What are Synthetic Fibres and give some Examples
Most clothing materials or fabrics we use in our day-to-day lives are made from thin, thread-like fibres. Fibres can be either natural or artificial.
Natural fabrics have been used for clothing since ancient times. But nowadays, synthetic fibres are largely used for clothing and other purposes.
Synthetic fibres
Fibres that are made by human beings are called synthetic fibres. Most synthetic fibres are obtained from coal, petroleum, and natural gas. A synthetic fibre consists of multiple units (each of which is a chemical substance), which are joined together to form a single unit called a polymer (poly: many; mer: unit). The structure of a polymer can be described as resembling numerous beads on a string, with the beads representing the individual units that are joined together.
Rayon, nylon, polyester, acrylic, and spandex are examples of synthetic fibres.
- Polyamides and polyesters are two groups of synthetic fibres with high strength, not easily stretched and used as textile.
- Nylon is an example of polyamide polymers. Terylene is an example of polyester polymers.
- Nylon and terylene are produced through condensation polymerisation.
- Nylon
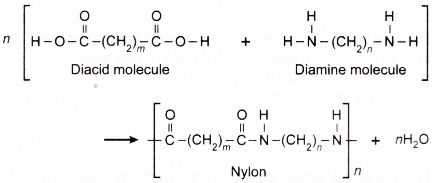
(a) Nylon is a general term given to the synthetic polymer made from two types of monomer, diamine molecules and diacid molecules.
(b) A diamine molecule has two -NH2 groups and a diacid has two -COOH groups.
(c) Diacid molecules and diamine molecules undergo condensation reaction to form nylon and water.
(d) Nylon-6,6 is manufactured from polymerisation of hexane-1,6-diamine and hexane-1,6-dioc acid.
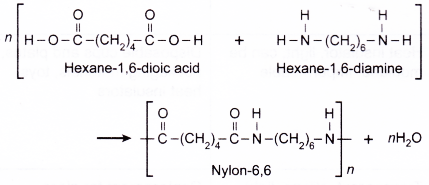
(e) Nylon-6,6 is a strong, tough and waterproof polymer and can be easily made into fibres.
(f) Nylon is used to make toothbrushes, ropes, fishing lines, parachutes, carpets, textile, threads and electrical insulators. - Terylene
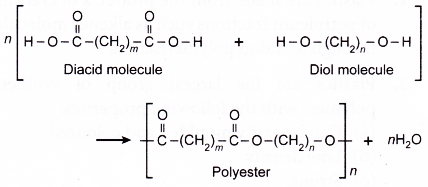
(a) The monomers used to make polyester are diol molecules and diacid molecules.
(b) A diol molecule has two -OH groups and a diacid molecule has two -COOH groups.
(c) When many diacid molecules condense with diol molecules, a polyester and water are formed.
(d) Terylene for example, is manufactured from ethane-1,2-diol and (benzene)benzoic- 1,4- dicarboxylic acid.
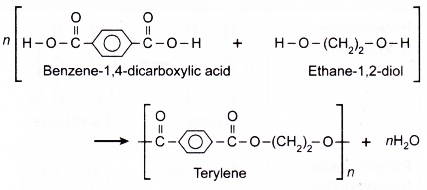
(e) Terylene is suitable for making textile, stocking, parachutes and fishing nets because it is elastic, chemically inert, can be coloured and easily made into fibre.
People also ask
- What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Fibres
- Is Polyester Synthetic or Artificial
- What is the most common type of plastic?
- How polymers are classified?
- Justify the uses of synthetic polymers in daily life
Rayon
Rayon, also called artificial silk, is prepared from cellulose (which comes from wood pulp).
Properties
- It absorbs sweat. Rayon clothes are, therefore, preferred over other synthetic fibres in summer.
- It is shiny and lustrous and resembles silk in appearance.
Uses
- Rayon is used for making shirts, ties, home furnishing (bed sheets, curtains, tablecloths, sofa covers, etc.), and bandages.

Rayon Ties
Nylon
Nylon was the first true synthetic fibre. It was first produced in the early 1930s by the scientists at the DuPont Company from coal, water, and air.
Properties
- It is elastic and does not lose strength even after repeated use.
- It is lustrous and easy to wash.
Uses
- Nylon is used for making saris, socks, stockings, tents, umbrellas, parachutes, and tarpaulins.
- Nylon fibres are used for making toothbrush bristles.
- Due to their high strength and elasticity, nylon threads are used for making fishing nets, climbing ropes, and strings of badminton and tennis racquets.

Strings of a tennis racquet are made of nylon.
Polyester
Polyester is of different types. The most commonly used polyester is Terylene. It is blended with natural fibres to improve its properties. Terrycot, a blend of Terylene and cotton, has better absorbing power as compared to Terylene. Terylene is blended with wool to make Terrywool, which is warm in addition to all the characteristics observed in polyesters.
Properties
- It is strong, lightweight, and has good elasticity.
- It resists wrinkling and springs back into shape when creased.
- Polyester fabrics can be washed and dried easily and quickly.
Note: Elasticity Ability of a material to return to its original shape after it has been stretched or compressed
Uses
- Polyester is used for making lightweight sails.

Sails made of polyester - Polyester films (commonly known as Mylar) are used for making magnetic recording tapes in audio cassettes, video cassettes, and floppy disks.
- Terylene is used for making conveyor belts as it is very elastic. Terrycot is commonly used for making shirts, skirts, and other dress materials.
- Terrywool is used for making formal suits.
Acrylic
Acrylic fibres, also known as Orion and Acrilan, closely resemble wool.
Properties
- It is warm, soft, light, and flexible.
- It is resistant to moths and chemicals.
Uses
- Acrylic is used for making sweaters, socks, shawls, carpets, and blankets.
Spandex
Spandex, also known as Lycra, was invented by the DuPont chemist Joseph Shivers in 1959.
Properties
- It has excellent elasticity, which makes it suitable for use in clothes that require snug fitting.
Uses
- Spandex is used for making swimming costumes. It is often mixed with other fibres, like cotton, to get stretch fabrics, which are used for making caps and T-shirts.
