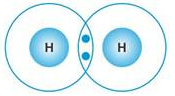
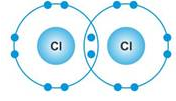
Selina Concise Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions Study of the First Element – hydrogen
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 7 Study of Gas Laws. You can download the Selina Concise Chemistry ICSE Solutions for Class 9 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Chemistry for Class 9 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 9 Study of the First Element – hydrogen
Exercise 9
Solution 1.
(a) The position of hydrogen in the periodic table
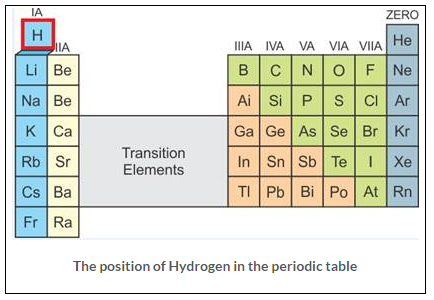
Hydrogen is first element in the periodic table. It has an atomic number l and an atomic mass of 1.00794 amu, occupying group – IA. Its position is peculiar because it is grouped with metals although it is a non-metal properties. Hydrogen relate to Group IA as well as Group VII A.
(b) The properties of hydrogen resemble the properties of Group IA elements (Alkali metals), and some of it resembles the properties of Halogens (VIIA), so Hydrogen was put at the top of the periodic table so that the symmetry of the modern periodic table is not disturbed.
- All elements in Group- IA have one electron in outermost shell, so they havevalency one.
- These elements in Group-IA are good reducing agents.
- All elements of this group formsoxide which are highly basic and dissolves in water to form strong alkalis.
- They impartcolour to a flame.
Solution 2.
Similarity of hydrogen with alkali metals and halogens
| Similarity of hydrogen with alkali metals [Group 1 (IA)] | Similarity of hydrogen with halogens [Group 17 (VIIA)] | |
| Electronic configuration | Electronic configuration = 1. Thus, 1electro in the outermost valence shell. Example: | One electron less than the nearest noble gas. Example: |
| Ion formation | Electropositive character exhibited. H 1e– → H1+ | Electronegative character exhibited. H + 1e– → H1- |
| Valency | Electrovalency of one exhibited. H1+ , Li1+ , Na1+ | Electrovalency and covalencyexhibited. Hydrogen: forms NaH (electrovalent)forms CH4(covalent) Chlorine: forms NaCl (electrovalent) |
| Reactions | Strong affinity for non-metals (example: O, S, Cl) Hydrogen: forms H2O; H2S; HCl Sodium: forms Na2O; Na2S; NaCl | __ |
| Reducing agent | Acts as a reducing agent. Hydrogen: CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O Sodium: CuO + 2Na → Cu + Na2O | __ |
| Atomicity | __ | Diatomic molecules are formed. (Two atoms linked by a single bond) Hydrogen Chlorine |
Resemblance with Halogens:
- Both exist in the form of diatomic molecules.
- Both show gaseous nature.
- Both have a valency of 1.
- Both are non-metals.
- Both lose electron to term anions.
Solution 3.
(a) Hydrogen is found in minute traces in the Earth’s crust and the Earth’s atmosphere. The atmosphere around the sun and stars is found to contain 1.1 % hydrogen.
(b) Henry Cavendish when prepared this gas from iron and dil. acids, he established its elementary nature and showed that when the gas burns in air, water is formed. It was on account of this property that Lavoisier in 1783 named it hydrogen (Greek word meaning water-former).
Solution 4.
(a) A monovalent metal
2Na + H2 → 2NaH
(Sodium hydride)
(b) A divalent metal
Ca + H2 → CaH2
(Calcium hydride)
Solution 5.
(a) Calcium: is not used in lab preparation of hydrogen because:
- The reaction and very violent and exothermic hence dangerous.
- The heat liberated ignites the hydrogen.
- Calcium is expensive.
(b) Iron: Iron reacts slowly at ordinary temperatures, hence requires heating. The hydrogen produced also contain impurities like sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. Hence, it is not used in lab preparation of hydrogen.
(c) Aluminium: It is not used in the lab preparation of hydrogen because oxides of this metal keep sticking to the surface of the metal. Thus the steam does not come in contact with metal and hence reaction stops. .
(d) Sodium: It is riot used in the lab preparation of hydrogen because the reaction is violent. The sodium melts into a globule and darts about freely on the surface of water hence the collection of hydrogen is difficult.
Solution 6.
Depending upon the nature of reaction taking place between metals and substances like air, water and acids, metals are arranged in a vertical series in order of their activity. Such a series is called activity series of metals.
The metals places near the top of the series are the most reactive, while those placed near the bottom are the least reactive.
When dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid react with the metals above hydrogen in the activity series, they produce hydrogen. But the metals below hydrogen in the activity series do not.
Solution 7.
(a) Reactants: Nitrogen and hydrogen (Haber process)
Chemical equation:
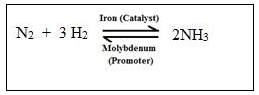
Observation and conditions
Three volumes of hydrogen and one volume of nitrogen react at temperature 450oC-500oC at the pressure of 200-900 atm, in presence of a finely divided iron which acts as a catalyst, and promoter molybdenum.
(b) Reactants: Chlorine and hydrogen
Chemical equation:
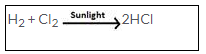
Observation and conditions
Hydrogen and chlorine (in their equal volumes) react slowly in diffused sunlight but reacts explosively in direct sunlight. A spontaneous reaction takes place with the release of a large amount of energy.
(c) Reactants: Sulphur and hydrogen
Chemical equation:
H2 + S → H2S
Observation and conditions
Hydrogen gas when passed through molten sulphur, it reacts to give another gas, hydrogen sulphide.
(d) Reactants: Oxygen and hydrogen
Chemical equation:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Observation and conditions
Hydrogen burns with a pop sound in oxygen. It burns with a pale blue flame forming water.
Solution 8.
(a) Among the given metals Zinc is most suitable.
(i) Copper: In case of copper, It is placed below hydrogen in the activity series. So it does not displace hydrogen from acid.
Cu + HCl → No reaction
(ii) In case of Mg; it is a very expensive metal.
(iii) In case of sodium, it reacts with explosively and violently.
(b) Among the given acids we prefer dilute sulphuric acid.
We reject concentrated sulphuric, dilute nitric and concentrated nitric acid because these are powerful oxidising agents and oxygen formed due to its decomposition oxidises the hydrogen to water.
(c) Modification: Collect the gas by downward displacement of water when all the air from the apparatus has been expelled. Drying Agent used is Calcium Chloride.
Solution 9.
(a) Iron reacts reversibly with steam. Hence the hydrogen formed is removed as it is released to prevent reduction of triferric tetraoxide.
Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2 ?
(Steam)
(b)
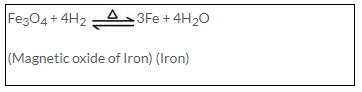
Solution 10.
(a) The metal is magnesium
(b) Mg + H2O → MgO + H2
Solution 11.
(a) Substance A is CuO and substance B is Cu.
(b) Test for water
(i) It is neutral to litmus
(ii) It changes anhydrous copper sulphate into blue salt.
(c) When substance A i.e, CuO reacts with hydrogen, it removes oxygen and we get free metal i.e. Cu.
(d) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(e) No, there is no reaction between substance B and dilute hydrochloric acid because copper does not displace hydrogen from acids.
(f) Cu + HCl → No reaction
Solution 12.
Magnesium lies above Hydrogen in reactivity series and can displace hydrogen from acid whereas, Mercury and silver lie below hydrogen in reactivity series and cannot displace hydrogen from acid and hence nothing happens.
Solution 13.
Soap bubbles containing hydrogen rapidly rise up in air as hydrogen is lighter than air.
Solution 14.
Bosch Process
Bosch process consists of following steps.
Step 1 :
Steam is passed over a hot coke (at 1000oC) in a special type of a furnaces called converters.
In this step carbon reacts with water to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas. This mixture is called water gas.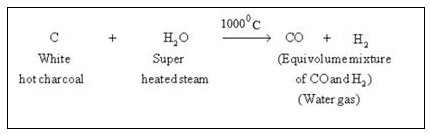
Step 2 :
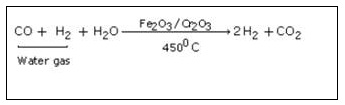
In this step excess of steam is mixed with water gas and entire mixture is passed over heated ferric oxide and chromic oxide. Ferric oxide acts as catalyst and chromic oxide as promoter.
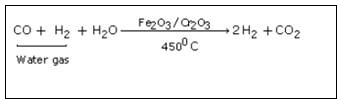
Step 3 :
In this step removal of carbon dioxide from reaction mixture takes place. The mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is forced through cold water under pressure at 30 atmospheric pressure or through caustic potash solution which dissolve carbon dioxide leaving behind hydrogen gas.
2KOH + CO2 → K2CO3 + H2O
Step 4 :
In this last step, mixture is passed through ammonical solution of cuprous chloride solution so as to dissolve carbon monoxide. CO is removed by bubbling the gas through ammoniacal cuprous chloride solution. The moisture is removed by cooling the gas about 20°C when water vapoursfreeze. The pure and dry hydrogen gas is collected in steel cylinders.
CuCl + CO + 2H2O → CuCl.CO.2H2O
Solution 15.
(a) Cold water:
Sodium metal wrapped in small piece of wire gauze or Sodium amalgamated with mercury is used. This prevents sodium from darting about.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 ↑
(b) Hot water:
Zn or Mg can be used.
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2 ↑
(boiling water)
(C) Steam:
Iron reacts with the steam and the reaction is reversible. Iron reacts with steam when it is red hot as hydrogen is blown out of contact with iron by the force of current of the steam.
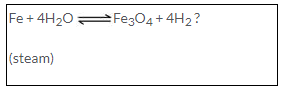
Solution 16.
Metals
Mg, Al, Zn, Fe do not react with cold water. It reacts with boiling water liberating hydrogen gas but the reaction is very slow.
Mg, Al, Zn, Fe react with the hot steam in the heated state and form the corresponding oxide and hydrogen gas.
Iron reacts with the steam and the reaction is reversible.
Magnesium
Reaction of boiling water with steam is slow but Mg liberates Hydrogen rapidly with steam.
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2 ↑
(boiling water)
Aluminium
Gets coated with Al2O3 on rubbing with sand paper its oxide coating is removed and then it reacts with steam to produce hydrogen.
2Al + H2O → Al2O3 + 3H2 ↑
(steam)
Zinc
Zinc reacts with steam and produce zinc oxide and H2
Zn + H2O → ZnO + H2 ↑
(steam)
Iron
Iron produces H2 when red hot the reaction is reversible but as soon as hydrogen is produced it is blown out of contact with iron by the force of the current of steam.
![]()
(steam)
Non-metals
Bosch Process (From Coke)
Bosch process consists of following steps.
Step 1 :
Steam is passed over a hot coke (at 1000oC) in a special type of a furnaces called converters.
In this step carbon reacts with water to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas. This mixture is called water gas.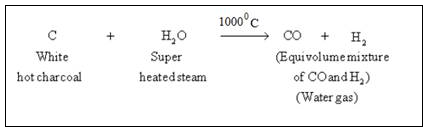
Step 2 :
In this step excess of steam is mixed with water gas and entire mixture is passed over heated ferric oxide and chromic oxide. Ferric oxide acts as catalyst and chromic oxide as promoter.
Step 3 :
In this step removal of carbon dioxide from reaction mixture takes place. The mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen is forced through cold water under pressure at 30 atmospheric pressure or through caustic potash solution which dissolve carbon dioxide leaving behind hydrogen gas.
2KOH + CO2 → K2CO3 + H2O
Step 4 :
In this last step, mixture is passed through ammonical solution of cuprous chloride solution so as to dissolve carbon monoxide. CO is removed by bubbling the gas through ammoniacal cuprous chloride solution. The moisture is removed by cooling the gas about 20C when water vapoursfreeze. The pure and dry hydrogen gas is collected in steel cylinders.
CuCl + CO + 2H2O → CuCl.CO.2H2O
Solution 17.
(a) Zinc and iron lie above hydrogen in reactivity series and can displace hydrogen from acid.
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 ↑
(dilute)
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2 ↑
(dilute)
(b) Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
(dilute)
Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2 ↑
(dilute)
Copper lies below hydrogen. Thus, it cannot displace hydrogen from acids.
Solution 18.
Two alkalis which can displace hydrogen are NaOH and KOH.
Aluminium
2Al + 6NaOH → 2Na3AlO3 + 3 H2 ↑
(Sodium aluminate)
2Al + 2KOH + 2H2O → 2KAlO2 + 3 H2 ↑
(Potassium meta aluminate)
Zinc
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2 ↑
(Sodium zincate)
Zn + 2KOH → K2ZnO2 + H2 ↑
(Potassium zincate)
Aluminium and Zinc have unique nature; They react with acids and can even react with hot concentrated alkalis to form hydrogen and a soluble salt. Salt s (oxides and hydroxide) of these metals are Amphoteric.
Question 19.
Complete and balance the following reactions.
(a) Na + H2O →_____________ +___________
(b) Ca + H2O →_____________ +___________
(c) Mg + H2O →_____________ +___________
(d) Zn + H2O →_____________ +___________
(c) Fe + H2O →_____________ +___________
(d) Zn + HCl →_____________ +___________
(e) Al + H2SO4 →_____________ +___________
(f) Fe + HCl →_____________ +___________
(g) Zn + NaOH →_____________ +___________
(h) Al + KOH + H2O→_____________ +___________
Solution:
(a) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
(b) Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
(c) Mg + H2O → MgO + H2
(d) Zn + H2O → ZnO + H2
(e) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(f) Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
(g) 2Al + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
(h) Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2
(i) Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
(j) 2Al + 2KOH + 2H2O → 2KAlO2 + 3H2
Solution 20.
