arrow in the figure to show the loss of water during transpiration.
(iv) Only one leaf vein has been shown in this section.
Question 3: Given below are the diagrams of a certain structure in plants in two conditions.
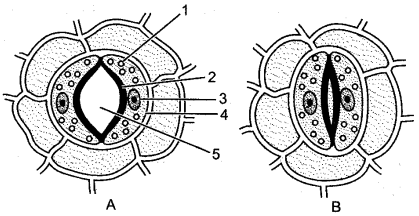
(i) Name the structure shown.
(ii) Name the parts numbered 1-5.
(iii) What is the most apparent difference between A and B in the structure shown ?
(iv) Describe the mechanism which brings about the change in the structure depicted in A and B.
Answer: (i) Stomata surrounded by epidermal cells.
(ii) 1. Chloroplast, 2. Inner wall of guard cells, 3. Nucleus, 4. Guard cells, 5. Stoma.
(iii) The stoma is open in A and is almost closed in B.
(iv) The opening and dosing mechanism of stomata is regulated by the amount of water and solutes present in the guard cells. The guard cells have a thick inner wall facing the opening and a thin outer wall on the opposite side; their cytoplasm contains chloroplasts. During the day guard cells begin photosynthesis and the sugar produced during the process increases the osmotic pressure which draws in water from the adjoining cells. Hence, the guard cells become turgid and bulge outward due to their thin outer wall, thus widening the stomatal opening lying in between (Fig. A). As the stomata open, the diffusion of gases in and out begins for fulfilling the need for photosynthesis and for allowing transpiration. If for any reason the water content of the leaf is falling short, the guard cells fail to remain turgid, they turn flaccid or lose turgidity, thereby closing the stomatal opening (Fig. B) and the transpiration stops.
Question 4: Given below is an experimental set up to study a particular process :
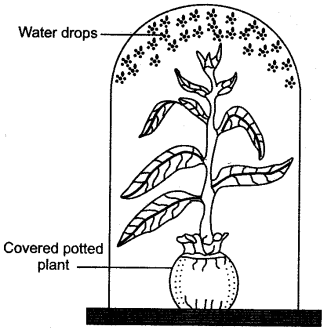
(i) Name the process being studied.
(ii) Explain the process named in (i) above.
(iii) Why is the pot covered with a plastic sheet ?
(iv) Mention one way in which this process is beneficial to the plant.
(v) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
Answer: (i) Transpiration.
(ii) It is process in which water in the form of vapours are released from the aerial parts like leaves and soft stems of the plant.
(iii) The plastic sheet will not allow the moisture of the mud of the pot to come out and affect the result.
(iv) It helps in ascent of sap in the plant.
(v) A similar apparatus is set up without the potted plant. In its place a same plastic bag, with its mouth tied, is kept in the bell jar. No water drops will appear in the bell jar.
Question 5: The figure given below represents an experimental set up with a weighing machine to demonstrate a particular process in plants. The experimental set up was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
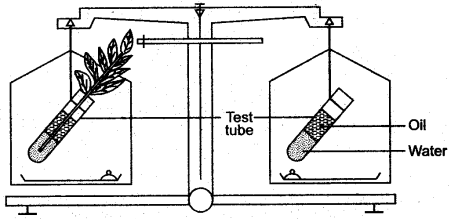
(i) Name the process intended for study.
(ii) Define the above mentioned process.
(iii) When the weight of the test tube (A & B) is taken before and after thee experiment, what is observed ? Give reasons to justify your observation in A & B.
(iv) What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental set up?
Answer: (i) Transpiration.
(ii) It is the release of water vapours from the aerial parts of the plant.
(iii) Weight of test tube A will decrease after the experiment because water will be lost from it through the leaves by transpiration,. Weight of test tube B will remain same after the experiment because water will not be lost by transpiration as there is no plant in and nor by evaporation as oil is spread over it, which will not allow evaporation.
