Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Evolution are part of Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Evolution.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Zoology Chapter Wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 |
| Chapter Name | Evolution |
| Number of Questions Solved | 68 |
| Category | Kerala Plus Two |
Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Evolution
Plus Two Zoology Evolution One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
S L Miller’s closed flask contained
(a) CH4
(b) H2
(c) NH3 and H2O
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Wings of insects and birds are
(a) analogous
(b) homologous
(c) vestigial
(d) atavism
Answer:
(a) analogous
Question 3.
Convergent evolution is shown by
(a) homologous organ
(b) analogous organ
(c) vestigial organ
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) analogous organ
Question 4.
Which of the following is the most primitive ancestor of man?
(a) Homo habilis
(b) Homo neanderthalensis
(c) Australopithecus
(d) Ramapithecus punjabicus
Answer:
(d) Ramapithecus punjabicus
Question 5.
Thoms of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbila are examples of
(a) analogous organs
(b) homologous organs
(c) vestigial organs
(d) retrogressive evolution
Answer:
(b) homologous organs
Question 6.
More than one adaptive radiation appeared to have occurred in an isolated geographical area is called as………..
Answer:
Convergent evolution
Question 7.
Explain Oparin and Haldane Hypothesis.
Answer:
According to Oparin and Haldane, the life could have originated form pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
Question 8.
In a class seminar, Varun says that some scientists believe that the life originated form the spores reached on earth from outer space. Name this theory of origin of life.
Answer:
Theory of panspermia
Plus Two Zoology Evolution Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Identify the Experimental set up in Evolution and answer the following.
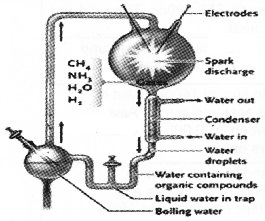
- Name the Experiment.
- Explain the significance of the given experimental setup.
Answer:
1. Urey and Miller experiment.
2. In laboratory primitive atmosphere is created. In closed flask (Spark discharge apparatus) CH4, H2, NH3, and water vapour is taken and heated at 8000c. S.L. Miller observed that the formation of amino acids. This supports theory of chemical evolution.
Question 2.
Fossils are the written document of evolution.
- Name the branch of biology which deals with the study of fossils?
- How can we calculate the age of fossil?
Answer:
- Paleontology
- Radioactive – dating
Question 3.
Examine carefully the details given and group similar one in the table. Give suitable title for each column. Analyse the importance of each group in evolution. (Wings of bat, flipper of whale, wings of butterfly, forelimbs of horse, wings of birds, rudementary body hair, wisdom teeth, vermiform appendix of man, patagium of draco).
Answer:

Question 4.
Choose the correct answers. (Convergent evolution, Gene flow, Adaptive radiation, Divergent evolution)
| a) Darwin’s finches | (a) |
| b) Homologous organ | (b) |
| c) | Migration |
| d) Analogous of gan | (d) |
Answer:
| a) Darwin’s finches | Adaptive radiation |
| b) Homologous organ | Divergent radiation |
| c) Gene flow | Migration |
| d) Analogous organ | Convergent evolution |
Question 5.

Figure shows white-winged moth and dark-winged moth on a tree trunk.
- in unpolluted area
- in polluted area
a. Which evolutionary theory is depicted by this figure?
b. What is industrial melanism?
c. Can you give any other example for this theory?
Answer:
a. Theory of Natural selection by Darwin
b. Industrial melanism is the development of dark colouration in populations that are exposed to industrial air pollution.
c. – Resistance of Mosquitoes against DDT.
– Resistance of some microbes against some antibiotics.
Question 6.
The two scientists set up their experimental apparatus by using following components.
(CH4, NH3, H2, Condenser, Electrode, Vaccum pumps, boiling chambers, gas chamber, ‘U’shaped tubes)
- State chemical evolution theory.
- Who experimentally proved this concept?
Answer:
- Chemical evolution states that first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules, for formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents.
- Urey Miller
Question 7.
- Evolution is a departure from Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. Comment on this statement.
- What are the five factors that affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium?
Answer:
1. Hardy-Weinberg principle says that allele frequencies in a population are stable and constant from generation to generation.
