ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry – Sulphuric Acid
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 10 Sulphuric Acid for ICSE Board Examinations. We provide step by step Solutions for ICSE Chemistry Class 10 Solutions Pdf. You can download the Class 10 Chemistry ICSE Textbook Solutions with Free PDF download option.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
Short Questions
Question 1: Sulphuric acid is said to be dibasic acid. What is meant by the term “dibasic” ?
Answer: Basicity of an acid is the number of H+ ions that one formula unit of an acid liberates, e.g.,
Monobasic = HCl, HNO3, etc.
Dibasic = H2SO4, H2SO3 etc.
Each acid can form as many kinds of salts, as it has hydrogen ions. Sulphuric acid can form two kinds of salts, i.e., SO42- and HSO4–. It ionizes in water to form two hydrogen ions. Hence, it is said to be dibasic.

These acids can yield two kinds of salts, i.e., the normal salt and the acid salt.
Question 2: Some bacteria obtain their energy by oxidizing sulphur, producing sulphuric acid as a by-product. In the laboratory, or industrially, the first step in the conversion of sulphur to sulphuric acid is to produce sulphur dioxide. Then sulphur dioxide is converted to sulphur trioxide which reacts with water, producing sulphuric acid.
(i) Name one catalyst used industrially which speeds up the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide.
(ii) Write the equation for the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide. Why does this reaction supply energy ?
(iii) What is the name of the compound formed between sulphur trioxide and sulphuric acid.
Answer: (ii) Platinum and Vanadium pentaoxide.
(i) When conversion of SO2 to SO3 takes place according to the following reaction.
SO2 + O2 ⟶ 2SO3 + 45 kcal.
The 45 kcal energy supplied by above reaction.
(iii) Oleum (H2S2O7).
Question 3: (i) Write balanced equations for the three chemical reactions that take place during the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphuric acid in the contact process.
(ii) Name the catalyst used in the contact process.
(iii) Name another ore which on roasting gives sulphur dioxide.
Answer:
(i) The chemical reactions are summarised as below:
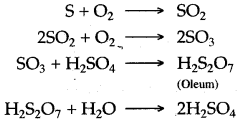
(ii) Platinized asbestos or V2O5
(c) Zinc blende or ZnS
2ZnS + 3O2 ⟶ 2ZnO + 2SO2 ↑
Question 4: (i) With the help of equations, give an outline for the manufacture of sulphuric acid by the contact process.
(ii) What property of sulphuric acid is shown by the reaction of concentrated sulphuric acid when heated with (a) potassium nitrate (b) carbon ?
Answer: (i)
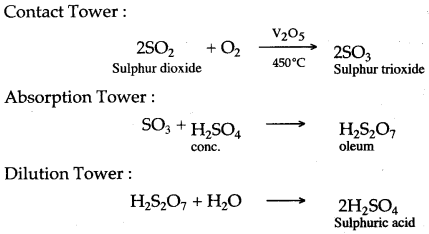
(ii) (a) Non-volatile nature. (b) Oxidising property.
Question 5: (i) Which two gases are combined during contact process ?
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction between zinc and the final product of the contact process ?
(iii) What happens when sulphur trioxide gas is passed into concentrated sulphuric acid.
Answer: (i) SO2 and O2 (sulphur dioxide and oxygen)
(ii) Zn + 2H2SO4 (Conc.) ⟶ ZnSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
(iii) Sulphur trioxide gas dissolves in concentrated sulphuric acid to form fuming sulphuric acid, commonly known as oleum.
SO3 + H2SO4 ⟶ H2S2O7 (Oleum)
Question 6: While diluting concentrated sulphuric acid, the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid. Explain ?
Answer: When equal volumes of the acid and water are mixed at room temperature, the temperature may reach up to 120°C. Therefore, dilution of the acid should be done by adding small quantity of acid into water.
