Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance are part of Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Zoology Chapter Wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 |
| Chapter Name | Molecular Basis of Inheritance |
| Number of Questions Solved | 88 |
| Category | Kerala Plus Two |
Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The process of copying genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA termed as
(a) translation
(b) transamination
(c) replication
(d) transcription
Answer:
(d) transcription
Question 2.
An enzyme that uses viral RNA as template for the synthesis of DNA is
(a) RNA polymerase
(b) reverse transcriptase
(c) viral nuclease
(d) RNA replicase
Answer:
(b) reverse transcriptase
Question 3.
The sequence of structural gene in Lac operon concept is
(a) Lac A, Lac Y, Lac Z
(b) Lac A, Lac Z, Lac Y
(c) Lac Y, Lac Z, Lac A
(d) LacZ, Lac Y, Lac A
Answer:
(d) LacZ, Lac Y, Lac A
Question 4.
During transcription, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA stand that is being coded is ATACG, then the nucleotide sequence in the mRNA would be
(a) TATGC
(b) TCTGG
(c) UAUGC
(d) UATGG
Answer:
(c) UAUGC
Question 5.
Anticodon is base triplet on
(a) mRNA complementary to a base sequence on rRNA
(b) mRNA complementary to a base sequence on tRNA
(c) tRNA complementary to a base sequence on rRNA
(d) tRNA complementary to a base sequence on mRNA
Answer:
(d) tRNA complementary to a base sequence on mRNA
Question 6.
There is a murder, which shocked the entire town. The dead body contains the blood smear of another person. The police suspected two persons. Name the method used to identify the murderer.
Answer:
DNA fingerprinting
Question 7.
In DNA molecule a nitrogenous base bonded with pentose sugar molecule through a………Bond.
Answer:
Phosphodiester bond.
Question 8.
Histone proteins are………Charged molecule.
Answer:
Positively Charged
Question 9.
Histone octamer bind to DNA to form………..
Answer:
Nucleosomes
Question 10.
The chromosomes are seen on which stage of the cell cycle.
Answer:
Metaphase
Question 11.
The virus which infects the bacteria are called…………
Answer:
Bacteriophage
Question 12.
Histones are the proteins found associated with eucaryotic DNA. Name the two Amino acids which is found in greater quantity in Histones.
Answer:
Lysines and Arginines
Question 13.
Pick the genetic material in human beings (RNA, mRN.tRNA, DNA)
Answer:
DNA
Question 14.
The DNA synthesis in leading strand is
(a) continuous
(b) not as single strand
(c) discontinuous
(d) as Okazaki fragments
Answer:
(a) Continuous.
Question 15.
Expand the following
mRNA = messenger RNA
tRNA = ……………….
rRNA = Ribosomal RNA
hnRNA = ………………
Answer:
tRNA = transfer RNA
hnRNA = heterogenous nuclear RNA
Question 16.
Pick the initiation codon from the triplets codons given below. AAA, UGA.AUG, GUA
Answer:
AUG
Question 17.
From the following triplet codes find out the stop codon (GAU, UCU, UAG, UGG)
Answer:
UAG
Question 18.
A DNA molecule in which both strands have radioactive thymidine is allowed to duplicate in an environment containing non-radioactive thymidine. What will be the correct number of DNA molecule that contain some radioactive thymidine after 3 duplications?
Answer:
Two DNA molecules
Question 19.
A change in a sequence of DNA occurs so that the mRNA codon reads AUC rather than AUU. Both of these code for the amino acid isoleucine. Argue that this is not a mutation.
Answer:
If one defines a mutation as a change in genetic material resulting in a different phenotypic expression. Hence this is not a mutation.
Question 20.
Histones are the proteins found associated with eucaryotic DNA. Name the two Amino acids which is found in greater quantity in Histones.
Answer:
Lysines and Arginines
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
To solve a dispute of parentage, the court put an order to conduct a test to prove the father of the child. Name the test used. Procedure of the test is given below, complete it.
- Isolation of DNA.
- DNA is cut using restriction endonuclease.
- ……………
- …………..
- hybridization using VNTR probe
- ………….
Answer:
Name of the test is DNA finger printing. The procedure is
- Isolation of DNA.
- DNA is cut using restriction endonuclease.
- Separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis.
- Blotting of separated DNA fragments on nitrocellulose.
- hybridization using VNTR probe
- Detection of hybridised DNA fragments by autoradiography.
Question 2.
DNA finger printing is a technique in molecular biology. Arrange the following steps in sequence. Blotting of DNA fragment to nitro cellulose. Digestion of DNA by restriction endonuclease. Deletion of DNA by restriction endonuclease. Isolation of DNA, separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis.
Answer:
- Isolation of DNA
- Digestion of DNA by restriction endonuclease.
- Separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis.
- Blotting of DNA fragment to nitrocellulose.
- Deletion of hybridised DNA by autoradiography.
Question 3.
Match the columns A, B, and C.
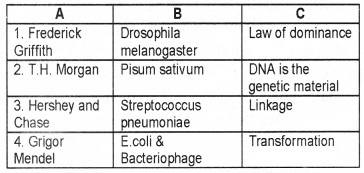
Answer:
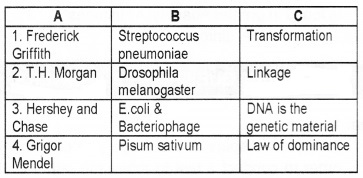
Question 4.
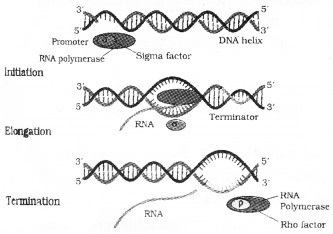
Process of Transcription in Bacteria is shown. Identify any two differences, found in eukaryotec transcription.
Answer:
1. There are 3 RNA polymerases, namely RNA Polymerase I – Transcribes rRNAs . RNA Polymerase II – Transcribes hn RNA (precursor of mRNA) RNA Polymerase III – TranscribestRNA, 5srRNA, SnRNAs.
2. There are complexities like splicing, capping, tailing, etc. in eukaryotic transcription.
Question 5.
Identify the following and differentiate them.
- AUG
- UGA
Answer:
- AUG – Codes for methionine and it acts as initiator codon.
- UGA – Does not code for any amino acids and acts as a stop codon.
Question 6.
Repetitive sequences in a DNA molecule are of no importance. Do you agree?
Answer:
Repetitive DNA is a small stretch of DNA repeated many times. They show a high degree of polymorphism and form the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
Question 7.
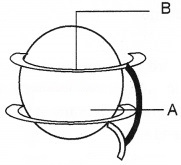
Observe the diagram and identify A & B.
Answer:
- Histone octamer
- DNA
Question 8.
Match the following experiments and conclusions with respective worker.
| a. Transforming Principle | i) Messelson & Stahl |
| b. DNA is genetic material | ii) Watson & crick |
| c. Semi conservative mode of DNA replication | iii) Fredrick Griffth |
| d. Proof of semi conservative replication | iv) Hershey & chase |
Answer:
| a. Transforming Principle | Fredrick Griffth |
| b. DNA is genetic material | Hershey & chase |
| c. Semi conservative mode of DNA replication | Watson & crick |
| d. Proof of semi conservative replication | Messelson & Stahl |
Question 9.

Name the process (a) and (b).
Answer:
a – Transcription,
b-Translation
Question 10.
In bacteria, three major types of RNAs are needed for the synthesis of protein.
- List them and mention their functions.
- What are the three steps in transcription in bacteria
Answer:
1. List them and mention their functions:
- mRNA – It provides the template
- tRNA – It brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
- rRNA – It plays structural and catalytic role during translation.
2. three steps in transcription in bacteria:
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
Question 11.
