Preparation of Bases
Bases can be prepared by the following methods.

Methods of preparation of bases
1. By the direct union of a metal with oxygen Some metals when heated in air or oxygen form the oxides of the metals.
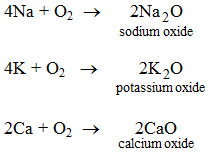
These oxides when dissolves in water make the hydroxides of metals.
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
K2O + H2O → 2KOH
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
2. By the action of water or steam on some active metals Some active metals like sodium and potassium react with cold water to form hydroxides with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
Magnesium reacts with steam to form magnesium oxide with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
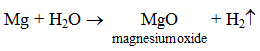
On passing superheated steam over red-hot iron, ferrosoferric oxide is formed and hydrogen gas is evolved.
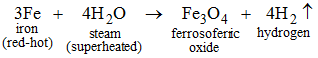
3. By heating carbonates of some metals When calcium carbonate is heated, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide are formed.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Similarly, when zinc carbonate is heated, zinc oxide and carbon dioxide are formed
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
4. By the action of an alkali on a salt solution For example, when an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is added to an aqueous solution of magnesium sulphate, magnesium hydroxide gets precipitated and sodium sulphate remains in the solution.
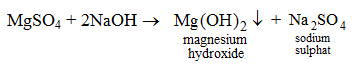
People also ask
- What is the definition of an acid and a base?
- What is the definition of an acid in chemistry?
- What is the definition of a base in chemistry?
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- What are the chemical properties of an acid?
- General Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- General Properties of Bases
- What determines a Strong Base and a Weak Base
- What are the uses of Bases
- How can we measure the strength of acids and alkalis?
- How to calculate concentration of acids and alkalis?
- How do you prepare a standard solution?
- What is meant by a neutralization reaction?
- How does titration determine concentration?
- Relationship between pH values and molarity of acids and alkalis
- Concept of the pH Scale
- Role of pH in everyday life
- What is the pH of a salt solution