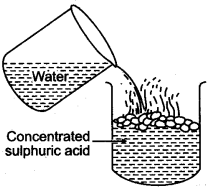
If water is added to concentrated sulphuric acid, the molecules of the acid try to grasp the molecules of water resulting in molecular tension, liberating heat and due to sudden rise in temperature, the acid starts splashing.
If a drop of concentrated acid is added to water, the molecules of acid go in different directions to pick up water which is available in plenty. Although the same amount of heat is formed but since the molecules are spread out, no splashing occurs.
Question 7: (i) Which property of sulphuric acid is used to prepare the hydrochloric and nitric acid respectively.
(ii) What is the catalyst used in catalytic chamber and what is the temperature used ?
Answer: (i) Non-volatile nature of sulphuric acid is responsible to prepare HCl and HNO3 by using H2SO4.
(ii) The catalyst used is platinized asbestos or vanadium pentaoxide and the temperature used is about 450°C.
Question 8: (i) (a) Name the acid formed when sulphur dioxide dissolves in water.
(b) What are the two necessary conditions for the direct combination of sulphur dioxide and chlorine forming sulphuryl chloride ?
(c) State the property of sulphur dioxide which causes potassium permanganate to change its colour from purple to colourless.
(ii) Answer the following questions related to dilute and concentrated sulphuric acid.
(a) Which acid does not react with metals that are placed below hydrogen in activity series ?
(b) Which acid will give white precipitates with barium sulphate.
Answer: (i) (a) Sulphurous acid
(b) Sunlight and absence of moisture
(c) Reducing.
(ii) (a) Dilute sulphuric acid.
(b) Dilutesiilphuric acid.
Question 9: Give one reaction in each case to illustrate the following properties of sulphuric acid:
(i) As an acid. (ii) As an oxidising agent.
(iii) As a dehydrating agent. (iv) As a less volatile acid.
Answer: (i) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with metals above hydrogen in the activity series, for example, magnesium to liberate hydrogen gas and magnesium sulphate.
Mg + H2SO4 ⟶ MgSO4 + H2 ↑
(ii) When sulphur is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid, it is oxidised to sulphur dioxide.
S + 2H2SO4 ⟶ 3SO2 (Sulphur dioxide) + 2H2O
(iii) Add few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid to blue coloured crystals of copper (II) sulphate. After sometime, white anhydrous copper (II) sulphate is left, due to loss of water of crystallization.
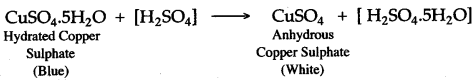
(iv) Concentrated sulphuric acid, when heated with sodium chloride, produces volatile hydrochloric acid.
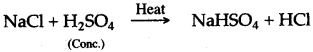
Question 10: What happens when cone, sulphuric acid reacts with:
(i) Potassium chloride
(ii) Zinc nitrate.
Answer: (i) Cone, sulphuric acid reacts with potassium chloride and forms hydrogen chloride and potassium hydrogen sulphate.
KCl + H2SO4 ⟶ KHSO4 + HCl
(ii) Cone, sulphuric acid reacts with zinc nitrate to form zinc sulphate and nitric add.
Zn(NO3)2 + H2SO4 ⟶ ZnSO4 + 2HNO3
Question 11: State how you can obtain:
(i) Sulphur dioxide from sulphur.
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide from iron (II) sulphide.
(iii) Oxalic add.
(iv) Sodium hydroxide
(v) Hydrogen sulphide gas
Answer: (i) When sulphur is bumtin a deflagerating spoon, it melts to form a reddish brown liquid which catches fire. It burns with a blue flame forming an extremely pungent gas sulphur dioxide.
S + O2 ⟶ SO2
(ii) In the laboratory, hydrogen sulphide gas is prepared by the action of dilute sulphuric acid on ferrous sulphide.
FeS + H2SO4 ⟶ FeSO4 + H2S
(iii) Concentrated sulphuric acid, when heated with oxalic acid crystals, it absorbs water from oxalic acid and-mixtures of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide is formed.
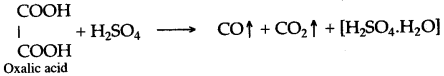
In this reaction sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent.
(iv) Sodium hydroxide solution reacts with dilute sulphuric acid to form sodium sulphate and water.
2NaOH + H2SO4 ⟶ Na2SO4 + 2H2O
In this reaction sulphuric acid acts as an acid as it neutralizes sodium hydroxide to form salt and water only.
(v) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through concentrated sulphuric acid, it is oxidized to free sulphur. Sulphur dioxide and water are also formed.
![]()
In this reaction sulphuric acid acts as an oxidizing agent.
Question 12: Which property of sulphuric acid is used in the following:
(i) As a source of hydrogen when treated in dilute form with metals like Zn, Mg, Fe, etc.
(ii) Production of hydrogen chloride on treating concentrated add with sodium chloride.
(iii) Production of sulphur dioxide on heating in concentrated form with copper turnings.
(iv) Liberation of sulphur from H2S with concentrated form.
(v) Charring of sugar with hot concentrated add.
(vi) Liberation of ethylene gas with hot concentrated add.
(vii) Liberation of carbon monoxide with hot concentrated add.
Answer: (i) Addic property. (ii) Non volatile nature.
(iii) Oxidising nature. (iv) Oxidising property.
(v) Dehydrating nature. (vi) Dehydrating nature.
(vii) Dehydrating nature.
Question 13: Some properties of Sulphuric add are listed below. Choose the property A, B, C or D which is responsible for the reactions (i) to (v). Some properties may be repeated:
A. Acid
B. Dehydrating agent
C. Non-volatile acid
D. Oxidizing agent
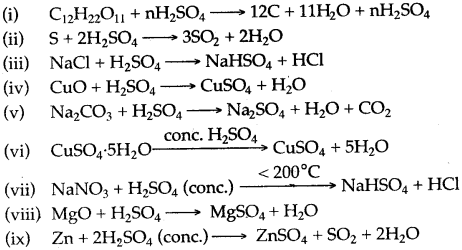
Answer: (i) B, (ii) D (iii) C, (iv) A (v) A (vi) B, (vii) C, (viii) A, (ix) D.
Question 14: A, B, C and D summarize the properties of Sulphuric acid depending on whether it is dilute or concentrated. Choose the property (A, B, C or D), depending on which is relevant to each of the preparations (i) to (iii):
A. Dilute acid (typical acid properties)
B. Non-volatile acid.
C. Oxidizing agent.
D. Dehydrating agent
(i) Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride.
(ii) Preparation of Ethene from Ethanol.
(iii) Preparation of Copper sulphate from Copper oxide.
Answer: (i) B (non-volatile acid).
(ii) D (dehydrating agent)
(iii) A (dilute acid).
Question 15: Name from the list of substances given below, the substances which you would use to prepare each of the following salts, named in parts (i) to (iv):
The substances are:
Copper, Lead, Sodium, Zinc, Copper oxide, Lead carbonate, Sodium Carbonate solution, Dilute hydrochloric acid, Dilute nitric acid and Dilute sulphuric acid:
(i) Zinc sulphate; (ii) Copper sulphate; (iii) Sodium sulphate; (iv) Lead sulphate.
Answer: (a) For zinc sulphate — Zinc and dilute sulphuric acid.
(b) For copper sulphate — Copper oxide and dilute sulphuric acid.
(c) For sodium sulphate — Sodium carbonate and dilute sulphuric acid.
(d) For lead sulphate — Lead carbonate + dil. nitric and then dil. sulphuric acid.
Question 16: Give examples of the use of sulphuric acid as:
(i) An electrolyte in everyday use. (ii) A non-volatile acid.
(iii) An oxidizing agent.
Answer: (i) In lead accumulators or in storage batteries.
(ii) In the manufacture of other acids like nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid.
(iii) For cleaning metals before enameling, electroplating and galvanizing, as a pickling agent.
Question 17: Some of the properties of six pure substances represented by A, B, C, D, E and F are given below:
A-when heated with concentrated sulphuric acid, it gives off a choking gas which dissolves in water giving an acid.
B- is a greenish-yellow gas which dissolves in water and when this aqueous : solution is exposed to sunlight, bubbles of a gas are evolved, which rekindles a glowing splinter.
C- is a metal which when treated with concentrated nitric acid, gives off a brown gas and a blue solution is obtained.
D- is a white solid, which when heated, gives off a sweet smelling gas which rekindles a glowing splinter.
E- is a heavy oily liquid which when added to moist sugar, chars it into a black porous mass.
F- is a gas which turns moist red litmus to blue. When the gas is passed over heated copper oxide, an inactive gas is obtained.
(i) Name the substances A, B, C, D, E and F.
(ii) Write equations for the following reactions involving A, B, C, D, E and F.
(a) A is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid.
(b) An aqueous solution of B is exposed to bright sunlight.
(c) Concentrated nitric acid and the metal C are heated.
(d) The action of heat on D.
(e) Oily liquid E is added to sugar.
(f) The action of F on heated copper (II) oxide.
Answer: (i) A is sodium chloride, B is chlorine gas, C is copper, D is ammonium nitrate, E is concentrated sulphuric acid and F is ammonia gas respectively.
(ii) When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid, hydrogen chloride gas is liberated and sodium sulphate is also formed.
![]()
(a) Chlorine gas reacts with water in the presence of sunlight to liberate oxygen gas and hydrochloric acid is formed.
![]()
(b) Copper and concentrated nitric acid when heated, a brown gas, nitrogen dioxide is evolved and-a blue coloured copper nitrate is formed.

(c) Ammonium nitrate on heating gives off a sweet smelling gas nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas and water is formed.

(d) Sulphuric acid acts as dehydrating agent and chars the sugar to black porous mass, i.e., carbon.
![]()
(e) When ammonia is passed over heated copper (II) oxide, it is oxidized to form nitrogen and water. Copper (II) oxide itself reduces to metallic copper.
![]()
Figure/Table Based Questions
Question 1: (i) Copy and complete the following table: Column 3 has the names of gases to be prepared using the substance you enter in column 1 along with dilute or concentrated sulphuric acid as indicated by you in column 2.

(ii) Write the equations for the laboratory preparation of:
(a) Sodium sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
(b) Lead sulphate using dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer: (i)
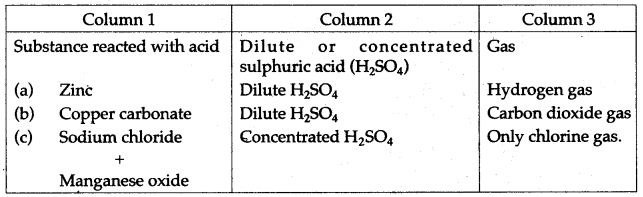
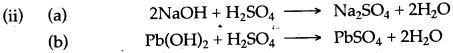
Question 2: Study the diagram given below, which illustrates the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
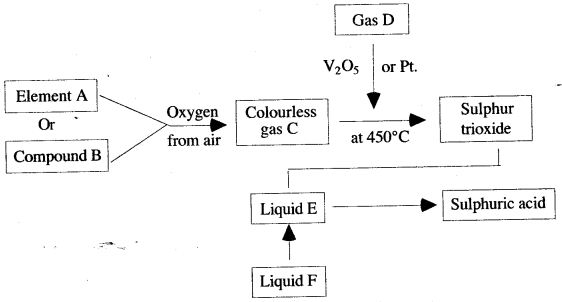
(i) Write the names of the substances A to F.
(ii) Describe how gas C could be identified.
(iii) Explain the purpose of V2O5 or Pt.
(i) A—Sulphur
B—Iron pyrites
C—Sulphur
D—Oxygen
E—Concentrated sulphuric acid
F—Water
(ii) The gas C will turn acidified potassium dichromate paper green.