State whether the following statements are true or false. If false rewrite them by changing the word understand.
- Double helical of DNA was proposed by Jacob and Monod.
- Sugar present in RNA is deoxyribose
- Introns are the coding sequences of a eukaryote gene.
- The common method of DNA replication is conservative.
Answer:
All are false.
- Watson and Crick
- Ribose
- Exons
- Semi conservative
Question 12.
The transcription is usually taking place from DNA to RNA. Can you explain any instance where transcription takes place in reverse order?
Answer:
Yes. In some viruses, it takes place by reverse transcription.
Question 13.
In the medium where E. Coli was growing, lactose was added, which induced the lac operon. Why does lac operon shut down after sometime addition of lactose in the medium?
Answer:
Lac operon is shut down after some times when the added lactose is utilized from the medium. It is be-cause the repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and prevent RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
Question 14.
While an mRNA strand is being translated in the ribosome subunit, the triplets in sequence were UAC and UAG. One of them codes for tyrosine. What is the significance of the other? Pick out the codon and specify.
Answer:
UAG acts as terminator codon thus leads to the termination of polypeptide chain. It does not specify any amino acid.
Question 15.
What are structural genes? Name the three structural genes present in the lac operon of Escherichia coil?
Answer:
Structural genes are those genes which actually synthesise mRNAs. The lac operon of Escherichia coli contains three structural genes (z, y and a)
Question 16.
In a classroom discussion your classmate says that the RNA is more stable than DNA. Do you agree with it. Explain the advantage of DNA over RNA.
Answer:
No. DNA is more stable
While DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose (in deoxyribose there is no hydroxyl group attached to the pentose ring in the 2 position). These hydroxyl groups make RNA less stable than DNA because it is more prone to hydrolysis. DNA have
- Replication
- Chemically and structurally stable
- Obey Mendelian Characters
Question 17.
- Mention any four goals of Human Genome Project.
- Name two methodologies involved in it.
Answer:
1. Identify 20000-25000 genes in human DNA., determine 3 billion base pairs, store information as database, improve tool for data analysis, transfer related technologies to other sectors such as industries.
2. Expressed Sequence Tag Sequence Annotation.
Question 18.
Explain the transforming principle and its experiment.
Answer:
Mouse + live S strain = mouse died Mouse + live R strain = mouse alive Mouse + heat-killed S strain = mouse alive Mouse + heat-killed S strain along with R strain = mouse died.
(certain factors from heat-killed S strain transforms non-virulent R strain to become S strain ie, transfer of genetic material)
Question 19.
The regulation of gene expression happened at various levels in eukaryotes. Point out the levels of gene expression.
Answer:
- Transcriptional level
- Processing level
- Transporting mRNA
- Translational level.
Question 20.
Chromatin is a lengthy molecule. How is it compactly packed in nucleus?
Answer:
Nucleosome Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called as histone octamer. The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamerto form a structure called Nucleosome.
Question 21.
Observe the figure and answerthe following.
- Name the biomolecule
- Explain the function of this molecule.
Answer:
- tRNA
- Activation and transport of amino acid Ribosome
Question 22.
Identify figure and answer the following.
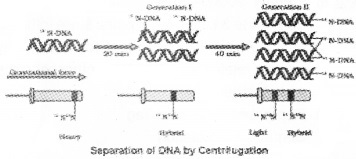
- Name the experiment.
- Briefly explain this experiments.
Answer:
- Meselson and Stahl Experiment
- They transferred the cells into a medium with normal 14NH4Cl and took samples at various definite time intervals as the cells multiplied, and extracted the DNA that remained as double-stranded helices.
The DNA that was extracted from the culture one generation after the transfer from 15N to 14N medium [E coil divides in 20 minutes] had a hybrid DNA.
DNA extracted from the culture after another generation [that is after 40 minutes, II generation] was composed of equal amounts of this hybrid DNA and of ‘light’ DNA.
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Both RNA and DNA are considered as genetic materials.
- What are the main criteria for a molecule to act as genetic material?
- Why DNA is considered as a better genetic material than RNA?
- Why RNA viruses mutate and evolve faster than DNA virus?
Answer:
1. Main criteria for a molecule to act as genetic material:
- Able to generate replica
- Chemically and structurally stable
- Provide scope for slow mutation, required for evolution.
- Able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’.
2. RNA, being catalytic, is chemically more reactive and less stable than DNA. Therefore DNA is a better genetic material as it is less reactive and structurally more stable.
3. RNA is unstable than DNA, so mutate at a faster rate. Viruses having RNA genome, with shorter life span mutate and evolve faster.
Question 2.
The sequence of nitrogen bases on one of the polynucleotide chains of a DNA strand is given below.
- Write the complimentary strand of this polynucleotide chain.
- Write the sequence of mRNA framed from the template strand.
- Name the process in which mRNA is formed.
- Name the enzyme that catalyses the formation of mRNA
Answer:
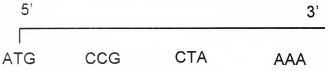
- TAC GGC GAT TTT
- UAC GGC GAU UUU
- Transcription
- RNA Polymerase
Question 3.
The most widely accepted scheme for replication was proposed by Watson & Crick.
- Name the scheme of replication.
- Who given the experimental proof forthis?
- Name the medium used.
Answer:
- Semi conservative DNA replication
- Messelson and Stahl
- Medium containing 15NH4Cl and normal 14NH4Cl. CsCl used for centrifugation.
Question 4.
- Identify the representative diagram.
- Mention its application and future challenge (anyone).
- Name the methods involved in it.
Answer:
1. Human genome.project (HGP)
2. Application – They can study all the genes in a genome.
Future challenge – Requires expertise and creativity of thousands of scientists of various disciplines.
3. Name the methods involved in it:
- Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs)
- SequenceAnnotation
Question 5.
The schematic representation of the Lac operon is given below:
![]()
- Label a, b, c, d.
- Name the inducer in this operon.
- Write any two other operon.
Answer:
- a – P b – z, c – y, d – a
- Lactose
- Trp operon, ara operon, etc.
Question 6.
In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II transcribes precursor of mRNA, called hnRNA.
- What is the full form of hnRNA?
- Describe the additional processings takes place in an hnRNA to become mRNA.
- What is gene splicing?
Answer:
1. Heterogeneous nuclear RNA
2. The additional processings takes place in an hnRNA to become mRNA:
i. Capping:
It is the addition of nucleotide (methyl guanosine triphosphate) at 51 – end of hnRNA.
ii. Tailing:
It is the addition of adenylate residues at 31 – end.
3. Gene splicing is the removal of non-functional introns and joining of exons in a defined order.
Question 7.
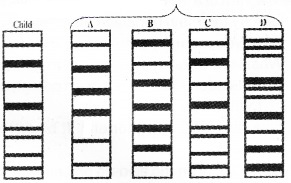
The above pictures are the DNA finger prints of a child and suspected persons as the father of the child.
- Out of the suspected persons, find the true father of the child.
- How will you identify the father?
- What is the principle behind this?
Answer:
1. C may be the true father.
2. As the bands presented is the finger print match between child and person C. It denotes that hereditary materials are more or less common in these two bands. Usually a child comes 50% of hereditary materials from his father. So ‘C’ may be the father of the child.
3. Principle behind it is VNTRs. Southern blotting using variable number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR) as a probe.
Question 8.
One of the salient features of genetic code is codon is triplet and 61 codons code for amino acids and 3 codons are stop codons. Make a list of other salient features of genetic code.
Answer:
1. Genetic code is unambiguous and specific:
A codon always specifies the same aminoacid, it cannot code for more than one amino acid.
2. Genetic code is deoenerate:
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
3. Genetic code is universal:
Each codon of it specifies or codes for the same kind of amino acid in all organisms. (Eg. UUU-phenyl alanine).
4. Genetic code is polarised:
In specifying a particular polypeptide, the genetic code has a definite initiation codon and a terminal codon.
Question 9.
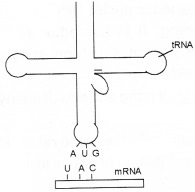
The diagram of a tRNA the adapter molecule is given.
- Identify the main parts and their role.
- What do you mean by aminoacylation of tRNA?
- What is the indication of end of translation?
Answer:
1. main parts and their role:
- Anticodon loop – It has been complementary to the code.
- Amino acid acceptor end. It binds to amino acids.
2. Activation of amino acids in presence of ATP and linking to tRNA is called aminoacylation or charging of tRNA.
3. At the end of translation, a release factor binds to the stop codon, to terminate translation and release polypeptide from ribosome.
Question 10.
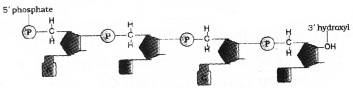
Diagram of a polynucleotide is given.
- Identify the 3 components of a nucleotide.
- Name the purines.
- Mention the types of linkage present in a polynucleotide.
Answer:
1. 3 components of a nucleotide:
- A nitrogen base
- A pentose sugar (Ribose/ Deoxyribose)
- Phosphate group
2. Adenine and Guanine
3. types of linkage present in a polynucleotide:
- N-glycosidic linkage
- Phosphoester linkage
- Phosphodiester linkage
Question 11.
DNA finger printing is widely used in forensic application. Some terms related to DNA finger printing are given. What are they?
- Repetitive DNA.
- VNTR
- PCR
Answer:
- A small stretch of DNA repeated many times is called repetitive DNA.
- Variable Number of Tandem Repeats
- Polymerase chain reaction – Synthesis of multiple copies of DNA of interest.
Question 12.
Look at the figure above depicting lac operon of E.coli.
- What could be the series of events when an inducer is pre^nt in the medium in which E.coli is growing?
- Name the Inducer.
- Who introduce operon model.
Answer:
- Inducer induces the operon by inactivating the repressor, allowing RNA polymerase access to promotor and transcription proceeds.
- Lactose
- Jacob and Monad
Question 13.
An mRNA strand has a series of codons out of which three are given below:
- AUG
- UUU
- UAG
1. What will these codons be translated into?
2. What are the DNA codons that would have transcribed these RNA codons?
Answer:
1. These codons be translated into:
- AUG signals the synthesis of polypeptide (start signal) and codes for the amino acid methionine.
- UUU codes for phenylalanine.
- UAG do not specify any amino acid and hence is called nonsense codon. It signals the termination of polypeptide chain (stop signal).
2. TACAAAATC.
Question 14.
The quest for finding out the complete DNA sequence of human genome lead to a mega project called HGP.
- Expand HGP.
- In which area of biology HGP is closely associated?
- Mention any four important goals of HGP.
Answer:
1. Human Genome Project (HGP)
2. Bioinformatics
3. The important goals of HGP are
- Identify all the genes (20,000-25,000) in human DNA.
- Determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA.
- Store this information in databases.
- Improve tools for data analysis.
- Transfer related technologies to other sectors, like industries.
- Address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise from the project.
Question 15.
Complete the flow chart of the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting.
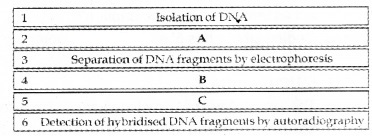
Answer:
- Digestion of DNA by restriction endonuclease
- Blotting of separated DNA fragments to synthetic membranes (nitrocellulose)
- Hybridisation using VNTR probe.
Question 16.
Identify the figure and answer the following.
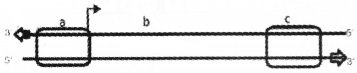
Name a, b and c
Answer:
a. Promoter
b. Structural Gene
c. Terminator
Question 17.
Name the process involved in the synthesis of protein from mRNA. Explain the process.