The gene pool remains constant, which is called genetic equillibrium. Disturbance in this equillibrium, ie. change of frequency of alleles in a population results in evolution.
2. Five factors are
- gene migration or gene flow
- genetic drift
- Mutation
- genetic recombination
- Natural selection
Question 8.
Abiotic origin of life is in progress on a planet other than earth. Based on the origin of life on earth what should be the conditions on the planet.
Answer:
- High Temperature
- Presence of gases such as C, H, N
- Anaerobic environment
- Torrential rain
- High energy radiation
- Primordial soup
Question 9.
As you know Lamarckism and Darwinism are two theories explaining the mechanism of evolution.
- Write the difference between acquired characters of Lamarck and variation theory of Darwin. Specify.
- How Darwin defined variation as a key to evolution?
- Give one example for Darwinism and Lamarckism.
Answer:
1. Acquired characters are inherited to the next generation. According to Darwin, only favourable varia¬tion is inherited to the next generation, which leads to speciation (origin of species).
2. According to Darwin variations are of two types, namely, somatic variation (in body) and genetic variation, which is a key to evolution.
3. Lamarckism – Origin of long necked giraffe. Darwinism – Industrial melanism in peppered moth.
Question 10.
The following diagram represents the operation of Natural selection on one trait.
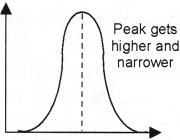
- Identify the type of selection.
- What is meant by Natural selection?
Answer:
- Stabilising selection
- Organism with favourable variations are selected by nature and those without them are rejected. This is called Natural selection.
Question 11.
Construct a flow chart showing Darwinism using following points. (Over production, Struggle for existence, Variation Natural Selection, Gurvival of the fittest, origin of species).
Answer:
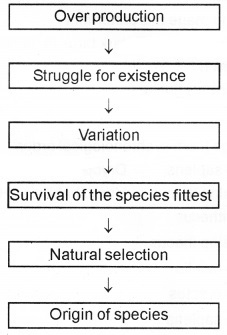
Question 12.
Name the gases filled in the gas chamber to design the condition of primitive earth.
Answer:
Methane, Ammonia, H2, water vapour
Question 13.
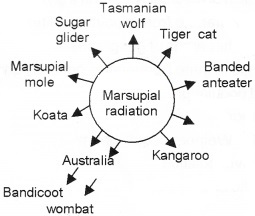
- Identify the type of evolutionary process shown here.
- Give one more example for this.
Answer:
- Adaptive radiation
- Darwin’s finches
Question 14.
“Darwin’s finches are excellent example for adaptive radiation.’’
- Name the place where Darwin’s finches found.
- Explain adaptive radiation.
Answer:
- Galapago islands
- Adaptive radiation is a process of evolution of different species in a geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography.
Question 15.
“Galapagos islands are the living laboratory of evolution”.
- Who made this statement?
- Name the small dark birds in these islands.
Answer:
- Darwin
- Darwin’s finches
Question 16.
Arrange them in chronological order. Homo sapiens, Dryopithecus, Australopithecus Homo habilis Homo erectus Answer:
- Dryopithecus
- Australopithecus
- Homo habilis
- Homo erectus
- Homo sapiens
Question 17.
Write one word for the following:
- Single-step large mutation causing speciation.
- Allelic frequencies remain constant from generation to generation.
- Evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography.
- Change in gene frequencies occur by chance in small population.
Answer:
- Saltation
- Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- Adaptive radiation
- Genetic drift
Question 18.
How do Darwin’s finches illustrate adaptive radiation?
Answer:
Original stock of seed-eating finches migrated to different habitats, adapted to different feeding methods, by altered beak structure, evolved into different types of finches.
Question 19.
Odd man out. Justify your answer.
- Recombination
- Genetic drift
- Gene migration
- Natural selection
- Mutation
- Speciation
Answer:
Speciation
All others are mechanisms for variation that leads to the origin of species (speciation).
Question 20.
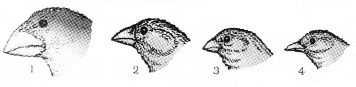
- Identify the evolutionary phenomenon shown? Explain.
- What is founder effect?