(iii) V2O5 or Pt acts as a catalyst and increases the rate of formation of sulphur trioxide from sulphur dioxide and oxygen.
Question 3: (i) Name the catalyst which helps in the conversion of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide in step C.
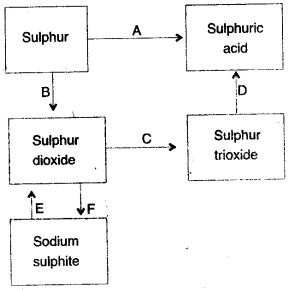
(ii) In the Contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid, sulphur trioxide is not converted to sulphuric acid by reacting it with water. Instead a two step procedure is used. Write the equations for the two steps involved in D.
(iii) What type of substance will liberate sulphur dioxide from sodium sulphite in step E ?
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction by which sulphur dioxide is converted to sodium sulphite in step F.
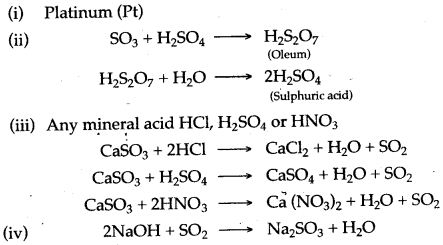
Answer:
Reasoning based Questions
Question 1: Why concentrated sulphuric acid is called the “oil of vitriol” ?
Answer: Concentrated sulphuric acid is called “Oil of vitriol” because of its oily appearance and the fact that it is present in vitreous or glassy substances like ferrous sulphate, alum, etc.
Question 2: For the production of concentrated sulphuric acid, sulphur trioxide is not directly dissolved in water. Why ?
Answer: Because with water, sulphur trioxide forms a mist of fine drops of sulphuric acid.
Question 3: The impurity of arsenic oxide must be removed before passing the mixture of sulphur dioxide and air through the catalytic chamber in contact process. Why ?
Answer: Because the impunty of arsenic oxide makes the catalyst poisonous.
Question 4: Why concentrated sulphuric acid is kept in air tight bottles ?
Answer: Concentrated sulphuric acid readily absorbs moisture from atmosphere and gets diluted. Hence, it is kept in air tight bottles.
Question 5: Why the level of concentrated sulphuric acid gets higher if it is left in an open vessel for a week ?
Answer: This is due to the hygroscopic nature of sulphuric acid. It absorbs water vapour from the atmosphere.
Question 6: Why sulphuric acid behaves as an acid when diluted with water ?
Answer: When sulphuric acid is diluted with water, it ionizes almost completely into hydrogen ions (H+) and sulphate ions (SO42-)
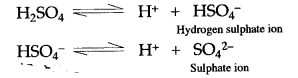
Since presence of H+ ions imparts acidic character, therefore solution of sulphuric acid in water behaves as an acid.
Question 7: Why the wooden shelves on which cone, sulphuric acid bottles are kept, stained black ?
Answer: Concentrated sulphuric acid is a very powerful dehydrating agent. It removes atoms of hydrogen and oxygen in the form of water from the cellulose [(C6H12O5)n], leaving behind carbon. It is black carbon which appears in the form of black stains.
Question 8: A black spongy mass is formed, when concentrated sulphuric acid is added to sugar. Why ?
Answer: Sulphuric acid has great affinity for water, hence when concentrated sulphuric acid is added to sugar, it absorbs water from sugar by removing hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the ratio of 2:1 from sugar molecules. The sugar is charred producing black spongy mass of carbon, which is known as sugar charcoal.
![]()
Question 9: When blue crystals of copper (II) sulphate are added to concentrated sulphuric acid crystals turn white. Why ?
Answer: Hydrated copper (II) sulphate, when added to concentrated sulphuric acid, loses water of crystallization and thus white anhydrous copper (II) sulphate is formed. The blue coloured hydrated copper (II) sulphate turns white due to the loss of water of crystallization.
