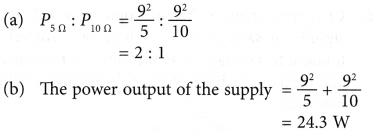Relationship between Energy Transferred, Current, Voltage and Time
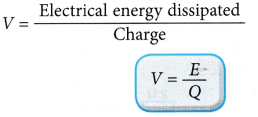
The potential difference or voltage, V across two points is defined as the energy, E dissipated or transferred by a coulomb of charge, Q that moves through the two points.
Therefore, potential difference,
Current is the rate of charge flow. Therefore, the total charges that flow through the two points is given as:
![]() Since the energy dissipated Or transferred is given by:
Since the energy dissipated Or transferred is given by:
![]() Therefore, the relationship between E, V, I and t can be written as:
Therefore, the relationship between E, V, I and t can be written as:
![]()
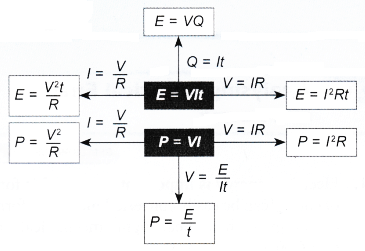
 Thus, the formulae for the energy dissipated or released by electric charges may be written in three different ways. The one that is chosen depends on the information given.
Thus, the formulae for the energy dissipated or released by electric charges may be written in three different ways. The one that is chosen depends on the information given.
People also ask
- What is Electric Current?
- What is an electric field and how is it created?
- What is the Relationship between Electric Current and Potential Difference?
- Electromotive Force, Internal Resistance & Potential Difference of a Cell/Battery
- How series and parallel circuits are different?
- Power Rating and Energy Consumption of Various Electrical Appliances
Relationship between Power Voltage and Current
Power is defined as the rate of electrical energy dissipated or transferred. Hence
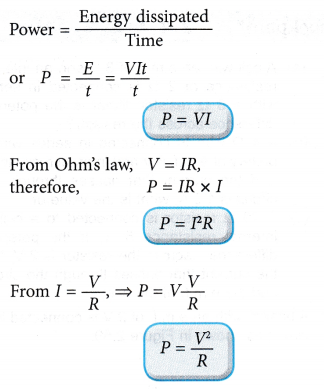
 Power is measured in joule per second (J/s) and the unit for power is watt The power of 1 watt means that 1 joule of electrical energy is being dissipated or released in every second.
Power is measured in joule per second (J/s) and the unit for power is watt The power of 1 watt means that 1 joule of electrical energy is being dissipated or released in every second.
Relationship between Energy Transferred, Current, Voltage and Time Problems with Solutions
- A current of 5 A flows through an electric heater when it is connected to a 240 V mains supply. How much heat is released after 2 minutes?
Solution:
E = VIt
= 240 x 5 x 2 x 60 J
= 144 000 J - Two resistors of 5 Ω and 10 Ω respectively are connected in parallel to a 9 V supply.
Calculate:
(a) The ratio of the power dissipated (used up) in the 5 Ω resistor to the 10 Ω resistor.
(b) The power output of the supply.
Solution: