What is the Shoot System of a Plant
Shoot system
All parts of a plant that are above the ground form the shoot system. It includes stem, leaf, flower, fruit, etc.
Stem
The stem is a very important part of the plant.
Functions of a Stem
- It holds leaves in position and helps them to spread out as the stem and its branches grow. This ensures that they get enough light for photosynthesis.
- It bears flowers, buds, leaves, and fruits.
- It conducts water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves.
Similarly, it carries the food manufactured by the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Green stem has chlorophyll and can carry out photosynthesis. - It has nodes from which leaves arise.
- The space between two nodes is called an internode.
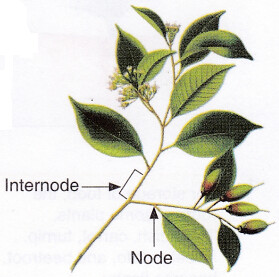
A stem showing nodes and internodes
Stem modifications
Stems of certain plants are modified to perform special functions. Some of the modifications and their functions are given below.
For storage of water Stems of plants like cactus and jade swell up to store water in them.
To manufacture food Stems of some plants become leaf-like and flattened like that of a cactus and perform photosynthesis.
For protection Stems may be modified as thorns, like in bougainvillea or may be in the form of hard and sharp prickles, as in rose, to protect the plant from being eaten by animals.

For support Stems of some climbers like grapes and passion flower are modified to form special structures called tendrils. These help the climber plants like, which have weak stems, attach themselves to others for support.

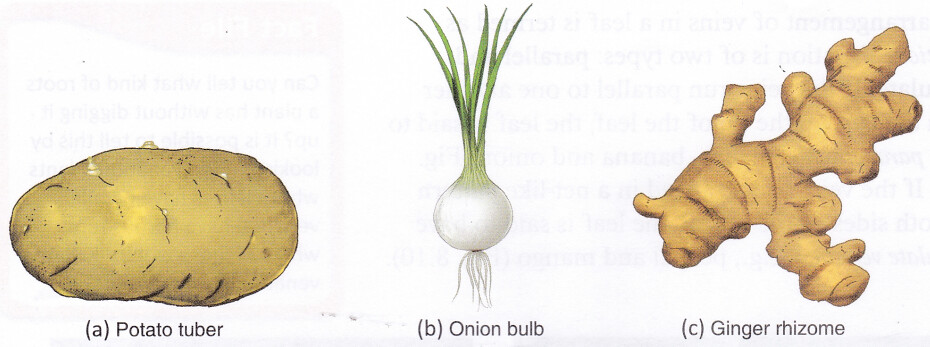
For storage of food Potato, onion, and ginger are modified stems that store food. There are three kinds of underground stems: tubers (e.g., potato), rhizomes (e.g., ginger), and bulbs (e.g., onion and garlic).
For multiplication of the plant Rhizomes, bulbs, and tubers also help in the multiplication of plant. Stem cuttings of some plants like rose, jasmine, and hibiscus grow into new plants.
Activity
Aim: To observe conduction by stem
Materials needed: A white flower with a short stem, a glass, some red food colouring agent, and water
Method:
1. Place the white flower in a glass containing some red food colouring agent such that the cut end of the stem is immersed in the coloured water.
2. Leave it for about a day.
Observation: The stem and the flower become reddish.
Conclusion: This is because water is taken up by the stem.
Note: This result is best observed in a white carnation.