Answer:
The activation of amino acids with ATP and linked to tRNA- a process commonly called as charging of tRNA or aminoacylation of tRNA
bF or initiation, the ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG) that is recognised only by the initiator tRNA.
In elongation, amino acid linked to tRNA. and bind to the codon in mRNA by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon.
The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one and translated into Polypeptide.
At the end, a release factor binds to the stop codon, terminating translation and releasing the complete polypeptide from the ribosome.
Question 18.
Observe the figure and complete table 1 with name .of gene and table 2 with enzymes produced by structural gene.
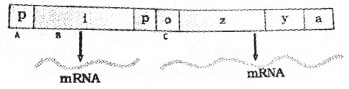
| Lable | Name of Gone |
| A | |
| B | |
| C |
Answer:
| Structural Genes | Enzymes |
| z | |
| y | |
| a |
Answer:
| Label | Name |
| A | Promoter gene |
| B | Repressor gene |
| C | Structural gene |
| Structural Genes | Enzymes |
| Z | p galactosidase |
| y | permease |
| A | transacetyl ase |
Question 19.
In a classroom discussion your classmate says that the RNA is more stable than DNA. Do you agree with it. Explain the advantage of DNA over RNA.
Answer:
No. DNA is more stable
While DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose (in deoxyribose there is no hydroxyl group attached to the pentose ring in the 2’ position). These hydroxyl groups make RNA less stable than DNA because it is more prone to hydrolysis. DNA have
- Replication
- Chemically and structurally stable
- Obey Mendelian Characters
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
If the sequence of coding strange in a transcription unit is written as follows:
5’-ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC-3’ Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Answer:
The sequence of template strand will be
3’-TACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTACGTACG-5’
Thus, the sequence of mRNA will be
5’-AUGCAAUGCAAUGCAAUGCAAUGCAAUGC
Question 2.
Describe In the medium where E. Coli was growing, lactose was added, which induced the lac operon. Then why does lac operon shut down after some time after addition of lactose in the medium?
Answer:
Lac operon is shut down after some times when the added lactose is utilised from the medium. It is because the repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and prevent RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
Question 3.
Explain (in one or two lines) the function of following:
- Promoter
- tRNA
- Exons.
Answer:
1. Promoter:
It acts as an initiation signal which function as recognition centre for RNA – polymerase provided the operator gene is switched on.
2. tRNA:
It acts as an adapter molecule which transfers amino acids to ribosomes for synthesis of polypeptides.
3. Exons:
These are coding sequences or expressed sequences in a eukaryotic gene. The exon sequences appear in mature or processed RNA.
Question 4.
Briefly describe the following:
- Transcription
- Polymorphism
- Translation
- Bioinformatics
Answer:
- Transcription is the process of creating a RNA copy of a DNA sequence.
- When different types of phenotype occur in the same species the situation is called polymorphism.
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Select the two correct statements out of the four (l-IV) given below about Lac operon.
I. Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it.
II. in the absence of lactose the repressor binds with the operator region
III. The z-gene codes for region
IV. This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monad
The correct statement are:
(a) II and III
(b) I and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I and II
Answer:
(c) II and IV
Question 2.
In the Lac operon system, beta-galactosidase is coded by
(a) a-gene
(b) i-gene
(c) l-gene
(d) z-gene
Answer:
(d) z-gene
Question 3.
Match the codons with their respective amino acids and choose the correct answer.
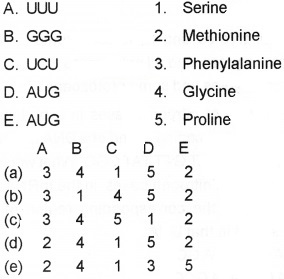
Answer:
(a) 3 4 1 5 2
Question 4.
What is antisense technology?
