How does Temperature Affect the Movement of Particles
Effect of Temperature Change
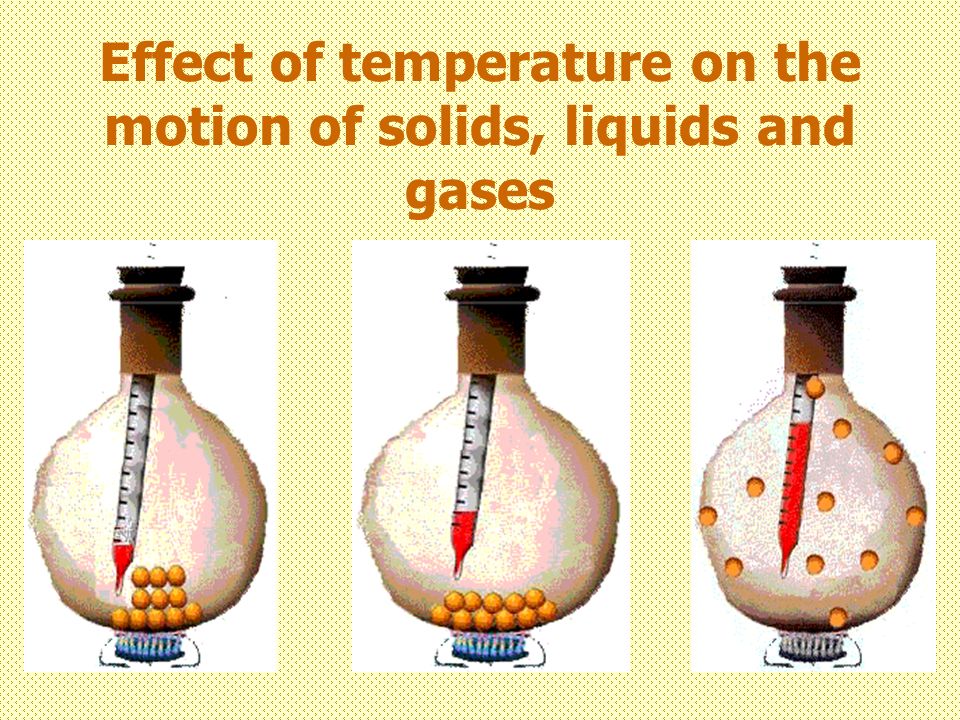
By increasing the temperature (by heating), a solid can be converted into the liquid state; and the liquid can be converted into a gaseous state (or vapour state). And by decreasing the temperature (by cooling), a gas can be converted into a liquid state; and a liquid can be converted into solid-state. Students can know more about how does temperature affect the motion of particles and how does temperature affect particle movement. How does heating and cooling affect the movement of particles, movement of particles are dependent on temperature.
1. Solid to liquid change : Melting
Defination : The process in which a solid substance changes into a liquid on heating, is called melting (or fusion).
Melting point : The temperature at which a solid substance melts and changes into a liquid at atmospheric pressure, is called melting point of the substance.
Ice is a solid. In solids, the particles are tightly packed together. When we heat a solid, its particles become more energetic and kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating more strongly with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the intermolecular forces of attraction between the particles. As a result, the particles leave their mean position and break away from each other. When this happens, the solid melts and a liquid is formed.
Ex. Melting point of ice = 0ºC
Melting point of wax = 63ºC
Melting point of iron = 1535ºC
The melting point of a solid is a measure of the force of attraction between its particles. Higher the melting point of a solid substance, greater will be the force of attraction between its particles.
 2. Liquid to gas change : Boiling (or vaporisation)
2. Liquid to gas change : Boiling (or vaporisation)
Defination : The process in which a liquid substance changes into a gas rapidly on heating, is called boiling.
Boiling point : The temperature at which a liquid boils and changes rapidly into a gas at atmospheric pressure, is called boiling point of the liquid.
In a liquid most of the particles are close together. When we supply heat energy to the liquid, the particles of water start vibrating even faster. Some of the particles become so energetic that they can overcome the attractive forces of the particles around them. Therefore, they become free to move and escape from the liquid. When this happens, the liquid evaporates i.e., starts changing into gas.
Ex. Boiling point of water = 100ºC
Boiling point of alcohol = 78ºC
Boiling point of mercury = 357ºC
The boiling point of a liquid is a measure of the force of attraction between its particles. Higher the boiling point of a liquid, greater will be the force of attraction between its particles.
When a liquid is heated, the heat energy makes its particles move even faster. At the boiling point the particles of a liquid have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding them together and separate into individual particles. And the liquid boils to form a gas.
3. Gas to liquid change : Condensation
The process of changing a gas to a liquid by cooling, is called condensation. Condensation is the reverse of boiling.
4. Liquid to solid change : Freezing
The process of changing a liquid into a solid by cooling, is called freezing. Freezing means solidification. Freezing is the reverse of melting. So, the freezing point of a liquid is the same as the melting point of its solid form.
Ex. Melting point of ice = 0ºC
Freezing poing of water = 0ºC