(iv) It is a control experiment where the purpose of using test tube B is to compare the level of water in both test tubes.
Question 6: Study the diagram given alongside and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Explain the physiological process being study.
(ii) What will be the observations in the two test-tubes after about 2-3 days?
(iii) Give a reason for your answer in (ii) above.
(iv) Why is the surface of water covered with oil.
(v) State the purpose of setting up test tube B.
Answer: (i) Transpiration: Loss of water as water vapour from aerial parts of the plant.
(ii) After 2-3 days the level of water falls in test-tube A while it remains constant in test tube B.
(iii) The fall in the level of water in test-tube A due to the absorption of water by the roots.
(iv) The oil has been put in each test-tube to prevent the loss of water by evaporation.
(v) The purpose of setting up test-tube B is to show that in the absence of plant, there is no change in the level of water.
Question 7: Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follows:
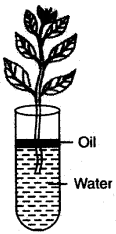
(i) Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
(ii) Explain the process mentioned in (i) above.
(iii) Why is oil placed over water?
Answer: (i) Transpiration
(ii) It is the process by which plants lose water as vapours through the aerial parts.
(iii) To prevent evaporation of water from the test tube.
(iv) 1. In bright sunlight the level of water decreases quickly.
2. In humid conditions level of water does not decrease for a long time.
3. On windy day level of water decreases very quickly.
(v) 1. The number of stomata may be reduced.
2. leaves may become narrow.
3. A thick layer of cuticle on the leaf surface help to decrease transpiration
Question 8: Given below is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
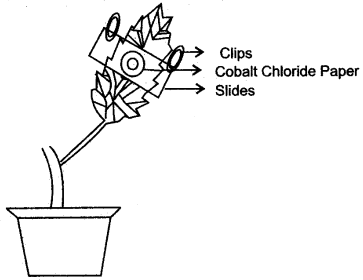
(i) What is the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper?
(ii) Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
(iii) Why axe glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
(iv) After about half an hour what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
(v) Define the term ‘transpiration’.
Answer: (i) The colour of dry cobalt chloride paper is blue.
(ii) Dicot leaf. It has reticulate venation.
(iii) To prevent water vapour of the air from interfering the experiment. .
(iv) The cobalt chloride paper placed on the lower surface of the leaf will show more pink dots as there are more stomata. The upper surface has less stomata than the lower surface.
(v) Loss of water as water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant.
Question 9: The apparatus shown here is Girreau’s poto-meter designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After a few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and
weighed again.
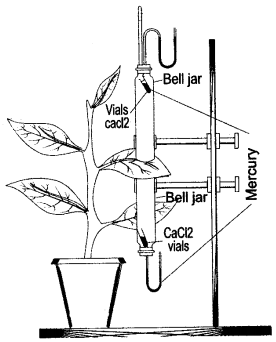
(i) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
(ii) After a few hours, the CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight ? If so, give reasons.
(iii) What was the purpose of using a mano-meter?
(iv) What do you mean by transpiration?
Answer: (i) The CaCl2 vials are kept inside the cup to absorb water.
(ii) After few hours, the weight of the CaCl2 vials will increase because they will absorb the water which is transpired by the leaf of the plant.
(iii) Manometers are used to indicate the unequal transpiration from two surfaces of a dorsiveritral leaf by showing difference in rise in their mercury levels.
(iv) Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the living plants.
Question 10: The following diagram is set up to demonstrate an experiment.
