What is the Significance of Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a mode of multiplication in which the young ones are produced through the process of formation & fusion of gametes.
Significance of sexual reproduction :
Variation :
Due to reshuffling of chromosomes and crossing over, sexual reproduction brings about variations in almost all characters so that no two individuals are similar.
Vigour and Vitality :
It maintains the vigour and vitality of the individuals.
Uniformity of Population :
Due to the flow of genes amongst individuals during sexual reproduction, the uniformity of population is maintained where there is a broad resemblance of all the individuals with one another.
Evolution :
Genetic changes brought about by sexual reproduction paly an important part in evolution of new forms.

Sexual reproduction in flowering plants :
A flower has following parts.
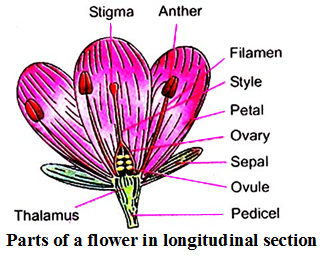 Sepals : Sepals are green outermost leaf-like floral organs which protect the flower in the bud stage. In the mature stage they provide support to other floral organs.
Sepals : Sepals are green outermost leaf-like floral organs which protect the flower in the bud stage. In the mature stage they provide support to other floral organs.
Petals : Petals are coloured accessory floral organs which lie above the sepals. Petals attract insects to flowers for pollination.
Stamens : Stamens are the male reproductive organs of the flowers. Each Stamen has a slender stalk called filament.
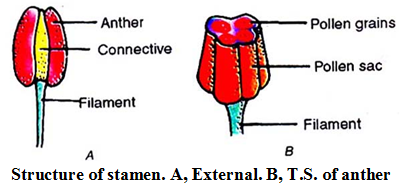 Each anther lobe has two long pollen sacs so that there are four pollen sacs in an anther. They produce yellowish coloured powder of haploid pollen grains.
Each anther lobe has two long pollen sacs so that there are four pollen sacs in an anther. They produce yellowish coloured powder of haploid pollen grains.
Carpels : Carpels form the central female reproductive organs of the flowers.
Read More:
- Vegetative Reproduction in Plants
- Reproduction in Humans
- Different Types of Asexual Reproduction
- Viviparous Reproduction
Pollination :
Pollen grains from the anther are transferred by air, water, insects, and other animals, to the stigma of a pistil.
”The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of same or other flower, is called as pollination”. On the basis of transfer of pollen grains to the stigma of same or other flower, pollination is of two types.
(A) Self pollination (B) Cross pollination
Self Pollination :
- The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of same flower, is called as ”Self-Pollination” or autogamy. e.q. Pea, Chinarose, Rice, Wheat.
- Self-pollination in bisexual flowers ensures continuity of the race.
- It helps to preserve the parental characters, as the gametes from the same flower are involved.
Cross Pollination :
- The process of transfer of pollen grain from the anther of a flower to the stigma of other flower, is called as ”Cross-pollination” or allogamy. e.q., musturd, rose.
- Seeds produced by cross pollination have much better germinating capacity.
- Variations are introduced by cross pollination.
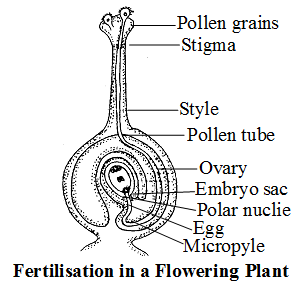
Fertilization in Plants :
Pollination is followed by fertilisation in plants.
- After reaching the stigma, the pollen grain develops the pollen tube.
- This pollen tube grows through the style and reaches the ovary where ovules are located.
- The pollen tube enters the ovule through a small opening called micropyle, where it releases two male gametes into the embryo sac.
- One male gamete fuses with the egg contained in the embryo sac of the ovule; and this fusion of male and female gametes is called syngamy and its product is the zygote.
- The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei and this process is called triple fusion, where three nuclei are involved in the fusion process, one male gamete and two polar nuclei.
- The process of double fertilisation occurs inside each embryo sac, in which two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion take place.
- After fertilisation, ovary develops into the fruit and ovules develop into the seeds.