Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Biodiversity and Conservation are part of Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Biodiversity and Conservation.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Zoology Chapter Wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Biodiversity and Conservation |
| Number of Questions Solved | 86 |
| Category | Kerala Plus Two |
Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Biodiversity and Conservation
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The species diversity of plants on earth will be
(a) 2.4%
(b) 22%
(c) 8.1%
(d) 85%
Answer:
(b) 22%
Question 2.
Which of the following rain forest is home to more than 40,000 species of plants, 3,000 of fishes, 1,300 of birds, 427 of mammals, 427 of amphibians, 378 of reptiles and more than 1,25,000 invertebrates?
(a) Amazonian
(b) Tropical
(c) Arctic tundra
(d) Temperate
Answer:
(a) Amazonian
Question 3.
Which one of the following pairs of geographical areas shows maximum biodiversity in our country?
(a) Sunderbans and Rann of Kutch
(b) Eastern ghats and West Bengal
(c) Eastern Himalaya and Western Ghats
(d) Kerala and Punjab’
Answer:
(c) Eastern Himalaya and Western Ghats
Question 4.
Which of the following is most dangerous to wildlife?
(a) Overexploitation
(b) Man-made forest
(c) Habitat destruction
(d) Introduction of foreign species
Answer:
(c) Habitat destruction
Question 5.
The extinction of cichlid fish in the lake is due to
(a) habitat loss and fragmentation
(b) overexploitation
(c) Alien species invansion
(d) Co-extinctions
Answer:
(c) Alien species invansion
Question 6.
Aquatic environment of Kerala is facing serious threat by alien species invasion. Can you say anyone example of a species by which our indigenous plants and animals are facing greater threat.
Answer:
Eichornia
Question 7.
Write the significance of seed banks in biodiversity conservation?
Answer:
Seeds of different genetic strains of commercially important plants and other plants can be kept for a long period.
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Global diversity of invertebrates are shown below:-
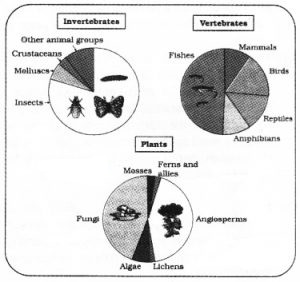
- Which invertebrate group shows highest biodiversity and why?
- Among vertebrates, which group has the highest biodiversity?
Answer:
- Insects (Arthropods), their cuticular exoskeleton gives high survival and diversity.
- Fishes
Question 2.
Define co-extinction.
Answer:
When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it also become extinct. This is called co-extinction.
Question 3.
Now a days the area of sacred grooves decreased. Suggest the role of sacred grooves in conservation of biosphere?
Answer:
Sacred grooves are tracts of forests set aside by many cultures, where all the trees and wild life are given total protection.
Question 4.
Introduction of exotic species is one of the major threats to biodiversity. Analyse this statement with any four examples in your locality.
Answer:
When exotic species are introduced, some may turn invasive and cause extinction of ndigenous species.
Eg: Carrot grass, Eichornia, Lantana, African cat fish.
Question 5.
“The biological wealth of our planet has been declining rapidly and the accusing finger is clearly pointing to human activities.”
- Mention any two activities leading to the loss of biodiversity.
- Mention the different ways to conserve biodiversity.
Answer:
- Habitat destruction Pollution and overexploitation
- i) Insitu conservation – National parks, Biosphere reserve etc.
ii) Exsitu conservation – Zoo, Botanical garden, Cryopreservation, etc
Question 6.
Arrange the following terms into two-column with proper title (Biological reserves, Zoological park, Sacred groves, National park, Cryopreservation of gametes, Wild life sanctuaries, In vitro fertilization, Botanical garden).
Answer:
| Exsitu conservation | Insitu conservation |
| Zoological park | Biological reserves |
| Cryopreservation of gametes | Sacred groves |
| Invitro fertilization | National park |
| Botanical garden | Wild life sanctuaries |
Question 7.
“Conservation of nature” is a slogan which is heard all over the world. Proposed by environmentalists in this conservation of biodiversity is very important.
- What are the different levels of biodiversity?
- Which are the threats of biodiversity?
Answer:
1. different levels of biodiversity
- genetic diversity
- Species diversity
- Ecological diversity
2. threats of biodiversity
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Over-exploitation
- Alien species invasions
- Co-extinction
Question 8.
Alien species invasion is one of the causes of biodiversity loss.
- Do you agree with this statement?
- Site any two examples of alien species in your locality.
Answer:
- Yes. Alien species cause decline or extinction of indigenous species. Eg: Lantana
- Eichhornia
Question 9.
The need for conservation of biodiversity is undoubtedly inevitable for the future existence of man kind.
- Name the strategies involved in biodiversity conservation. Give examples for each.
- What is endemism?
- Expand IUCN.
Answer:
1. i) Insitu conservation
Eg: Biosphere, reserve, national parks, and wild life sanctuaries.
ii) Ex-situ conservation
Eg: Zoo, Botanical garden, tissue culture, seed banks.
2. Species confined to a region and not found anywhere else. Endemic species are rich in hotspots.
3. International Union for conservation of nature and natural resources.
Question 10.
Scientists estimate that species diversity decreases as we move away from equator towards the poles. Tropical Amazonian rainforest in South America has the greatest diversity on earth.
Do you agree that there is something so special about tropics that might account for greater biodiversity. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes. The specialities of tropics are
They remained undisturbed for millions of years. The tropical environment is less seasonal, more constant and predictable. There is more solar energy, which contribute to higher productivity.
Question 11.
The accelerated rates of species extinctions that the world is facing now are largely due to human activities.
- Mention the evil quatret which cause extinction.
- Name two ex-situ method to conserve diversity.
Answer:
1. The evil quatret which cause extinction
- Habitat loss
- Overexploitation
- Alein species invasion
- Coextinction
2. Two ex-situ method to conserve diversity
- Zoo
- Botanical garden
Question 12.
“The Central Govt. declared the buffer zone to the silent valley National Park.” Predict advantages of this decision.
Protective area
Answer:
- Research/Education
- Reduce human settlement
- Reduce destruction of forest resource
- Area of park increase
- Reduce the pressure
Question 13.
Alien species are a threat to native species, justify taking examples of an animal and a plant alien species.
Answer:
The Nile Perch introduced in lake Victora in East Africa led eventually to the extinction of more than 200 species of Ci child fish in the lake. African cat fish (Clariasgariepinus) for aquaculture purpose is posing threat to the indigenous catfishes in our rivers.
Invasive weed species Eicchornia (water hyacinth). Parthenium (carrot grass). Lantana have posed a threat to our native species.
Question 14.
“We can develop a proper perspective through an analogy. The rivet popper hypothesis’ regarding the importance of species diversity to the ecosystem”. Substantiate?
Answer:
Analogy rivet popper hypothesis, used by Paul Ehrlich, indicates the importance of each species to the ecosystem. In a plane (ecosystem) all parts are joined together using thousands of rivets (species).
The extinction of a species affects the normal functioning of ecosystem, like removal of rivets of a plane. Damage of more number of species affects the ecosystem dangerously.
Question 15.
In our biosphere, immense diversity exists in all levels of biological organisation. Describe the most important levels of biodiversity.
Answer:
- Genetic diversity: Diversity of genes within a species.
- Species diversity: The diversity at the species level.
- Ecological diversity: Diversity at the ecosystem level.
Question 16.
The extinction of the bird ‘Dodo’ in Mauritius island also lead to the extinctinon of the tree named ‘Calvaria major’. Explain the process that is a cause of a biodiversity loss?
Answer:
Co-extinction. When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. This is called co-extinction.
Analogy rivet popper hypothesis, used by Paul Ehrlich, indicates the importance of each species to the ecosystem. In a plane (ecosystem) all parts are joined together using thousands of rivets (species).
The extinction of a species affects the normal functioning of ecosystem, like removal of rivets of a plane. Damage of more number of species affects the ecosystem dangerously.
Question 17.
‘Evil Quartet’ is a sobriquet used to describe the cause of biodiversity loss.
- What are the evil quartets of biodiversity loss?
- Write two ill effects of biodiversity loss?
Answer:
1. Habitat loss and fragmentation, Over-exploitation, Alien species invasion and Co-extinction.
2. effects of biodiversity loss
- decline in plant production
- Lowered resistance to environment
Question 18.
‘Amazon forests are called the lungs of the planet’ Why?
Answer:
Amazon rain forest is huge and harbor millions of species and it is estimated to produce, through photosynthesis, 20% of the total oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere.
Question 19.
The following pie diagram represents global biodiversity of invertebrates and vertebrates. Complete the graph by giving suitable group of animals to the missing sectors A and B.