Answer:
- Adaptive radiation
- The effect where original drifted population becomes founders is called founder effect.
Question 21.
Prior to industrialization, there were far more white winged moths on trees than melanised moths in England. However, after industrialization, the distribution pattern of these two kinds of moths reversed. What does the above observation indicate? Explain giving reasons.
Answer:
It indicates that predators will spot a moth against a contrasting background.
1. After industrialization, the tree trunks became dark due to deposition of soot and smoke; under such a condition, the white winged moths stood out conspicuously and easily detected by the predators and hence they reduced in number.
2. The dark-winged moths could merge with the black colour and they escaped the predators and hence increased in number.
Question 22.
‘Darwin finches are the example of adaptive radiation’. Justify.
Answer:
The beak modifications in finches occurred due to difference in food gathering and feeding habitats of different Islands
Question 23.
Arrange the following into two categories under the heading.
Analogous organ and homologous organ.
Eyes in Human beings and octopus.
Flippers of penguin and dolphin.
Vertebrate hearts.
Thorns and tendril.
Wings of butterfly and birds
Forelimb of vertebrates
Answer:
| Analogous Organ | Homologous Organ |
| Eyes in Human beings and octopus. | Vertebrate hearts. |
| Flippers of penguin and dolphin. | Thorns and tendril |
| Wings of butterfly and birds | Forelimb of vertebrates |
Question 24.
- Explain Hardey-Weinberg equilibrium?
- Mention the factors affecting Hardey-Weinberg equilibrium.
Answer:
1. Allele frequencies in a population are stable and constant from generation to generation. (p2+2pq+q2 =1), p, q are individual frequencies of alleles.
2. The factors are gene migration, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination, and natural selection.
Plus Two Zoology Evolution Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
During his voyage, Darwin went to Galapago islands and observed an amazing diversity of particularly, some black birds, called Finches. Darwin’s Finches represent a best example for an evolutionary phenomenon.
- Name the phenomenon.
- In which feature, they showed diversity?
- Give another example forthis phenomena.
Answer:
- Adaptive radiation
- Showed variety in beak structure based on food habits – from seed-eating to insectivorous, vegetarian, etc.
- Australian Marsupials.
Question 2.
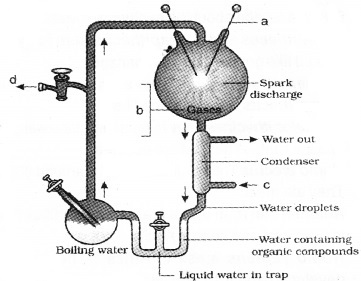
Diagrammatic representation of Miller’s experiment is shown.
1. Label the parts a,b,c,d.
2. Miller’s experiment provided evidence for the theory of………
3. Sequence of substances appearing during the origin of life would have been.
- Amino acids, ammonia, phosphates, nucleic acid
- Ammonia, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids
- Nucleotides, amino acids, nucleic acids, enzymes
- Enzymes, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Answer:
1. a – electrodes
b- mixture of gases (CH4, NH3, H2, H2O)
c – cold water
d – vacuum pump
2. Organic evolution (chemical evolution)
3. ii) Ammonia, amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids.
Question 3.
A list of human ancestry is given. Pick the correct ancestor from the table.
Neanderthal man
Java man
Australopithecus
Cro-magnon man
Dryopithecus
Homo habilus
- First man ape
- The stone tool maker
- Buried their dead.
- User of fire for hunting, defence and cooking.
- Hunter with domesticated dog and did cave paintings.
- Pre-man
Answer:
- Australopithecus
- Homo habilus
- Neanderthal man
- Java man
- Cro-magnon man
- Dryopithecus
Question 4.
Briefly describe the evolution of Man.
Answer:
1. Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus: were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees.
2. Ramapithecus: was more man-like while
3. Dryopithecus: was more ape-like.
4. Australopithecines: They hunted with stone weapons and ate fruit… They did not eat meat.
5. Homo erectus: Their brain capacity is around 900cc. They ate meat.
6. Neanderthal man: with a brain size of 1400cc lived in near east and central Asia
7. Homo sapiens: arose in Africa. Cave art developed about 18,000 years ago and agriculture around 10,000 years back.
Question 5.