(a) A cell displaying a foreign antigen used for synthesis of antigens
(b) Production of somaclonal variants in tissue cultures
(c) When a piece of RNA that is complementary in sequence is used to stop expression of a specific gene
(d) RNA polymerase producing DNA
Answer:
(c) When a piece of RNA that is complementary in sequence is used to stop expression of a specific gene
Question 5.
An enzyme that uses viral RNA as template for the synthesis of DNA is
(a) RNA polymerase
(b) reverse transcriptase
(c) viral nuclease
(d) RNAreplicase
Answer:
(b) reverse transcriptase
Question 6.
During translation initiation in prokaryotes, a GTP molecule is needed in
(a) association of 30S, mRNA with formyl-met tRNA
(b) association of 50S subunit of ribosome with initiation complex
(c) formation of formyl- met- tRNA
(d) binding of 30 subunits of ribosome with mRNA
Answer:
(a) association of 30S, mRNA with formyl-met tRNA
Question 7.
The central dogma of protein synthesis in teminism is
(a) rRNA → DNA → mRNA → Protein
(b) DNA → gRNA → mRNA → Protein
(c) DNA → DNA → mRNA → Protein
(d) mRNA → gRNA → DNA → Protein
Answer:
(a) rRNA → DNA → mRNA→ Protein
Question 8.
Which of the following groups of codons codes for amino acid serine?
(a) CUC, CUC, CUAandCUG
(b) UAU, UAC, UGU, and UGC
(c) UCU, UCC, UCA, and UCG
(d) GUU, GUC, GCU, and GCC
Answer:
(c) UCU, UCC, UCA, and UCG
Question 9.
Jacob and Monod studied lactose metabolism in E.coli and proposed operon concept, applicable for
(a) all prokaryotes
(b) all prokaryotes and some eukaryotes
(c) all prokaryotes and all eukaryotes
(d) all prokaryotes and some protozoans
Answer:
(a) all prokaryotes
Question 10.
The sequence of nitrogen bases in a particulars region of the non-coding stand of a DNA molecule was found to be CAT GTTTAT CGC. What would be the sequence of nitrogen bases in the mRNA that is synthesized the corresponding region of the coding strand in that DNA?
(a) GUACAAAUAGCG
(b) GTA CAAATA GCC
(c) CAU GUU UAU CGC
(d) CAAGAATAU GCC
Answer:
(c) CAU GUU UAU CGC
Question 11.
The process of reverse transcription was brought to light by the work of
(a) Geroge Beadle and Edward Tatum
(b) Garrod
(c) HMTemin and D Baltimore
(d) RW Holley and Grover
(e) Marashall and W Nirenberg
Answer:
(c) HMTemin and D Baltimore
Question 12.
Dr. Khurana and his colleagues synthesized an RNA molecule with repeating sequence of UGN bases (UG UG UG UG UG UG). It produced a tetrapeptide with alternating sequence of cysteine and valine. It proves that codons for cysteine and valine is
(a) UGU and GUU
(b) UGUandGUG
(c) UUG and GGU
(d) GUGandUGU
(e) GUU and UGU
Answer:
(a) UGU and GUU
Question 13.
Degeneracy of genetic codes is due to
(a) functional 61 codons and 20 amino acids
(b) functional 64 codons and 20 amino acids
(c) functional 20 codons and 20 amino acids
(d) functional 20 codons and 61 amino acids
Answer:
(a) functional 61 codons and 20 amino acids
Question 14.
A single amino acid is often coded by more than one triplet code. In most of the cases the first two bases are the same but the third base is different. This feature of the genetic codes is called
(a) universality
(b) non-overlapping and commaless
(c) redundancy and degeneracy
(d) non-ambiguity
Answer:
(c) redundancy and degeneracy
Question 15.
Which of the following pairs of chromosomal mutation are most likely to occur when homologous chromosomes are undergoing synapasis?
(a) Deletion and inversion
(b) Duplication and translocation
(c) Deletion and Duplication
(d) Inversion and translocation
Answer:
(c) Deletion and Duplication
Question 16.