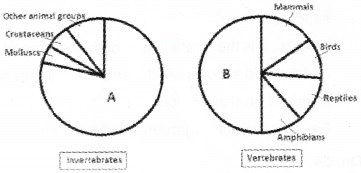
Answer:
- Insects
- Fishes
Question 20.
‘India is one of the 12 Mega Biodiversity countries of the world’. Justify?
Answer:
India has approximately 8.1% of global species diversity, probably has more than 100000 species of plants and 200000 animal species, India has western Ghats, Indo Burma, and Himalaya as hotspots.
Question 21.
‘Gametes of threatened species can be preserved in a viable and fertile condition for a long time’
- Identify the preservation technique used?
- Why is it considered as an Ex-situ conservation approach?
Answer:
- Cryopreservation
- In the ex-situ approach threatened animals/ plants/ gametes/ seeds are taken from their natural habitat and placed in special condition.
Question 22.
Categorize the following into ex-situ and in-situ conservation strategies. Seed banks, Tissue culture, sacred grooves, national parks, zoological parks, biosphere reserve, botanical garden, sanctuaries.
Answer:
- Ex-situ: Sacred groves, National Park, Biosphere reserve, Sanctuaries
- In-situ: Tissue culture, Zoological park, seed banks, Botanical garden.
Question 23.
Compare in situ and ex situ conservation strategies with examples?
Answer:
1. In-situ: Protect the whole ecosystem, its biodiversity at all levels. Eg: Biosphere reserve, national park, sanctuaries, etc.
2. Ex-situ: it is the strategy to protect threatened and endangered species which needs urgent measures to save it from extinction. Eg: zoo, botanical garden, seed bank, etc.
Question 24.
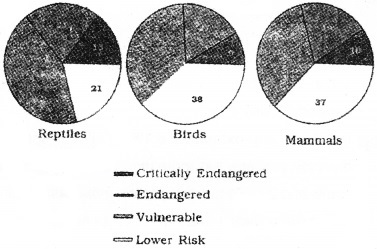
Read the statement and state whether true or false.
1.
- Endangered species are more in reptiles than in birds and mammals.
- Critically endangered species are more in birds than in reptiles and mammals.
2. What is the role of Alien species invasions in extinction?
Answer:
1.
- True
- False
2. Alien species are foreign species, when introduced, some of them turn invasive and cause decline or extinction of indigenous species.
Question 25.
What are hot spots in biodiversity? Why endemism is considered an important criteria for identifying hot spots?
Answer:
1. Hot spots: are the regions with high levels of species richness and high degree of endemism.
2. Endemism: is the number of species confined to a particular region and not found anywhere else. High degree of endemism means species richness is more and are not found anywhere else and should be protected to prevent extinction.
Question 26.
The species diversity of the plants (22%) is much less that of animals (72%). What could be the explanations to how animals achieved greater diversification?
Answer:
Compared to plants, animals have increased size and genetic variation. Also, the animals possess complex nervous system to control and coordinate various body activities.
Animals possess receptor organs for receiving various environmental stimuli and able to respond against them. The ability of locomotion is also a factor for greater diversification of animals.
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Amazonian rain forest has the greatest biodiversity on earth. List any two hypothesis that are proposed by the biologists to account for the greater biological diversity.
Answer:
The hypothesis are:
1. Speciation is generally a function of time; unlike temperate regions which are subjected to frequent glaciations in the past, tropical latitudes have remained undisturbed for millions of years and hence had a long time for species diversification.
2. Tropical environments are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable; such constant environments promote niche specialization and lead to a greater species diversity.
3. There is more solar energy available in the tropics, which contributes to higher productivity; this in turn might contribute indirectly to species diversity.
Question 2.
Introduction of exotic species is one of the major threats of biodiversity.
- Cite any two examples of these exotic species in your locality.
- Recent illegal introduction of a fish for aquaculture poses a threat to indigenous catfishes in our rivers. Name it.
- How co-extinctions affects biodiversity?
Answer:
- Eichornia- Lantana Camera
- African catfish (clarius gariepinus)
- When a species becomes extinct, the species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. This is called co-extinction.
Question 3.
Observe the graph.
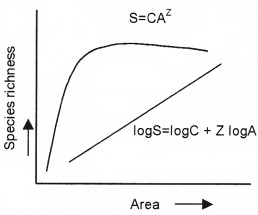
- What does this graph represent?
- Who proposed this relationship?
- What does the alphabets S, C, A, Z represent?
Answer:
- Species – Area relationships
- Alexander Von Humboldt
- S-Species richness A – Area Z – Slope of the line C-Y-Intercept.
Question 4.
There are many reasons, some obvious and others not so obvious, but all equally important to conserve biodiversity. They are grouped into three categories.
- Name them.
- Among 3 categories, which one has a scope of ‘bioprospecting’, for exploring biodiversity for products of economic importance.
- Give examples for Ex-situ conservation.
Answer:
- Narrowly utilitarian argument.
Broadly utilitarian argument. - Narrowly utilitarian argument.
- Zoological parks, botanical gardens, Cryopreservation, tissue culture, seed banks, pollen banks, etc.
Question 5.
Bio-diversity is not uniform throughout the world, but shows a rather uneven distribution.
- What is latitudinal gradients in diversity?
- What is so special about tropics that might account for their greater biological diversity.
- Which is the area that has the highest biodiversity on earth?
Answer:
1. The distribution of diversity of plants and animals decreases as we move away from equator towards the poles.
2. biological diversity
- Tropical latitudes have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years, thus had a long evolutionary time for species diversification.
- Tropical environments are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable.
- More solar energy is available which contributes to high productivity and greater diversity.
3. Amazonian rain forest in South America.
Question 6.
Observe the given graph
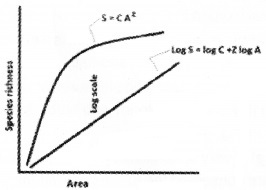
- What does the above graph represent?
- What does S and A indicate?
- Write the significance of ‘Z’ value?
Answer:
- Species area relationship
- S = Species richness, A = area
- Z is the slop of the line (regression coefficient).
Question 7.
How do the following factors affect biodiversity? Answer with suitable examples.
- Alien species invasion
- Co extinction
- Overexploitation
Answer:
1. Alien species turn invasive and cause decline or extinction of indigenous species. Nile perch introduced into Lake Victoria in east Africa led to the extinction of more than 200 species of cichlid fish in the lake.
2. When a species become extinct the plants and animals associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct, coevolved. Plant-pollinator mutualism where extinction of one species leads to the extinction of the other.
3. It happen when need turns greed and over utilization of natural resources in an irrecoverable way. Extinction of Steller’s sea cow, passenger pigeon was due to humans.
Question 8.
Narrow utilitarian, broad utilitarian and ethical arguments are the three major arguments/ reasons for conserving biodiversity. Briefly explain the basis of these three arguments?
Answer:
1. Narrowly utilitarian:
Humans get economic benefits from nature food (cereals, pulses, fruits), firewood, fibre, construction material, industrial products (tannins, lubricants, dyes, resins, perfumes) and products of medicinal importance.
2. broadly utilitarian:
Biodiversity plays a major role in ecosystem services. Amazon forest is through photosynthesis produce 20 percent of the total oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere.
Pollination is another ecosystems service by bees, bumblebees, birds, and bats. Nature provides aesthetic pleasures of watching spring flowers in full bloom and bulbul’s song in the morning.
3. Ethical:
Every species has an intrinsic value so they are conserved for future generations.
Question 9.
What are the factors responsible for the greater biodiversity in tropical regions?
Answer:
- Tropics have remained undisturbed for millions of years and had a long evolutionary time for species diversification.
- Constant and predictable tropical environments promote niche speciation and greater diversity.
- More solar energy in tropics contributes higher productivity and indirectly to greater diversity.
Question 10.
Write the three components of Biodiversity. Select the component which deals with ecosystem levels of biodiversity?
Answer:
- Genetic diversity
- Species diversity
- Ecological diversity.
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the three important of biodiversity.
Answer:
- Genetic diversity
- Species diversity
- Ecosystem diversity
Question 2.
How do ecologists estimate the total number of species present in the world?
Answer:
They make a statistical comparison of the species richness of exhaustively studied groups of insects of the temperate and tropical regions and extrapolate this ratio to other groups of animals and plants to calculate gross estimate of the total number of species present on the earth.
Question 3.
Give three hypothesis for explaining why tropics show greatest levels of species richness.
Answer:
Biodiversity is not uniformly distributed throughout the world. Polar regions have very little biodiversity whereas South America has the greatest biodiversity on the earth. There are many hypothesis for higher biodiversity in tropics:
1. There are no unfavourable seasons in tropics. Continued favourable environmental condition has helped tropical organisms to flourish more.