Match the following
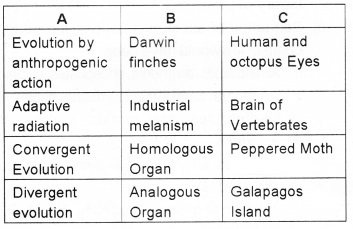
Answer:
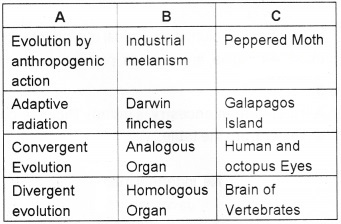
Plus Two Zoology Evolution NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Attempt giving a clear definition of the term species
Answer:
A species is a group of similar individuals differing from the members of other species which interbred freely and relatively stable. Species is the smallest of classification.
Question 2.
Try to trace various components of human evolution (Hint: brain size and funct skeletal structure, dietary preference, etc.).
Answer:
Changes involved in human evolution are as follows
- Flattening of face
- Reduction in body hair
- Development of curves in the vertebral column for erect posture.
- Bipedal locomotion, arms are shorter than legs
- Increase in brain size and intelligence
- Start eating cooked food.
Question 3.
List 10 modern-day animals and from internet resources link it to a corresponding fossil.
Answer:
Different birds-Archaeopteryx.
Question 4.
Describe one example of adaptive radiation.
Answer:
Darwin’s finches of Qalapago island exhibiting a variety of beaks.
Question 5.
Can we call human evolution as adaptive radiation?
Answer:
No, because in human evolution, brain size, skeletal structure, dietary preference and social and cultural evolution occured while in adaptive radiation, the origin, basic structure and the devleopment of the organs remain same only morphological changes occurs.
Plus Two Zoology Evolution Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
‘Continuity of germplasm’ theory was given by
(a) Hugo de Vries
(b) Weismann
(c) Darwin
(d) Lamarck
Answer:
(b) Weismann
Question 2.
‘Hot dilute soup’ was given by
(a) Oparin
(b) Haldane
(c) Urey
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Haldane
Question 3.
Which one of the following theories was proposed by Weismann?
(a) Law of inheritance
(b) Theory of inheritance of acquired characters
(c) Theory of natural selection
(d) Theory of germplasm
Answer:
(d) Theory of germplasm
Question 4.
Coacervatesare
(a) protobionts having polysaccharide, protein, and H2O
(b) protein aggregate
(c) protein and lipid aggregates
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) protobionts having polysaccharide, protein, and H2O
Question 5.
The idea that the life originates from pre-existing life is referred as
(a) biogenesis theory
(b) special creation theory
(c) abiogenesis theory
(d) extraterrestrial theory
Answer:
(a) biogenesis theory
Question 6.
Synthesis of amino acids to prove that amino acids were formed in primitive ocean was experimentally proved
(a) Oparin
(b) Haldane
(c) Sydney fox
(d) Stanley Miller
Answer:
(d) Stanley Miller
Question 7.
The abiogenesis occurred about how many billion years ago?
(a) 1.2 billion
(b) 1.5 billion
(c) 2.5 billion
(d) 3.5 billion
Answer:
(d) 3.5 billion
Question 8.
Pasteur and Koch are related to
(a) discovery of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
(b) discovery of ultracentrifuge
(c) germ theory of disease
(d) gene splicing
Answer:
(c) germ theory of disease
Question 9.
Wings of insects and birds are
(a) analogous
(b) homologous
(c) vestigial
(d) atavism
Answer:
(a) analogous
Question 10.
Convergent evolution is shown by
(a) homologous organ
(b) analogous organ
(c) vestigial organ
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) analogous organ
Question 11.
Which one of the following is not a vestigial structure in Homo sapiens?
(a) Third molar
(b) Epiglottis
(c) Plica semilunaris
(d) Pyramidalis muscle
Answer:
(b) Epiglottis
Question 12.
Which of the following presumably possesses a cranial capacity larger than modem man?
(a) Neanderthal man
(b) Peking man
(c) Australopithecus
(d) Cromagnon man
Answer:
(d) Cromagnon man
Question 13.