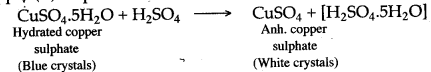
Question 10: Why brisk effervesence is seen when H2SO4 is added to sodium carbonate ?
Answer: This brisk effervescence is seen due to the evolution iof carbon dioxide gas.
Chemical Tests
Question:
1. Dilute sulphuric acid and dilute hydrochloric acid.
2. Chlorine gas and sulphur dioxide gas
Answer: When barium chloride solution is added to the dilute sulphuric acid, thick white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed which is insoluble in any mineral acid such as nitric acid or hydrochloric acid
![]()
With dilute hydrochloric acid, no effect is observe.
Chlorine gas turns starch iodide paper blue and sulphur dioxide gas turns moist acidified potassium dichromate paper green.
Balancing/Writing the Chemical Equations
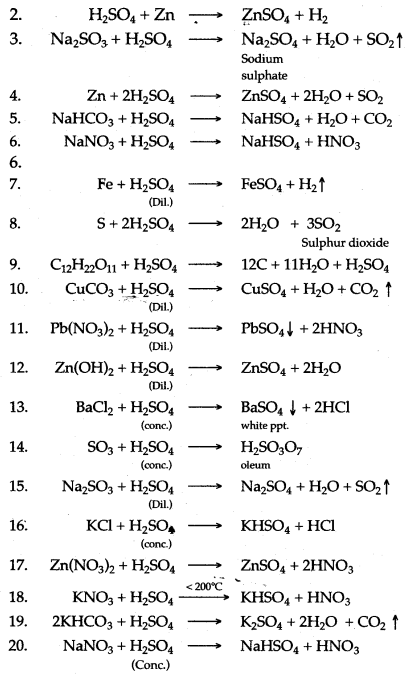
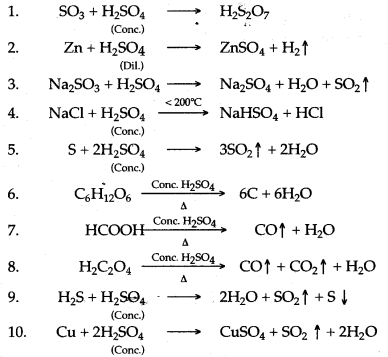
Question 1: Write balanced chemical equation for the following :
1. Action of concentrated sulphuric acid on carbon.
2. Dilute sulphuric add produdng hydrogen.
3. Dilute sulphuric add is poured over sodium sulphite
4. Zinc reacts with cone. Sulphuric add.
5. Sodium bicarbonate and dilute sulphuric acid.
6. Sodium nitrate and cone. Sulphuric add.
7. Iron reads with dil sulphuric acid.
8. Sulphur is heated with concentrated sulphuric add.
9. Concentrated sulphuric acid is poured over sugar.
10. Dilute sulphuric add with Copper carbonate.
11. Dilute sulphuric acid with Lead nitrate solution.
12. Dilute sulphuric acid with Zinc hydroxide.
13. Concentrated sulphuric acid with barium chloride.
14. Concentrated sulphuric add with sulphur trioxide.
15. Sodium sulphite with dilute sulphuric acid.
16. Concentrated sulphuric acid with potassium chloride.
17. Concentrated sulphuric add with zinc nitrate.
18. Concentrated sulphuric add with potassium nitrate.
19. Potassium hydrogen carbonate and sulphuric add.
20. Sodium nitrate and concentrated sulphuric acid.
Answer:

Question 2: Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
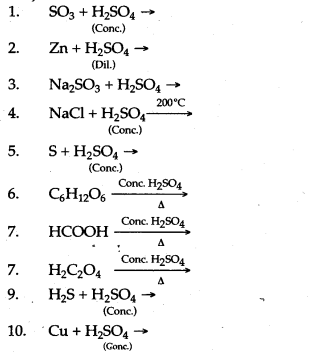
Answer:
For More Resources
