Polyhedra
Singular: polyhedron Plural: polyhedra
Polyhedron
A polyhedron is a three-dimensional solid figure in which each side is a flat surface. These flat surfaces are polygons and are joined at their edges. The word polyhedron is derived from the Greek poly (meaning many) and the Indo-European hedron (meaning seat or face).
A polyhedron has no curved surfaces.
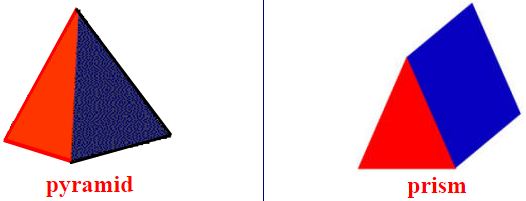
 The common polyhedron are pyramids and prisms.
The common polyhedron are pyramids and prisms.
 A polyhedron is called regular if the faces are congruent, regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are a total of five such convex regular polyhedra called the Platonic solids.
A polyhedron is called regular if the faces are congruent, regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. There are a total of five such convex regular polyhedra called the Platonic solids.

Euler’s Polyhedron Theorem:
Euler discovered that the number of faces (flat surfaces) plus the number of vertices (corner points) of a polyhedron equals the number of edges of the polyhedron plus 2.
F + V = E + 2
Non-Polyhedra
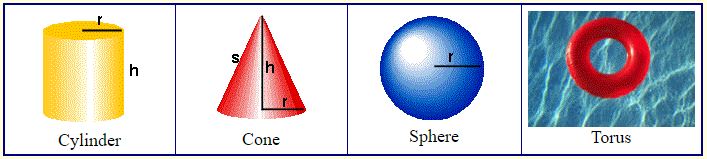
The following solids are not polyhedra since a part or all of the figure is curved.
 A torus is a “tube shape”. Examples include an inner tube, a doughnut, a tire and a bagel. Small r is the radius of the tube and capital R is the distance from the centre of the torus to the center of the tube.
A torus is a “tube shape”. Examples include an inner tube, a doughnut, a tire and a bagel. Small r is the radius of the tube and capital R is the distance from the centre of the torus to the center of the tube.
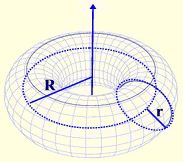 While the torus has a hole in the center,
While the torus has a hole in the center,
the Surface Area: SA = 4π2Rr
the Volume: V = 2π2Rr2