The gas mixture used by Miller in his experiment comprised
(a) CH4,C02,N2,H2O
(b) NH3,C02,H2O, N2
(c) CH2,NH3,N2,H2O
(d) CH4,NH3,H2,H2O
Answer:
(d) CH4,NH3,H2,H2O
Question 14.
The Mesozoic era is also called as
(a) the golden age of the amphibians
(b) the golden age of the reptiles
(c) the golden age of the mammals
(d) the golden age of the birds
Answer:
(b) the golden age of the reptiles
Question 15.
Darwin travelled in which of the following ship?
(a) HNS Eagle
(b) D Matrica
(c) H M S Beagle
(d) Titanic
Answer:
(c) H M S Beagle
Question 16.
There are two opposing views about origin of Modem man. According to one view, Homo erectus in Asia were the ancestors of modem man. A study of variations of DNA however suggested African origin of modem man. What kind of observation on DNA variation could suggest this?
(a) Greater variation in Africa than in Asia.
(b) Variation only in Asia and no variation in Africa
(c) Greater variation in Asia than in Africa
(d) Similar variation in Africa and Asia
Answer:
(c) Greater variation in Asia than in Africa
Question 17.
Big bang theory is connected with
(a) origin of earth
(b) origin of universe
(c) origin of moon
(d) origin of life
Answer:
(b) origin of universe
Question 18.
The primitive earth contains
(a) oxygen, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia
(b) Water vapour, methane, oxygen, and ammonia
(c) methane, carbon dioxide an ammonia
(d) Water vapour, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia
Answer:
(d) Water vapour, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia
Question 19.
The first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules like RNA, protein. This was proposed by
(a) Oparin and Haldane
(b) Charles Darwin
(c) Louis Pasteur
(d) Alfred Wallace
Answer:
(a) Alfred Wallace
Question 20.
The spark discharge apparatus that was used by millercontains
(a) CH4, O2, H2, NH3 and water vapaur
(b) CH4, O2, NH3 and water vapaur
(c) CH4, O2, NH3, and H2
(d) CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapaur
Answer:
(d) CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapaur
Question 21.
The first non-cellular forms of life could have originated
(a) 3000 mya
(b) 2000 mya
(c) 2bya
(d) 4bya
Answer:
(a) 3000 mya
Question 22.
The type of evolution leads to the formation of analogous organs
(a) convergent evolution
(b) divergent evolution
(c) microevolution
(d) chemical evolution
Answer:
(a) convergent evolution
Question 23.
The white winged moth survived and the dark-coloured moth were picked out by predators before industrial revolution in England. It supports the theory that proposed by
(a) Lamark
(b) Darwin
(c) Hugo De Vries
(d) Oparin
Answer:
(b) Darwin
Question 24.
In Galapogos island the original seed-eating features of finches of birds changed and become insectivorous and vegetarian finches. This process of evolution radiating to other areas of geography and results
(a) more than two types of beaks in finches
(b) all finches of islands subjected to adaptive radiation
(c) all finches of islands subjected to discontinuous variation
(d) adaptive radiation not leads to evolution
Answer:
(b) all finches of islands subjected to adaptive radiation
Question 25.
A colony of bacteria growing on a given medium utilise a feed component but change in the medium composition affect the population and can survive under the new conditions. This is come under the theory of
(a) Lamark
(b) Darwin
(c) Louis Pasteur
(d) Malthus
Answer:
(b) Darwin
Plus Two Zoology Evolution SCERT Sample Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Arrange the following primates in correct sequence of evolution to man.
- Dryopethicus
- Homo erectus
- Homo habilis
- Neanderthal man (2)
Answer:
Dryopithecus – Homo habilis – Homo erectus – Neanderthal man.
Question 2.
Carefully read the following statement and answer the questions. “A population remain constant and stable in its allele frequency from generation to generation. Such population shows genetic equilibrium’.
- Name the underlying principle in the above statement. (1)
- Name any two factors which affect genetic equilibrium. (1)
Answer:
- Hardey – Weinberg Principle
- Mutation, Natural Selection Migration, Genetic drift.
We hope the given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Evolution will help you. If you have any query regarding Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Evolution, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
