Plus Two Zoology Notes Chapter 2 Reproductive Health is part of Plus Two Zoology Notes. Here we have given Plus Two Zoology Notes Chapter 2 Reproductive Health.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Zoology Notes |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Reproductive Health |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Zoology Notes Chapter 2 Reproductive Health
Reproductive health – problems and strategies
The Govt of India has started family planning (1951)and ‘Reproductive and Child Health Care (RCH)
programmes’ that helps
1. To create awareness among people about various reproduction related aspects.
2. Introduction of sex education in schools to avoid myths and misconceptions about sex-related aspects.
3. The information about reproductive organs, adolescence and related changes, safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STD), AIDS, etc., would help adolescent age group to lead a reproductively healthy life.
4. The information of available birth control options, care of pregnant mothers, post-natal care of the mother and child, importance of breastfeeding, equal opportunities for the male and the female child, etc., are the important components build up a socially responsible and healthy society.
5. The ban on amniocentesis for sex-determination helps to legally check increasing female foeticides, massive child immunisation, etc., are some programmes.
Population Explosion And Birth Control
According to the census report of 2001

Population increased due to decreased
- Maternal mortality rate (MMR)
- Infant mortality rate (IMR)
According to the 2001 census report, the population growth rate was 1.7 percent.
Marriageable age raised to 18 years for females and 21 years for males. The government was taken measures to check this population growth rate by contraceptive methods.
An ideal contraceptive should be user-friendly, easily available, effective and reversible with no or least side-effects.. Natural/Traditional, Barrier, lUDs, Oral contraceptives, Injectables, Implants and Surgical methods.
Natural Methods:
Periodic abstinence – Here the couples avoid or abstain from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle.
Withdrawal or coitus interruptus is another method in which the male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination.
Lactational amenorrhea This method is based on the fact that ovulation and therefore the cycle do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. So chances of conception are almost nil.
Barrier Method:
Condoms (Nirodh’) are barriers made of thin rubber/ latex sheath that are used to cover the penis in the male or Wagina and cervix in the female, just before coitus. This can prevent conception.
Use of condoms have additional benefit of protecting the user from STDs and AIDS. Both the male and the female condoms are disposable.
Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are also barriers made of rubber that are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix during coitus. So it helps to prevent conception by blocking the entry of sperms through the cervix.

Intra-Uterine Devices (lUDs):
IUDs are ideal contraceptives for females. These devices are inserted by doctors or expert nurses in the uterus through vagina.
Two types are copper releasing lUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and the hormone-releasing lUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20)
IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus and the Cu ions released suppress sperm motility and the fertilising capacity of sperms.
The hormone-releasing lUDs make the uterus unsuitable for implantation It is one of most widely accepted methods of contraception in India.
Oral contraceptives(pills) contain either progestogens or progestogen-estrogen combinations.
Pills have to be taken daily for a period of 21 days starting within the first five days of menstrual cycle. After a gap of 7 days (during which menstruation occurs) it has to be repeated in the same pattern to prevent conception.
It helps to inhibit ovulation and implantation as well as to prevent entry of sperms, eg-Saheli.
Saheli-a new oral contraceptive for the females-was developed by scientists at Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow.
Administration of progestogens or progestogen-estrogen combinations or lUDs within 72 hours of coitus have been found to be very effective as emergency contraceptives to avoid possible pregnancy due to rape or casual unprotected intercourse.
Surgical Methods (Sterilisation):
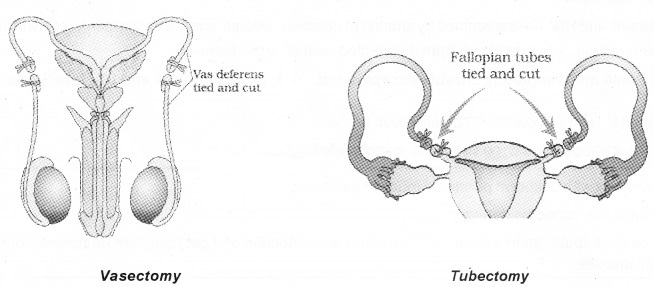
In male it is called ‘vasectomy’ a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small incision on the scrotum.
In female, ‘tubectomy’ a small part of the fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina.
Medical Termination Of Pregnancy (MTP)
Government of India legalised MTP in 1971 to avoid its misuse. So it helps to check indiscriminate and illegal female foeticides which are reported to be high in India.
It is important to avoid unwanted pregnancies either due to casual unprotected intercourse or failure of the contraceptive used during coitus or rapes.
MTPs are also essential in the cases where continuation of the pregnancy could be harmful or even fatal either to the mother or to the foetus or both.
MTPs are considered relatively safe during the first trimester, i.e., upto 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Diseases or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse are called sexually transmitted diseases (STD) or venereal diseases (VD) or reproductive tract infections (RTI).
Common STDs.
| Gonorrhea |
| Syphilis |
| Genital herpes |
| Chlamydiosis |
| Genital warts |
| Trichomoniasis |
| Hepatitis-B |
| AIDS |
Early symptoms of most of these are minor and include itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swellings, etc., in the genital region.
Hepatitis-B and HIV are transmitted by sharing of injection needles, surgical instruments, etc. with infected persons and transfusion of blood, from an infected mother to the foetus.
All diseases are completely curable except hepatitis-B, genital herpes, and HIV infections.
The important steps to control STDs are given below.
| (i) Avoid sex with unknown partners / multiple partners. (ii) Always use condoms during coitus. (iii) In case of doubt, go to a qualified doctor for early detection and get complete treatment if diagnosed with disease. |
Infertility
In the case of infertility, corrections are not possible, the couples could be assisted to have children through certain special techniques commonly known as assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
| In vitro fertilisation (IVF—fertilisation outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body) followed by embryo transfer (ET). | |
| In test tube baby programme | Ova from the wife/donor (female) and sperms from the husband/donor (male) are collected and are induced to form zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory. |
| The zygote or early embryo (with upto 8 blastomeres) is transferred into the fallopian tube (ZIFT – Zygote intra fallopian transfer) and embryos with more than 8 blastomeres, into the uterus (IUT – intra uterine transfer). |
| Transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube (GIFT – gamete intra fallopian transfer) of another female who cannot produce one. |
| Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICS) sperm is directly injected into the ovum. It is the procedure to form an embryo in the laboratory. |
| Infertility cases either due to inability of the male partner to inseminate the female or due to very low sperm counts in the ejaculates, could be corrected by artificial insemination (Al) technique. |
| In this technique, the semen collected either from the husband or a healthy donor is artificially introduced either into the vagina or into the uterus (lUI-Intra uterine insemination) of the female. |
We hope the Plus Two Zoology Notes Chapter 2 Reproductive Health help you. If you have any query regarding Plus Two Zoology Notes Chapter 2 Reproductive Health, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
