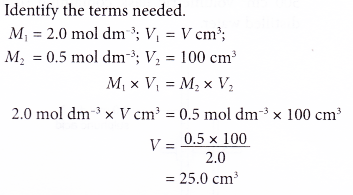How do you prepare a standard solution?

Preparation of a standard solution by weighing method
- A solution whose concentration is accurately known is called a standard solution.
- A standard solution can be prepared by weighing method in the following way.
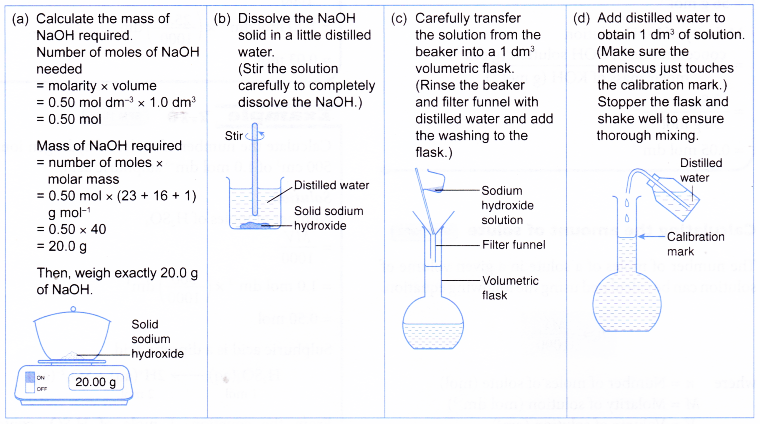
(a) The mass of solute needed is calculated and weighed.
(b) The solute is dissolved in some distilled water in a beaker.
(c) The solution is transferred into a volumetric flask.
(d) More distilled water is added to obtain the required volume. The flask is stoppered and shaken. - For example, to prepare 1.0 dm3 of 0.50 mol dm-3 aqueous sodium hydroxide.
- A very accurate standard alkaline solution cannot be prepared using sodium hydroxide as the primary standard. This is because
(a) sodium hydroxide is deliquescent. It absorbs moisture and dissolves to form a solution.
(b) sodium hydroxide may not be pure. It reacts with carbon dioxide from the air:
2NaOH(s) + CO2(g) → Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l)
Hence, the concentration of this alkaline solution is not accurate. - Pure anhydrous sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, is used to prepare a primary standard alkaline solution.
- Solid organic acids such as oxalic acid, H2C2O4.2H2O, is used to prepare primary standard acidic solution.
- A standard solution can also be prepared by dilution method.
People also ask
- What is the definition of an acid and a base?
- What is the definition of an acid in chemistry?
- What is the definition of a base in chemistry?
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- What are the chemical properties of an acid?
- General Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- Preparation of Bases
- General Properties of Bases
- What determines a Strong Base and a Weak Base
- What are the uses of Bases
- How can we measure the strength of acids and alkalis?
- How to calculate concentration of acids and alkalis?
- What is meant by a neutralization reaction?
- How does titration determine concentration?
- Relationship between pH values and molarity of acids and alkalis
- Concept of the pH Scale
- Role of pH in everyday life
- What is the pH of a salt solution
Preparation of a standard solution by dilution method
- A standard solution can also be made by dilution. Bench acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid are all prepared by diluting the commercial concentrated acids (stock solutions) with varying amounts of distilled water.
- Adding water to a concentrated solution:
(a) changes the concentration of the solution
(b) does not change the number of moles of solute present - This means that the total number of moles of solute particles before dilution is equal to the total number of moles of solute particles after the dilution is carried out.
Moles of solute before dilution = moles of solute after dilution - A dilution equation can be derived as shown below.
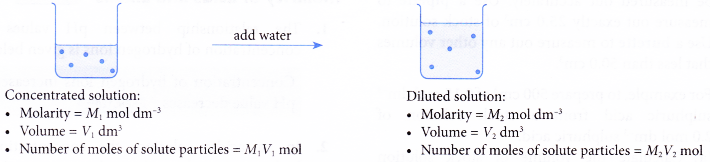
Since adding water does not change the number of moles of solute particles,
M1V1 = M2V2
Figure shows how Example is carried out in the laboratory.
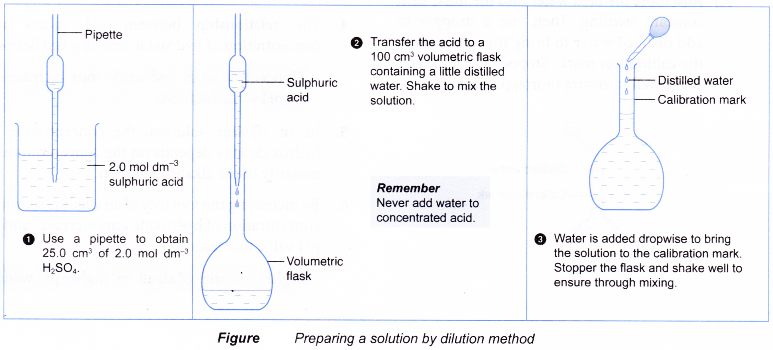
- The volume of stock solution required must be measured out accurately. Use a pipette to measure out exactly 25.0 cm3 of stock solution. Use a burette to measure out any other volumes that less than 50.0 cm3.
- For example, to prepare 500 cm3 of 0.15 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid from a stock solution of 2.0 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid.
(a) Calculate the volume of stock solution required.

(b) Fill a burette with the stock solution.
Run out 37.5 cm3 of stock solution into a 500 cm3 volumetric flask containing some distilled water.
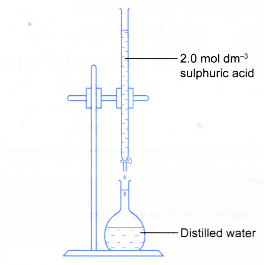
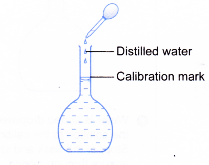
(c) Add more distilled water into the flask, with constant swirling. Then, use a dropper to add distilled water to bring the meniscus to the calibration mark. Stopper the flask and shake well to ensure thorough mixing.
1. Calculate the volume of concentrated nitric acid, 18 mol dm-3 which is required to prepare 5.0 dm3 of 2.0 mol dm-3 nitric acid.
Solution:

2. What volume of 2.0 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid is needed to prepare 100 cm3 of 0.5 mol dm-3 sulphuric acid?
Solution: