Selina Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions Current Electricity
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 9 Current Electricity. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 9 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 9 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 9 Current Electricity
Exercise 9(A)
Solution 1S.
Source of D.C.: Cell
Source of A.C.: Mains
Solution 2S.
Direct current (D.C.) is a current of constant magnitude flowing in one direction but alternating current (A.C.) is a current which reverses its magnitude and direction with time.
Solution 3S.
An electric cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. When connected in a circuit, it acts as a source of D.C. current.
Solution 4S.
Chemical energy changes into electrical energy.
Solution 5S.
Constituents of cell: Two electrodes and an electrolyte in a vessel.
Solution 6S.
Two kinds of cells:
- Primary cell: e.g. Leclanche cell
- Secondary cell: Lead (or acid) accumulator
Solution 7S.
Primary cells are cells which provide current as a result of irreversible chemical current.
Examples: Simple Voltaic cell and Leclanche cell.
Solution 8S.
Secondary cells are cells which provide current as a result of reversible chemical reactions. It converts electrical energy into chemical energy when current is passed in it (i.e. during charging), while it converts chemical energy into electrical energy when current is drawn from it (i.e., during discharging).
Example: Lead (or acid) accumulator.
Solution 9S.
| Primary Cell | Secondary cell |
1. Chemical reaction is irreversible. 2. Only chemical energy is converted into electrical energy when current is drawn from it. 3. It cannot be recharged and its internal resistance is high. | 1. Chemical reaction is reversible. 2. It converts electrical energy into chemical energy when current is passed in it (i.e., during charging), while converts chemical energy into electrical energy when current is drawn from it (i.e., during discharging). 3. It can be recharged and its internal resistance is low. |
Solution 10S.
Current is the rate of flow of charge across a cross-section. It is a scalar quantity.
Its S.I. unit is ampere (coulomb per second).
If 1 ampere current flows through a conductor, it means that 6.25 x 1018 electrons pass in 1 second across that cross-section of conductor.
Solution 11S.
Charge on an electron is -1.6 x 10-19 coulomb.
Solution 12S.
![]()
Solution 13S.
A rheostat is used to control current in an electric circuit.
Solution 14S.
A: Ammeter – It measures the current flowing through the circuit.
B: Cell – It acts as a source of direct current for the circuit.
C: Key – It is used to put the current on and off in the circuit.
D: Load – It is an appliance connected in a circuit. It may just be a resistance (e.g., bulb) or a combination of different electrical components.
E: Voltmeter – It is used to measure the potential difference between two points of a circuit.
F: Rheostat – It is used to control the current in the circuit.
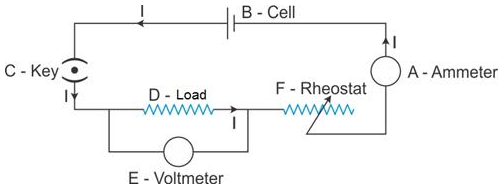
Solution 15S.
A key or switch is used to put on or off, the current in the circuit.
Solution 16S.
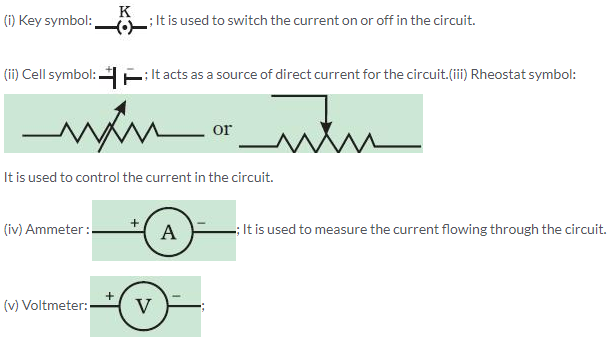
It is used to measure the potential difference between two points of a circuit.
Solution 17S.
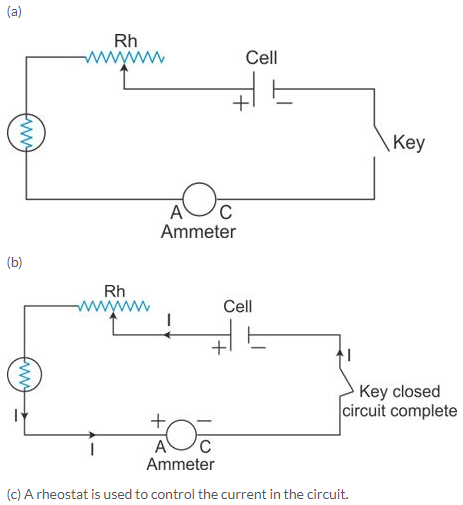
Solution 18S.
The substances which allow electric current to flow through them easily are called conductors. Examples: Impure water and metals.
The substances which do not allow the electric current to flow through them are called insulators. Examples: Rubber and wood.
Solution 19S.
Copper wire, acidulated water and human body.
Solution 20S.
Conductors have a large number of free electrons and they offer a very small resistance in the path of current but insulators have no free electrons and they offer a very high resistance in the path of current.
Solution 21S.
A circuit is said to be closed when every part of it is made of a conductor and on plugging in the key or on being complete, current flows through the circuit.
A circuit is said to be open when no current flows through it. It can happen when the key is not plugged in or when any one of its components is not made of a conductor or when the circuit is broken.
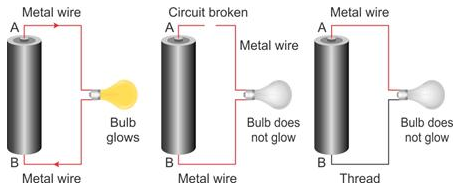
Solution 22S.
For an electric circuit to be closed, every part of it must be made of conductors.
Solution 1M.
provide current in a circuit
Solution 2M.
ampere
Solution 3M.
silk
Solution 1N.
Current (I) = Charge (q)/time (t)
Or, I = 0.5/ 5 = 0.1 A
Solution 2N.
Charge (q) = Current (I) x time (t)
Or, q = 1.5 x 2 = 3 C
Solution 3N.
Current (I) = Charge (q)/time (t)
Or, I = 24/ 0.8 = 30 A
Exercise 9(B)
Solution 1S.
When both the conductors are joined by a metal wire:
- Electrons will flow from A to B.
- Current will flow from B to A.
Solution 2S.
Current always flows from high potential to low potential.
Solution 3S.
Electric potential difference between two conductors is equal to the work done in transferring a unit positive charge from one conductor to other conductor.
Solution 4S.
Electric potential difference is the difference in electric potential (V) between the final and the initial location when work is done upon a charge to change its potential energy. In equation form, the electric potential difference is
![]()
Solution 5S.
S.I. unit of potential difference is volt (joule per coulomb).
Potential difference between two points is said to be 1 volt if work done in transferring 1 coulomb of charge from one point to the other point is 1 joule.
Solution 6S.
Potential difference between two points is 1 volt; it means 1 joule of work is done in transferring 1 coulomb of charge from one point to the other point.
Solution 7S.
The obstruction offered to the flow of current by the filament or wire is called its electrical resistance.
Solution 8S.
A metal wire has free electrons which move in random directions. When the ends of the wire are connected to a cell, the electrons start moving from the negative terminal of the cell to its positive terminal through the metal wire. During their movement, they collide with the free electrons and fixed ions of the wire. This causes them to lose their speed and change their direction. As a result, the electrons slow down and slowly drift towards the positive terminal. Thus, the wire offers resistance to the flow of current (or electrons) through it.
Solution 9S.
The S.I. unit of resistance is ‘ohm’ (volt per ampere).
The resistance of a conductor is said to be 1 ohm if a current of 1 ampere flows through it when the potential difference across it is 1 volt.
Solution 10S.
Ohm’s law states that the electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V across its ends provided its temperature remains the same.
Solution 11S.
Potential difference = Current x Resistance
i.e., V = I R
Solution 12S.
The resistance of a wire is 1 ohm; it means a current of 1 ampere will flow through the wire when the potential difference across it is 1 volt.
Solution 13S.
V = IR or, I = V/R….(i)
If R is doubled,
Then, I’ = V/2R = I/2……………(ii)
From (i) and (ii), it is clear that current will be halved.
Solution 14S.
Resistance of a wire depends upon:
- Length of wire: Resistance is directly proportional to the length of a wire.
- Area of cross-section of wire: Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section the wire.
- The temperature of wire: Resistance of a wire is directly proportional to the temperature of the wire.
Solution 15S.
(a) Resistance of a wire is directly proportional to the length of a wire; so if the length is doubled, resistance is also doubled.
(b) Resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section the wire. Thus, if radius is doubled, area increases four times and hence the resistance becomes one-fourth.
Solution 16S.
The temperature of the filament increases when it glows. So, when the temperature of the wire (bulb filament) increases, ions in it vibrate violently. As a result, the number of collisions increases and hence the resistance increases.
Solution 17S.
(i) Potential difference (ii) charge (iii) resistance (iv) current.
Solution 1M.
In direction from high potential to low potential.
Solution 2M.
volt
Solution 3M.
Decreases
Solution 1N.
Potential difference (V) = work done (W) / charge (q)
Or, V = 9/1.5 = 6 volt.
Solution 2N.
Given, potential difference (V) = 12 V
Resistance, R = 24 Ω
Therefore, current (I) = V / R
Or, I = 12/24 = 0.5 A
Solution 3N.

Solution 4N.

Exercise 9(C)
Solution 1S.
Efficient use of energy means to reduce cost and amount of energy to be used to provide us the various products and services.
Solution 2S.
Two ways to save energy:
- Instead of fossil fuels, other renewable sources of energy such as the biogas prepared from animal dung should be used.
- The use of hydroelectric energy, wind energy etc. should be given priority.
Solution 3S.
By properly insulating a home, it is possible to maintain a comfortable temperature inside. It will reduce the cost of heating devices in winter and cooling devices in summer.
Solution 4S.
LED or light emitting diodes are most efficient for lighting purposes.
Solution 5S.
Modern appliances like refrigerators make use of significantly less energy than older appliances as they have star rating according to their efficient use of electricity. Higher the star rating, higher is the efficiency.
Solution 6S.
Three ways to use energy efficiently:
- The use of compact fluorescent lights (CFL) saves 67% energy and may last 6 to 10 times longer than the incandescent lamps.
- The use of advanced boilers and furnaces in industry can save sufficient amount of energy in attaining high temperatures while burning less fuel. Such technologies are more efficient and less polluting.
- The fuel efficiency in the vehicles can be increased by reducing the weight of the vehicle, using the advanced tyres and computer controlled engines.
Solution 7S.
The following social initiatives need to be taken:
- Public awareness can be improved through mass-media and children’s participation in campaigns and eco-club activities.
- Community involvement need to be done to reduce the misuse of electricity.
- NGO’s can be used to create social awareness of the sensitive use of resources.
Solution 1M.
The most non-polluting and efficient lighting device is the LED.
Solution 2M.
IEA is the short form of international energy agency.
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Concise Physics Class 9 Solutions
- Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Selina Concise Biology Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Selina Class 9 Maths Solutions
