What is the definition of an acid in chemistry?
What is an acid according to chemistry?
The term ‘acid’ has its origin in the Latin word acidus, meaning sour. In fact, anything that tastes sour contains an acid. For example, lemon juice, tomato, vinegar, etc., all taste sour. So, each of these substances must contain an acid.
Substances containing an acid (from Latin acere meaning sour) are called acidic substances.
Acids are of two types: mineral acids and organic acids.
1. Mineral Acid:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3) are examples of mineral acids that are used in the laboratory.

2. Organic Acid:
Organic acids occur naturally in animal and plant materials.
Some of the naturally occurring substances that contain acids are given in Table.
Substance | Acid present |
1. Orange, lemon | Citric acid, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) |
| 2. Apple | Malic acid |
3. Tamarind (imli), grape | Tartaric acid |
| 4. Vinegar | Acetic acid |
5. Curd | Lactic acid |
6. Tomato, Spinach | Oxalic acid |
| 7. Gastric juice | Hydrochloric acid |
8. Tea | Tannic acid |
| 9. Red ants, Bees | Formic acid |
Aqueous solutions of acids are generally sour in taste. Acids turn blue litmus red, conduct electricity and react with bases to form salts and water. [Bases and salts are discussed a little later.]
An acid may be defined in various ways. Here, we shall study the definition given by Liebig in 1838. According to Liebig, an acid is a compound which contains hydrogen that can be replaced partially or wholly by a metal or a group of elements acting like a metal, to produce a salt.
For example, sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is an acid because of the following reasons.
(i) It contains hydrogen atoms in its molecule.
(ii) The two hydrogen atoms present in its molecule can be replaced partially or wholly by a metal like sodium (Na) to produce sodium hydrogensulphate or sodium sulphate.
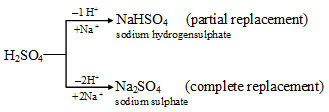
The hydrogen atoms in H2SO4 can also be partially or wholly replaced by a group of elements, like an ammonium ion to form ammonium hydrogensulphate (NH4HSO4) or ammonium sulphate ((NH4)2SO4) respectively.
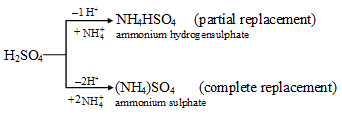
The substances NaHSO4, Na2SO4, NH4HSO4 and (NH4)2SO4 are all salts.
(iii) The acid dissolves in water to make a solution that turns blue litmus red.
(iv) It is sour in taste.
(v) It reacts vigorously with a base to produce a salt.
The hydrogen atoms present in an acid that can be replaced by a metal or a group of elements are called replaceable hydrogen or acidic hydrogen.
People also ask
- What is the definition of an acid and a base?
- What is the definition of a base in chemistry?
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- What are the chemical properties of an acid?
- General Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- Preparation of Bases
- General Properties of Bases
- What determines a Strong Base and a Weak Base
- What are the uses of Bases
- How can we measure the strength of acids and alkalis?
- How to calculate concentration of acids and alkalis?
- How do you prepare a standard solution?
- What is meant by a neutralization reaction?
- How does titration determine concentration?
- Relationship between pH values and molarity of acids and alkalis
- Concept of the pH Scale
- Role of pH in everyday life
- What is the pH of a salt solution
