What is the Structure and Function of Mitochondria
Mitochondria :
A single mitochondrion is present in unicellular green alga, Microsterias. Number of mitochondria varies from 50–50,000 per cell. Mitochondria of a cell are collectively known as chondriome.
Historical Account :
C. Benda (1897) gave the name Mitochondria (Mitos, thread + Chondrion, granules).
Term ‘Bioplast’ for mitochondria was used by Altman.
Ultrastructure :
- Mitochondria are rod shaped organelles, bounded by a double membrane envelope.
- The outer membrane is smooth, the inner membrane surrounds a central cavity of matrix. Central cavity is filled with jel like substances.
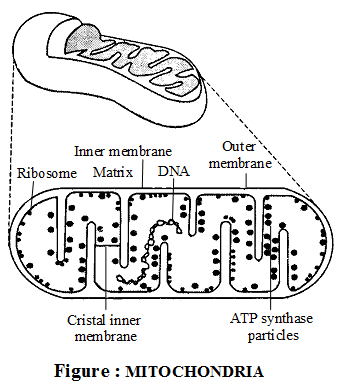
- Inner membranes folds are called cristae, these folding are tubular and called microvilli.
- Mitochondria contain electron transport systems aggregated into compact structure. F1 particles or oxysome, tennis racket like bodies on inner membrane involved in oxidation & phosphorylation.
- Kreb’s cycle occurs in mitochondria.
- Each particle is made up of base, stalk and head.
Functions of Mitochondria :
- Mitochodria are called power plants or power houses or cellular furnaces.
- Synthesis of ATP (Adenosine Tri-phosphate) in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation.
- Mitochondria as place of cellular respiration was first observed by Hogeboom.