(a) Lead reacts with dilute sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid and forms an insoluble coating of lead sulphate and lead chloride respectively. Hence, further reaction is prevented.
(b) When potassium and sodium react with dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4 or dilute HCl, the reaction is highly explosive and practically not feasible.
Solution 21.
(a) Sodium hydroxide + zinc → hydrogen + Sodium zincate
(b) Calcium + water calcium → hydroxide + Hydrogen
Solution 22.
- Hydrogen gas is collected by the downward displacement of water. This is because-
- It is virtually insoluble in water.
- It forms an explosive mixture with air and therefore, cannot be collected by downward displacement of air, even though it is lighter than the air.
- A candle when brought near the mouth of the jar containing hydrogen gas starts burning but the candle is extinguished when pushed inside the jar because, Because hydrogen is a combustible gas but a non-supporter of combustion i.e. it burns itself but does not allow substances to burn in it.
- An oxy-hydrogen flame is used for welding and cutting metals because, when a mixture, of hydrogen and oxygen is burnt, temperatures as high as 2500°C is produced. This forms the basis for its use in oxy-hydrogen flame used in cutting and welding of flames.
- Apparatus for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen should be air tight and away from a naked flamebecause, mixture of hydrogen and air explodes violently when brought near a flame.
Question 23.
a. Helium is preferred to hydrogen for filling balloons because it is:
i. lighter than air
ii. almost as light as hydrogen
iii. non-combustible
iv. inflammable
b. Reacting with water, an active metal produces
i. oxygen
ii. nitric acid
iii. a base
iv. none of these
c. A metal oxide that is reduced by hydrogen is
i. Al2O3
ii. CuO
iii. CaO
iv. Na2O
d. Which of the following statements about hydrogen is incorrect?
i. It is an inflammable gas
ii. It is the lightest gas.
iii. It is not easily liquefied
iv. It is a strong oxidizing agent.
e. For the reaction PbO + H2→ Pb + H2O, which of the following statements is wrong?
i. H2 is the reducing agent.
ii. PbO is the oxidizing agent.
iii. PbO is oxidized to Pb.
iv. H2 is oxidized to H2O.
f. Which metal gives hydrogen with all of the following: water, acids, alkalis?
i. Fe
ii. Zn
iii. Mg
iv. Pb
g. Which of the following metals does not give hydrogen with acids?
i. Iron
ii. Copper
iii.Lead
iv. Zinc
Solution:
(a) (iii) non-combustible
(b) (iii) a base (c) (iii) CaO
(d) (iv) It is strong oxidising agent.
(e) (iii) PbO is oxidised to Pb
(f) (ii) Zn
(g) (ii) Copper
Question 11.
Choose terms from the options given in brackets to complete these sentences.
a. When CuO reacts with hydrogen,………………… is reduced and ……………….is oxidized to ………………… .
(CuO, H2,Cu,H2O)
b. Hydrogen is ………………… soluble in water.
(sparingly, highly, moderately)
c. Metals like …………….. , ……………… and ……………… give H2 with steam.
(iron, magnesium, aluminium, sodium , calcium)
d. Sodium ………………. reacts smoothly with cold water.
(metal, amalgam, in the molten state)
e. A metal …………….. hydrogen in the activity series gives hydrogen with …………… acid or …………… acid.
(above, below, dilute hydrochloric, concentrated hydrochloric, dilute sulphuric).
Solution 24.
(a) CuO, H2O
(b) sparingly
(c) amalgam
(d) iron, magnesium, aluminium
(e) above, dilute hydrochloric, dilute sulphuric.
Question 25.
Correct the following statements:
- Hydrogen is separated from CO by passing the mixture through caustic potash solution.
- All metals react with acids to give hydrogen.
- Hydrogen is dried by passing it through conc. H2SO4.
- Very dilute nitric acid reacts with iron to produce hydrogen.
- Conc. H2SO4 reacts with zinc to liberate hydrogen.
Solution:
(a) Hydrogen is used as a fuel in the form of coal gas, water gas and liquid hydrogen.
(b) All metals above hydrogen in reactivity series react with acids to give hydrogen.
(c) Metals like palladium or platinum or nickel absorb hydrogen at room temperature.
(d) The reaction of hydrogen with oxygen is explosive with pop sound.
(e) Concentrated sulphuric acid reacts with zinc to liberate sulphur dioxide.
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 9 ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Class 9 Chemistry Solutions
- Selina Class 9 ICSE Physics Solutions
- Selina Concise Biology Class 9 Solutions
- Selina Publishers Mathematics for Class 9