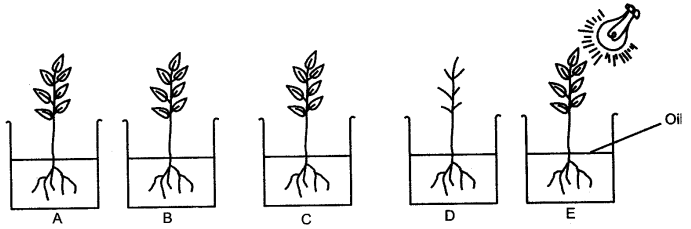
Five plants A, B, C, D and E were placed in a beaker containing water. The water in each beaker was covered with a layer of oil. The leaves were removed from plant D in plant B, upper surfaces of all the leaves were covered with Vaseline, in plant C the lower surfaces of all the leaves were covered with Vaseline and plant E was exposed to strong light. The beakers were then left for few hours and at the end of the experimental period, weights of each beaker were
taken.
Write the correct answer out of the five available choices given under each question:
I. In which beaker would you expect the greatest decrease in weight?
(i) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (v) E
II. In which beaker the change of weight would be minimum?
(i) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (v) E
III. Which plant would remain healthy for a longer period of time?
(i) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (v) E
IV. In this experiment which plant can be considered as the uncontrolled one?
(I) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (v) E
V. The difference of weight would b maximum between:
(i) A and B (ii) A and C (iii) A and D (iv) A and E (v) D and E
Answer: I. (v) E, II. (iv) D, III. (i) A, IV. (i) A, V. (v) D and E.
Question 11: Given below is an apparatus used to study a particular process in plants. Study the same and ansvver the questions that follow :
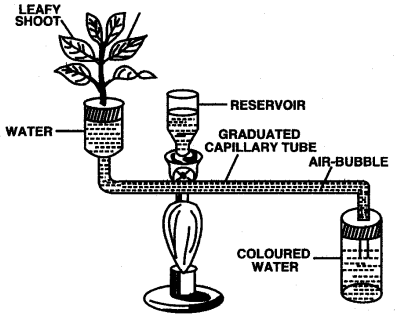 (i) Name the apparatus.
(i) Name the apparatus.
(ii) Mention one limitation of this apparatus.
(iii) Which phenomenon is studied with the help of this apparatus?
(iv) What is the function of the part marked ‘reservoir’?
(v) What is the role of the air bubble in the experiment?
Answer: (i) Garreau’s Potorneter.
(ii) The capillary tube should be properly dipped into the water.
(iii) Transpiration.
(iv) It is used to adjust the position of air bubble in graduated capillary tube.
(v) The movement of air bubble in graduated tube in a minute gives the rate of transpiration.
Sketch and Label the Diagram
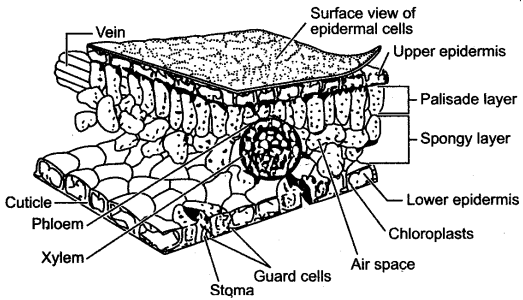
Question 1: Draw a labeled diagram of the stomatal apparatus and label the following in it: Stoma, Guard cells, Chloroplast, Epidermal cells and Cell wall.
Answer:
Question 2: Draw a neat diagram of the stomatal apparatus found in the epidermis of leaves and label the Stoma, Guard cells, Chloroplast, Epidermal Cells, cell wall and Nucleus.
Answer:
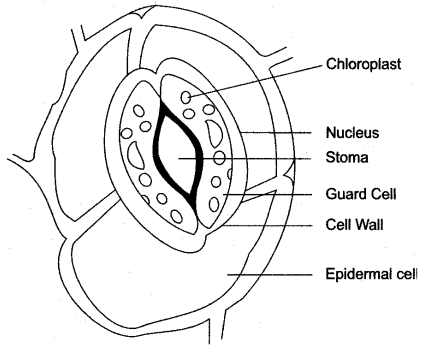
Explain the Terms
Question:
1. Transpiration
2. Cuticular transpiration
3. Lenticular
4. Stomatal transpiration
5. Guttation
6. Bleeding
7. Lenticel
8. Hydathode
9. Wilting
Answer: 1. Transpiration is defined as the loss of water vapour by the plant. It may take place from any part of the plant body.
