Reported Speech: The act of reporting the words of a speaker is called narration. There are basically two ways in which a speaker can convey the intended message/idea to the listener.
Looking for an easy way to Learning of English Grammar Exercises for Class 10 ICSE. You have to learn basic English Grammer topics like Tenses Verbs, Nouns, etc… In this article, we will review the best English Grammer Topics and compare them against each other.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 ICSE With Answers
Direct Speech (Direct Narration)
Direct speech is the speech inside quotation marks. It is used to tell/report the words of a speaker as it is.
Example: Divisha said, “I like to study Geography”.
Indirect Speech (Indirect Narration)
While Direct narration is okay for sharing stories with friends, this is not the best way to , report a conversation, either in speech or in writing. Therefore, we need to report the words spoken by somebody else in our own words. This is called Indirect narration.
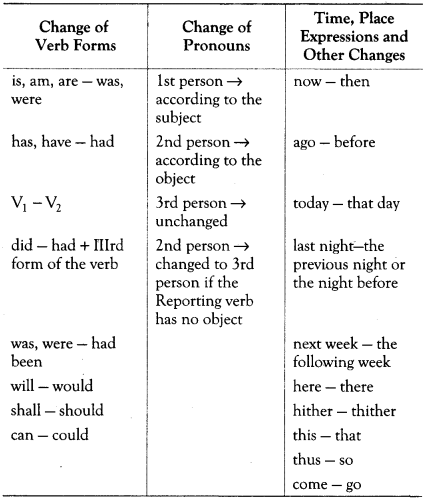
In case of Indirect narration, the pronouns (I, we, you, they etc), the tense of the statement, time words (like today, tomorrow etc), words denoting place (here, there etc), may change as the time and place of the original speech may be different from the time and place of narration.
Therefore, the above statement in indirect narration will be:
• Divisha said that she liked to study Geography.
Now, before we learn the rules of changing direct narration into indirect narration, let us get to know Reporting verb and Reported speech.
Reporting Verb
The first verb part of the sentence that comes before the quotation marks is called the Reporting verb.
Reported Speech
The statement (words) spoken by the speaker and which is written in quotation marks (“ ”) is called the
Reported speech.
Example:
Divisha said, “I like to study Geography”.
Reporting Verb Reported Speech
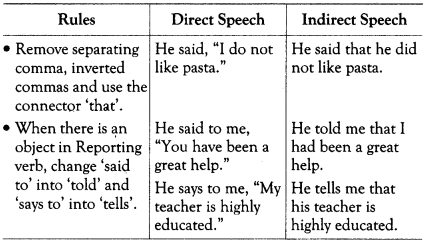
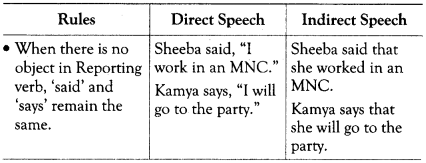
Some Basic Rules to Change Direct Speech to Indirect Speech
Indirect Speech
- Put the statement within “ ” (inverted commas).
- The Reporting verb is separated from the Direct speech by a comma.
- The first word in inverted commas begins with a capital letter.
Indirect Speech
- No inverted commas are used.
- The comma separating the Reporting verb from the Reported speech is removed.
- The Indirect speech is introduced by some connectors like – that, if, whether, what, where, how, why etc depending on whether you want to transform a statement, question or request etc into Indirect speech.
- The Reporting verb changes according to the sense conveyed by the speech.
- The tense of the Reporting verb remains unchanged.
- All kinds of sentences turn into assertive statements.
- Other changes in the person, verb forms, time and place expressions follow.
Rules for Changing Simple Direct Speech into Indirect Speech
Changes in Reported Speech when Reporting Verb is in Past Tense
Note:
If the Reporting verb is in the present or future form, the tense of the verb in the Reported speech remains unchanged.
Examples:
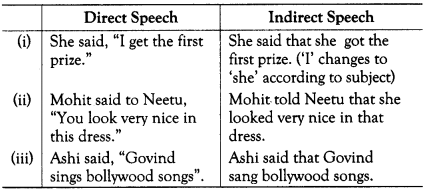
(i) Riya says, “I stay in a girls’hostel here.” (Direct)
Riya says that she stays in a girls’ hostel here. (Indirect)
(ii) Swara says to Ragini, “I need your help.” (Direct)
Swara tells Ragini that she needs her help. (Indirect)
(iii) Alhad will say to the man, ”I have seen you somewhere before.” (Direct)
Alhad will tell the man that he has seen him somewhere before. (Indirect)
(iv) The teacher will say to the students, “You will not make a noise.” (Direct)
The teacher will tell the students that they will not make a noise. (Indirect)
Tensewise Conversion of Direct into Indirect Speech
Present Tense
Present Simple Changes to Simple Past
Exception:
If the Reported speech is a universal truth or a general fact, then its ‘tense’ does not change irrespective of the Reporting verb.
Example:

Present Continuous Changes to Past Continuous
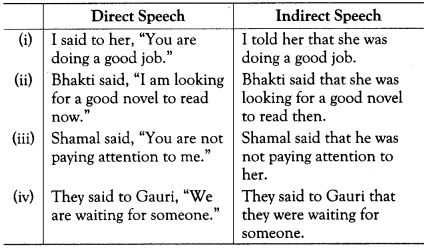
Present Perfect Changes to Past Perfect

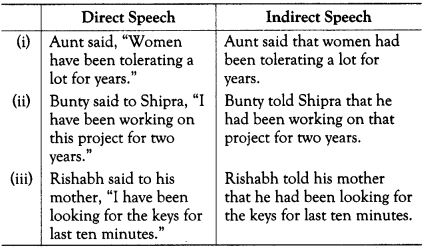
Present Perfect Continuous Changes to Past Perfect Continuous
Past Tense
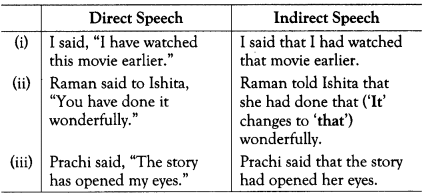
Simple Past Changes to Past Perfect
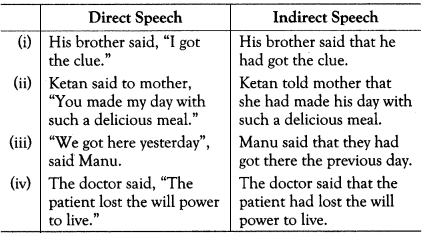
Past Continuous Changes to Past Perfect Continuous
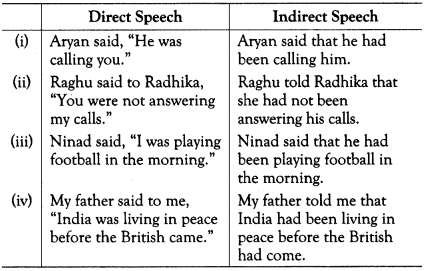
Past Perfect remains Past Perfect

Future Tense
Simple Future (Shall/Will) Changes to (Should/Would)
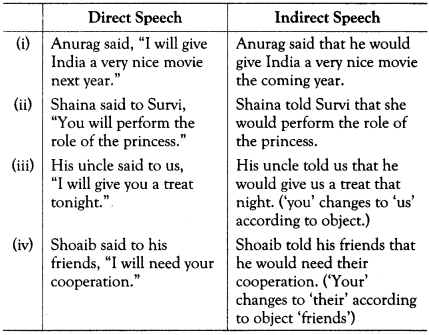
Future Continuous (Shall be/Will be) Changes to (Should be/Would be)
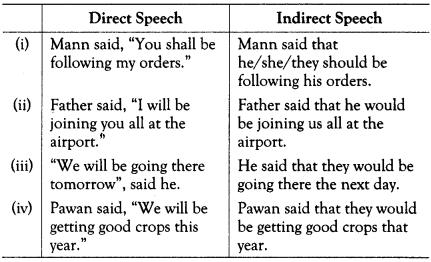
Future Perfect (Shall/Will + have) Changes to (Would + have)
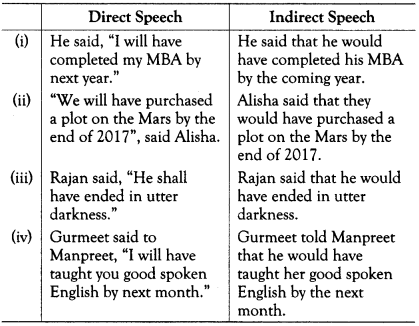
Rules for Changing Interrogative Sentences into Indirect Speech
Interrogative sentences are of two types
(i) Yes-No type questions or verbal questions
(ii) Wh-type questions
Yes-No Type Questions
When the Reported speech is a yes-no type question, the conjunction ‘if or ‘whether’ is used and the interrogative sentence (or question) is converted into an assertive sentence.
The other changes (tense, pronouns etc) are made as usual and the question mark is removed.
Most importantly, the Reporting verb is changed from ‘says’, ‘said’ to ‘asks’, ‘asked’ as the Reported speech is a question.
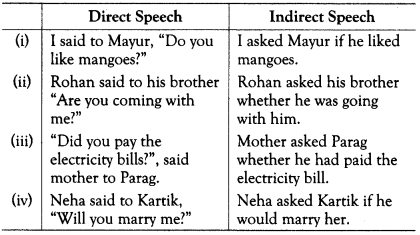
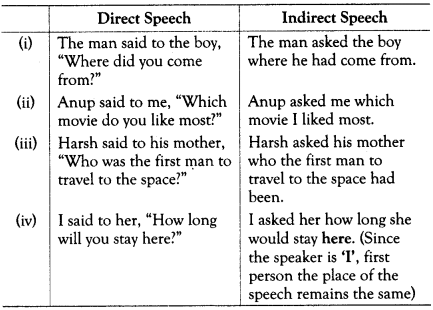
Wh-Type Questions
• No conjunction is used whereas the Wh-word itself works as a conjunction to join the Reporting verb with the Reported speech.
• All other changes are made in the same manner as the yes-no type questions.
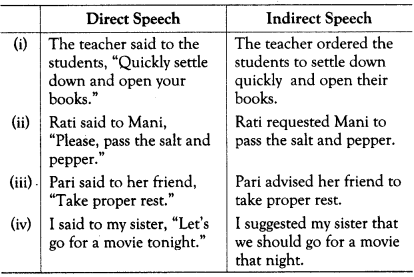
Rules for Changing Imperative Sentences into Indirect Speech
• In case of imperative sentences, the preposition ‘to’ is used in place of conjunction after the Reporting verb.
• Depending upon the type of imperative sentence (i.e. order, suggestion, advice, request etc), the Reporting verb is changed into ordered, suggested, advised, requested etc.
• In case of negative imperative sentences (such as don’t play there), ‘to’ is put after not that follows Reporting verb.
• In case of sentences beginning with ‘Let’s’, the Reporting verb is changed to proposed or suggested.
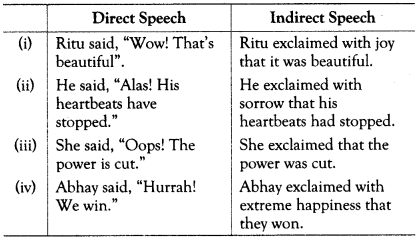
Rules for Changing Exclamatory Sentences into Indirect Speech
The sentences containing sudden expressions of joy, sorrow, anger, applause, surprise or contempt are called exclamatory sentences.
• We replace the Reporting verb with ‘exclaimed with joy,’ ‘exclaimed with sorrow’, ‘exclaimed with surprise’ etc according to the sense of the Reported speech.
• The conjunction ‘that’ is used.
Reported Speech Worksheets
1. Transform the following sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
My friend said to me, “What is your cat’s name?”
Answer:
My friend asked me what my cat’s name was.
Question 2.
Anubhav said to me, “Please lend me your bike for a day.”
Answer:
Anubhav requested me to lend him my bike for a day.
Question 3.
He said, “I shall leave these papers here.”
Answer:
He said that he would leave those papers there.
Question 4.
The teacher said, “Gandhiji died in 1948.”
Answer:
The teacher said that Gandhiji died in 1948.
Question 5.
The mother said to her son, “Change your shoes.”
Answer:
The mother asked her son to change his shoes.
2. Transform the following into direct speech.
Question 1.
The father asked me if I was happy.
Answer:
The father said to me, “Are you happy?”
Question 2.
Pravesh asked Seeta whether her brother was playing cricket.
Answer:
Pravesh said to Seeta, “Is your brother playing cricket?”
Question 3.
Kavita asked Minakshi if she watched television.
Answer:
Kavita said to Minakshi, “Do you watch television?”
Question 4.
The teacher asked Shubham whether he would join extra class the hext day.
Answer:
The teacher said to Shubham, “Will you join extra class tomorrow?”
Question 5.
Pushpa asked her teacher respectfully if she might take her book.
Answer:
Pushpa said to her teacher, “Sir, may I take my book?”
3. Transform the following sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
Sushma said to Asmita, “Where are you going?”