Which of the following is generally used for induced mutagenesis in crop plants?
(a) Alpha particles
(b) X-rays
(c) UN (260nm)
(d) Gamma rays (from cobalt 60)
Answer:
(d) Gamma rays (from cobalt 60)
Question 17.
The most likely reason for the development of resistance against pesticides in insect damaging a crop is
(a) random mutations
(b) genetic recombination
(c) directed mutations
(d) acquired heritable changes
Answer:
(a) random mutations
Question 18.
Double helix model of DNA structure was elucidated through X- ray diffraction studies conducted by Watson and Crick with assistance of
(a) Nirenberg and Ochao
(b) Franklin and Wilkins
(c) Har Gobind Khorana
(d) George Gamov
Answer:
(b) Franklin and Wilkins
Question 19.
The approximate distance between the adjacent base pair is
(a) 0.34 nm
(b) 3.4nm
(c) 340 nm
(d) 034nm
Answer:
(a) 0.34 nm
Question 20.
DNA replication takes place in a semi-conservative manner was experimentally proved by
(a) Griffith
(b) Messolson and Stahl
(c) Hershey and Chase
(d) McCarthy, Mecloid, and Avery
Answer:
(b) Messolson and Stahl
Question 21.
Okasaki fragments are
(a) short stretch of DNA
(b) long stretch of DNA
(c) joined DNA fragments by ligase
(d) stretches of DNA in leading strand
Answer:
(a) short stretch of DNA
Question 22.
Messolson and Stahl explained the types of DNA molecule formed in different generations as
(a) light DNA
(b) hybrid DNA
(c) heavy DNA
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 23.
The base pairs of DNA double helix is given below. Select the suitable mRNA strand that derived from transcription is
31-ATTT C C-51
51-TAAAGG-31
(a) UAAAGG
(b) CUUUCC
(c) GAAAGG
(d) CCUUUC
Answer:
(a) UAAAGG
Question 24.
The number of amino acids formed by the various combination of triplet code is
(a) 61
(b) 20
(c) 64
(d) 16
Answer:
(b) 20
Question 25.
RNA processing occurs in
(a) bacteria
(b) viruses
(c) fungi
(d) vi raids
Answer:
(c) fungi
Question 26.
The amino acid serine is coded by
(a) UGC
(b) AGG
(c) UAG
(d) UCC
Answer:
(d) UCC
Question 27.
The significant aspect of reverse transcription is
(a) the flow information from DNA to RNA
(b) the flow information from RNA to DNA
(c) the flow information from RNA to proteins
(d) both a and c
Answer:
(b) the flow information from RNA to DNA
Plus Two Zoology Molecular Basis of Inheritance SCERT Sample Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Read the following and select the correct statement/statements.
(a) 23 s RNA act as a enzyme in prokaryotes.
(b) In prokaryotes DNA is monocistronic
(c) Francis Crick proposed the Central Dogma of Molecular biology.
(d) In Eukaryotes three types of RNA polymerases are present. (an only, a and b, a and c, a and d) (1)
Answer:
(a) 23 s RNA act as an enzyme in prokaryotes
(d) In Eukaryotes three types of RNA polymerases are present.
Question 2.
Study the mRNA segment given below which is ready to be translated into a polypeptide chain and answer the following questions.
![]()
- What is A and B denotes?
- Write the triplet codon for A and B (1)
Answer:
- A – start codon B – stop codon
- A – AUG B – UAA, UGA, UAG
Question 3.
Carefully read the statement given below and correct the digits in the brackets a and b, if it is wrong.

Answer:
- 2968 instead of 1968
- No change
Question 4.
Write the functions of the following
- 5-methyl Guanosine triphosphate (5m GPPP)
- DNA Ligase (2)
Answer:
- act as cap. In capping an unusual nucleotide (methyl guanosine triphosphate) is added to the 5′- end of hnRNA.
- Joints DNA fragments during replication
We hope the given Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance will help you. If you have any query regarding Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