2. There is more solar energy available in the tropics due to which productivity is higher and this contribute to greater diversity.
The tropical environment is older thus allowing more time for the evolution of greater number of plants and animals.
Question 4.
What is the significance of the slope of regression in a species-area relationship?
Answer:
Alexander Von Humboldt observed that within a definite region the species richness increases upto some extent with increase in area. This relationship between species richness and area is a hyperbola fora large variety of taxa.
On a logarithmic scale it is a straight line
Log S = log C + Z log A
Where S = species richness
Z = slope of line (regression coefficient)
C = Y-intercept
A = Area
Z is generally 0.1 -0.2 regardless of taxonomic group or region i.e., when analysis of speices-area relationship is done among small areas, the values of slopes of regression are remarkably similar regardless of the taxonomic group or the region.
If analysis of a species-area relationship is done among very large like a whole continent, the slope of regreesion line would be much steeper.
Question 5.
What are the major causes of species losses in a geographical region?
Answer:
- Habit loss and fragmentation
- Over-exploitation
- Introduction of exotic species
- Co-extinctions.
Question 6.
Can you think of a situation where we deliberately want to make a species extinct? How would you justify it?
Answer:
This situation may appear when alien species is introduce unintentionally or deliberately into an area. Some of them may become invasive and cause damage to indigenous species.
For example Nile perch introduced into lake Victoria in East Africa led to extinction of 200 species of Cichlid fish in the lake. Introduction of African catfish Clariasgariepinuslor aquaculture is threatening the indigenous catfishes in rivers of India.
Question 7.
What are sacred groves? What is their role in con¬servation?
Answer:
Sacred groves are sacred forest patches around places of forest. In such cases, nature is protected by prevailing religious and cultural traditions. Here tracts of forests are set aside and all plants and animals are venerated and provided with complete protection.
Some examples of sacred groves are Khasi and initial hills in Meghalaya. Aravalli hills in Rajasthan, Western ghat regions of Karnataka, Maharashtra and Sargiya, Chanda and Bastar areas of M.P. In Sikkim, Khecheopalri lake is declared sacred lake by people, thus protecting the aquatic flora and fauna.
Many rare and threatened plants have been protected in sacred groves of Meghalaya. Such areas have been found to be most undisturbed and they are usually surrounded by most degraded landscapes.
Question 8.
Among the ecosystem services are control of floods and soil erosion. How is this achieved by the biotic components of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Earth’s rich biodiversity is vital for indirect benefits like control of floods and soil erosion. Species richness checks soil erosion by binding the soil particles thereby reducing the rate of water velocity, hence reducing the chances of floods.
Question 9.
The species diversity of plants (22 percent) is much less than that of animals (72 percent). What would be the explanations to how animals achieved greater diversification?
Answer:
Animals bear nervous system for control and co-ordination of activities. They also bear receptors to respond to environment stimuli. Many responses become adaptive for survival. Thus animal bears higher species diversity than plants.
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Spot out the zone of our country considered as the hot spot of biodiversity and regarded as the ‘Cradle of Speciation’.
(a) Western ghats
(b) North East
(c) Himalayan base
(d) Deccan plateau
Answer:
(b) North East
Question 2.
One of the most important functions of botanical gardens is that
(a) one can observe tropical plants there
(b) they allow exsitu conservation of germplasm
(c) they provide the natural habitat for wild life
(d) they Provide a beautiful area for recreation
Answer:
(b) they allow exsitu conservation of germplasm
Question 3.
The diversity of the habitats over the total geographical area is called
(a) alpha diversity
(b) beta diversity
(c) gamma diversity
(d) delta diversity
Answer:
(c) gamma diversity
Question 4.
Biosphere reserves differ from national parks and wild life sanctuaries because in the former
(a) human being are not allowed to enter
(b) people are an integral part of the system
(c) plants are paid greater attention than the animals
(d) living Organisms are brought from all over the world and preserved for posterity
Answer:
(b) people are an integral part of the system
Question 5.
An institution, where valuable plant material-likely to become irretrievably lost in the wild or in cultivation is preserved in a viable condition is known as
(a) genome
(b) gene library
(c) gene bank
(d) herbarium
Answer:
(c) gene bank
Question 6.
Biological diversity day is
(a) 5th June
(b) 21st March
(c) 14th January
d) 29th December
Answer:
(d) 29th December
Question 7.