Answer:
Sushma asked Asmita where she was going.
Question 2.
Manmeet said to me, “Why did I fail in my exams?”
Answer:
Manmeet asked me why he had failed in his exams.
Question 3.
They said to us, “Who has broken the wall of the school?”
Answer:
They enquired from us who had broken the wall of the school.
Question 4.
Mohit said to his brother, “When will you give me a new shirt?”
Answer:
Mohit asked his brother when he would give him a new shirt.
Question 5.
The father said to Apoorva, “Change the dress.”
Answer:
The father asked Apoorva to change the dress.
4. Transform the sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
The officer said, “Move fast.”
Answer:
The officer commanded them to move fast.
Question 2.
Mahima said to Anubhav, “Please give me a new book.”
Answer:
Mahima requested Anubhav to give her a new book.
Question 3.
Shardha said, “Keep quiet and listen to my words.”
Answer:
Shardha urged them to keep quiet and listen to her words.
Question 4.
I said to my friend, “Take care of your health.”
Answer:
I advised my friend to take care of his health.
Question 5.
The teacher said to the student, “Do not make a noise.”
Answer:
The teacher ordered the student not to make a noise.
5. Transform the sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
He said, “Let us move to the party.”
Answer:
He proposed that they should move to the party.
Question 2.
The police said, “Let no one leave this room.”
Answer:
The police officer ordered that no one should leave that room.
Question 3.
He said to us, “Let us have some tea.”
Answer:
He suggested us that we should have some tea.
Question 4.
The union leader said, “Let’s show the management that we are always together.”
Answer:
The union leader urged the employees to show the management that they were always together.
Question 5.
Sarita said to me, “Let you not miss the chance to study.”
Answer:
Sarita urged me not to miss the chance to study.
6. Transform the sentences into direct speech.
Question 1.
Neena exclaimed that the doll was pretty
Answer:
Neena said, “How pretty the doll is!”
Question 2.
The doctor wished that Mohan might live long.
Answer:
The doctor said to Mohan, “May you live long!”
Question 3.
Kavita exclaimed with sorrow that she was ruined.
Answer:
Kavita said, “Alas! I am ruined”.
Question 4.
Arpit applauded me saying that I had won the match.
Answer:
Arpit said to me, “Bravo! You have won the match”.
Question 5.
The captain exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
Answer:
The captain said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.”
7. Transform the sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
He said, “I write a letter.”
Answer:
He said that he wrote a letter.
Question 2.
She said, “He goes to school daily.”
Answer:
She said that he went to school daily.
Question 3.
They said, “We love our country.”
Answer:
They said that they loved their country.
Question 4.
He said, “He does not like computers.”
Answer:
He said that he did not like computers.
Question 5.
She said, “He has finished his job.”
Answer:
She said that he had finished his job.
8. Transform the sentences into direct speech.
Question 1.
He said that he had started a job.
Answer:
He said, “I have started a job.”
Question 2.
I said that she had eaten the meal.
Answer:
I said, “She has eaten the meal.”
Question 3.
They said that they had not gone to New York.
Answer:
They said, “We have not gone to New York.”
Question 4.
He said that he had been studying since 3 o’clock.
Answer:
He said, “I have been studying since 3 o’clock.”
Question 5.
She said that it had been raining for three days.
Answer:
She said, “It has been raining for three days.”
9. Transform the sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
I said, “She has been working in this office since 2007.”
Answer:
I said that she had been working in that office since 2007.
Question 2.
He said to me, “You answered correctly.”
Answer:
He told me that I had answered correctly.
Question 3.
John said, “They went to the cinema.”
Answer:
John said that they had gone to the cinema.
Question 4.
He said, “I made a table.”
Answer:
He said that he had made a table.
Question 5.
She said, “I didn’t buy a car.”
Answer:
She said that she had not bought a car.
10. Transform the sentences into indirect speech.
Question 1.
They said, “We were enjoying the weather.”
Answer:
They said that they had been enjoying the weather.
Question 2.
He said to me, “I was waiting for you.”
Answer:
He told me that he had been waiting for me.
Question 3.
I said, “It was raining.”
Answer:
I said that it had been raining.
Question 4.
She said, “I was not laughing.”
Answer:
She said that she had not been laughing.
Question 5.
“We have had no rain since January”, Ramu said.
(Begin : Ramu said that they …………..)
Answer:
Ramu said that they had had no rain since January.