2. Cuticular transpiration takes place through the cuticle (waxy layer) covering the leaves.
3. Lenticular transpiration takes place through the small openings in the corky tissue covering the stem.
4. Stomatal transpiration takes place through the stomata on the leaves. .
5. Guttation is defined as the loss of water in the form of water droplets from the leaves of intact plants. It is also called exudation.
6. Bleeding is the flow of the plant sap at the sites of injury or cuts.
7. Lenticel: A pore in the periderm of a woody stem. It acts as an organ of gaseous exchange.
8. Hydathode: A water secreting gland found on the edges and tips of leaves of many plants.
9. Wilting: The collapse of leaves due to unfavourable water relations. It may be due to excessive transpiration as compared to absorption of water by roots. It may also be due to blocking of the xylem elements, pathogens or parasites.
Name the Following
Question:
1. The process of getting rid of excess water in the form of water vapour through the stomata.
2. Season in which transpiration rate is the highest.
3. Holes present on the surface of the stems and twigs for transpiration.
4. Potometer is an instrument for measuring the rate of the most transpiration in a herbaceous plant like Balsam occurs through which part.
5. Plants in which lenticular transpiration.
6. A plant having sunken stomata.
7. Loss of water as droplets through leaves of an intact plant.
8. The structures through which guttation occurs.
9. The escape of plant sap from the ruptured or cut surfaces of the plant due to root pressure.
Answer:
1. Transpiration
2. Summer
3. Lenticels
4. Stomata
5. Woody trees
6. Xerophyte
7. Guttation
8. Hydathodes
9. Bleeding
Give Technical Terms
Question:
1. Loss of water from the aerial parts of a plant.
2. Opening found on the under surface of dorsiventral leaf.
3. Which side of the leaf has more stomata ?
4. When cobalt chloride paper is placed on lower and upper surface of the leaf, the paper of which side becomes more pink ?
5. The substances which check the rate of transpiration.
6. The paper which is used to show loss of water through stoma of a leaf.
7. A chemical used to prevent excessive transpiration in plants.
8. Main function of lenticel.
9. The apparatus used to compare the rate of transpiration in cut shoot.
10. The process by which excess of water is forced out directly from the tips of veins in the leaf.
Answer:
1. Transpiration
2. Stomata
3. Lower side
4. Lower side
5. Anti-transpirants
6. Cobalt chloride paper
7. Silicon emulsions/phenyl mercuric acetate
8. Exchange of gases and transpiration
9. Darwin’s potometer
10. Guttation
Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences with appropriate words :
1. Plants become cool as a result of Transpiration.
2. Transpiration is the loss of water In the form of water vapour from the leaves of the plant.
3. Transpiration normally takes place in the presence of Sunlight.
4. 95% of the total transpiration takes place through Stomata.
5. In Nerium, the stomata are present in Sunken pits.
6. Openings found on the under surface of the dorsiventral leaf are Stomata.
7. The leaves of the Xerophytic plants have cuticular wax.
8. Guttation takes place generally at Night.
True & False
Mention, if the following statements are True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
1. Transpiration is a physiological process. (True)
2. Root hairs are the extensions of the outer epidermal cells of the root. (True)
3. More transpiration occurs from the upper surface of a leaf. (False, More transpiration occurs from the under surface of a leaf.)
4. Transpiration takes place only in green plants. (True)
5. The pH of the guard cells increases during day time. (True)
6. Evaporation is a physiological process. (False, Evaporation is a physical process.)
7. Potometer is an instrument, used for measuring the rate of transpiration. (True)
8. Low humidity in the atmosphere results decrease in the rate of transpiration. (False, High humidity in the atmosphere results decrease in the rate of transpiration.)
9. Calcium chloride paper is used to demonstrate transpiration. (False, Cobalt chloride paper is used to demonstrate transpiration.)
10. Moist cobalt chloride paper is blue in colour. (False, Moist cobalt chloride paper turns pink in colour.)
11. Guttation occurs through stomata. (False, It occurs through hydathodes.)
State the Location
| Name | Location |
| Stomata | Present in the epidermis of green, aerial parts of plants, especially the leaves. |
| Lenticels | Present in the bark of woody plants. |
| Cuticle | It is a non-cellular waxy layer secreted by the epidermis and it surrounds the epidermis. |
| Hydathodes | Present on the edges and tips of leaves of many plants. |
| Guard cells | Present in the stoma (plural of stoma is stomata). |
State the Function
Write the functional activity of the following structures:
| Name | Function |
| Stomata | (a) Loss of water vapours due to transpiration. (b) Gaseous exchange. |
| Lenticels | They help in gaseous exchange. |
| Cuticle | It protects the surface and reduces water loss. |
| Hydathodes | Plants secrete excess of water through hydathodes when atmosphere is very humid and transpiration process cannot occur. |
| Guard cells | (a) Control the size of the aperture. (b) Also help in photosynthesis as they contain chloroplasts also. |
Choose the Odd One Out
1. Transpiration, Photosynthesis, Phagocytosis, Guttation. (Phagocytosis)
2. Cuficular transpiration, Lenticular transpiration, Stomatal transpiration, Gutation. (Guttation)
3. Stomata, Cuticle, Lenticels, Hydathodes. (Hydathodes)
Multiple Choice Questions
1. In the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata, the important factor is :
(a) The presence of chloroplast in the guard cells
(b) The turgid and flaccid state of the guard cells
(c) The protein content of the cells
(d) The starch content of the cells
2. Stomata open during day and close at night because :
(a) Photosynthesis occurs during day time only
(b) Enzymes convert starch into sugar at elevated pH in night
(c) Loss of sugar increases osmotic concentration of the cell sap
(d) Loss of starch in day time raises OP of subsidiary cells
3. In hot summer days, plant cooling is due to :
(a) Loss of water vapours from leaves (b) Transport of water in plant
(c) Loss of lkjuid water (d) Loss of water from entire plant
4. If the rate of transpiration becomes more than the rate of photosynthesis, plants will:
(a) Continue to live, but will not be able to store food
(b) Be killed instantly
(c) Grow more vigorously because more energy will be available .
(d) Stop growing and gradually die of starvation
5. Transpiration is very low during storms due to :
(a) Presence of moisture in the wind
(b) Low temperature during storms
(c) High velocity of wind
(d) None of the above
6. Transpiration pull will be maximum under which of the following conditions ?
(a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
(b) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and well irrigated soil
(c) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and dry soil
(d) Close stomata, dry atmosphere and dry soil
7. Plants lose water by guttation when:
(a) Rate of transpiration is high
(b) Soil is wet and the atmosphere is humid
(c) Soil is dry and atmosphere is dry
(d) Soil is wet and atmosphere is dry
8. Guttation is the elimination of excess of water from plants through :
(a) Stomata (b) Hydathodes
(c) Lenticels (d) Wounds
Match the Column
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with the suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Transpiration | (a) Cacti plants |
| (ii) Movement of water | (b) Stomata |
| (iii) Guttation | (c) Maize plant |
| (iv) Low rate of transpiration | (d)Xylem |
| (v) High rate of transpiration | (e) Hydathodes |
Answer: (i) (b) (ii) (d) (iii) (e) (iv) (a) (v) (c)
ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- Cell Division Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Fundamentals of Genetics Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Absorption by Roots Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Transpiration Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Photosynthesis Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- The Circulatory System Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- The Excretory System Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- The Nervous System and Sense Organs Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- The Endocrine System Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- The Reproductive System Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Human Population Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Physical Health and Hygiene Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
- Pollution Class 10 ICSE Questions and Answers