Biodiversity is determined by
(a) number of individuals in an area
(b) species richness
(c) evenness
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 8.
Rare endangered and endemic taxa can be found intact and flourishing in
(a) sacred groves
(b) buffer zone
(c) tropical forests
(d) temperate forests
Answer:
(a) sacred groves
Question 9.
In situ conservation and national genetic resources can be achieved by Establishing
(a) National Park
(b) Wildlife Sanctuaries
(c) Biosphere Reserve
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 10.
IUCN, now called World Conservation Union (WCU) has its headquarter at
(a) South Africa
(b) America
(c) India
(d) Switzerland
Answer:
(d) Switzerland
Question 11.
If forest cover is reduced to half, what is most likely to happen on a long term basis?
(a) Tribals living in these areas will starve to death
(b) Domestic animals in these and joining areas will die due to lack of fodder
(c) Large biomes will become deserts
(d) Crop breeding programmes will suffer due to a reduced ability of variety of germplasm
Answer:
(c) Large biomes will become deserts
Question 12.
The management of biosphere in such a way that it may yield one greatest suitable benefit to present generation, while maintaining its potential to meet the needs of future generation is
(a) conservation
(b) aforestation
(c) fossilization
(d) over-exploitation
Answer:
(b) aforestation
Question 13.
The first Biosphere Reserve establish in India for conserving the gene pool of flora and fauna and the life style of tribals is
(a) Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
(b) Nandadevi Biosphere Reserve
(c) Uttarakhand Biosphere Reserve
(d) Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve
Answer:
(a) Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve
Question 14.
The government of India in 1980s has introduced a concept to work closely with the local communities for protecting and managing forests. The concept is
(a) forest research institutes
(b) panel of local communities for forest management
(c) joint forest management
(d) jhum cultivation
Answer:
(c) joint forest management
Question 15.
The percentage of forest cover recommended by the national forest policy (1988)is
(a) 33% for plains and 67% for hills
(b) 37% for plains and 63% for hills
(c) 20% for plains and 70% for hills
(d) 23% for plains and 77% for hills
Answer:
(a) 33% for plains and 67% for hills
Question 16.
The species diversity is maximum in
(a) Western Ghats
(b) Eastern Ghats
(c) Alpine meadows
(d) wetlands.
Answer:
(a) Western Ghats
Question 17.
According to the IUCN (2004), the number of species on the earth that dominates
(a) plants
(b) animals
(c) bacteria
(d) plants
Answer:
(b) animals
Question 18.
The greatest biodiversity in world is reported in
(a) Amazonian forest
(b) coniferous forest
(c) W ghats
(d) Scandinavian forest
Answer:
(a) Amazonian forest
Question 19.
Tropical environments are less seasonal and constant that lead to a greater species diversity, it is come under
(a) niche specialization
(b) species richness
(c) genetic erosion
(d) genetic equilibrium
Answer:
(b) species richness
Question 20.
The equation log S = log C +Z log A represent
(a) species richness and area
(b) genetic diversity and area
(c) allelic frequency and speciation
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) species richness and area
Question 21.
The extinction of Steller’s sea cow is due to
(a) overexploitation
(b) alien species invasion
(c) habitat loss and fragmentation
(d) co extinctions
Answer:
(a) overexploitation
Question 22.
The major cause of reduction in biodiversity is due to
(a) habitat fragmentation
(b) overexploitation
(c) overproduction
(d) both a and b
Answer:
(d) both a and b
Question 23.
The introduction of fish that is more serious threat to the indigenous catfishes in river, they are
(a) hilsa
(b) Clarias
(c) carp
(d) catla
Answer:
(b) Clarias
Question 24.
If two species are in obligatory relationship, the extinction of one species affect the other. This is called
(a) competitive exclusion
(b) competitive release
(c) co extinction
(d) co evolution
Answer:
(c) co extinction
Plus Two Zoology Biodiversity and Conservation SCERT Sample Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- Arrange the following terms into two based on the mode of biodiversity conservation. Hot spots, Zoological Park, Sacred groves, wild life Safari Parks (2)
- Fill in the blank box noted as A. (1)
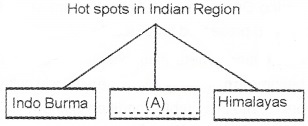
Answer:
- Hotspot and sacred grove Zoological Park and Wild Life Safari Park
- A. Western ghats
We hope the given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Biodiversity and Conservation will help you. If you have any query regarding Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Biodiversity and Conservation, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
