Preparation of Salts
Preparation of salts in the laboratory
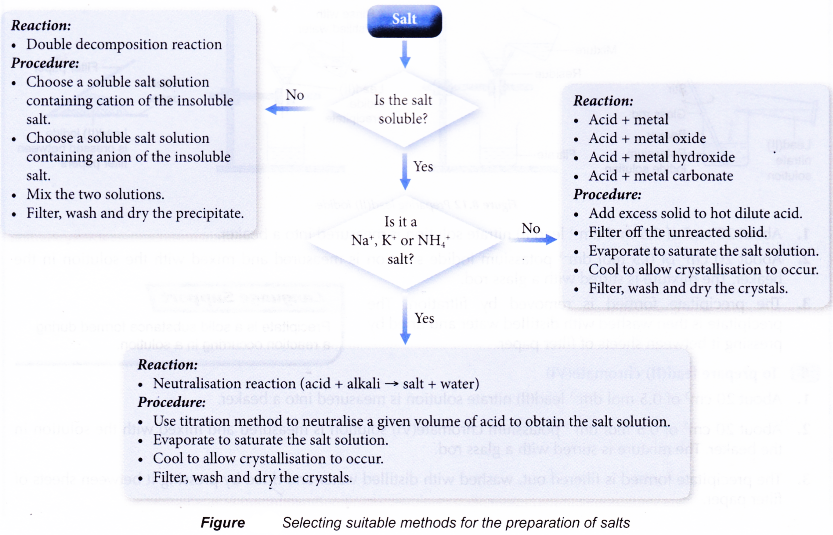
- The method used to prepare a salt depends on the solubility of the salt in water.
- A soluble salt can be prepared from a reaction between an acid and a metal, a base or a carbonate.
- Reaction 1: Acid + alkali → salt + water
- Reaction 2: Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
- Reaction 3: Acid + base → salt + water
- Reaction 4: Acid + metal carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
- Reaction 1 is used to prepare ammonium salts, sodium salts and potassium salts.
- Reactions 2, 3 and 4 are used to prepare soluble salts except ammonium salts, sodium salts or potassium salts.
- Recrystallisation is carried out to obtain pure crystals of the salt from the solution.
1. By the reaction between metal and acid : Certain metals (for example, Zn and Mg) react with HCl or H2SO4 to form salt and hydrogen.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
2. By the reaction between an acid and a base : All acid-base reactions (neutralization reactions) produce salts.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
CuO + 2HCl → CuCl2 + H2O
3. By direct union of a metal and a nonmetal : Sodium and chlorine combine directly to form sodium chloride.
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
Similarly, when sulphur is heated with iron filings, ferrous sulphide (FeS) is formed.
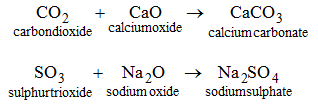
4. By the union between an acidic oxide and a basic :
5. By the reaction between a metal and a base : When zinc is heated with an aqueous solution of NaOH, sodium zincate (salt) is formed with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
People also ask
- Classification of Salts
- General Properties of Salts
- Uses of different salts in daily life
- Describe the preparation of soluble and insoluble salts
- Qualitative Analysis of Salts
- Action of Heat on Salts
- Test for Cations and Anions in Aqueous Solutions
- Constructing ionic equations using the continuous variation method
- What is stoichiometry and why is it used in chemistry?
How to select suitable methods for preparation of salts?
The flow chart below can help you select suitable methods for preparation of salts.