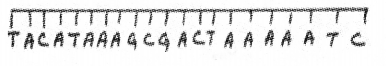Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 4 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Question 1.
Observe the diagram below: (MAY-2010)

Which among the following is the complimentary sequence of the DNA fragment shown above?
a) 5′ -> ATTCG -> 3′
b) 3′ -> ATTCG -> 5′
c) 3′ -> TAAGC -> 5′
d) 3′ -> CGAAT -> 5′
Answer:
3′ -> TAAGC -> 5′
Question 2.
DNA sequence is provided below: (MAY-2010)
TACGAGTTATATATACAT
a) Write down the triplet codon- it codes for.
b) If a nitrogen base is added in between 4th & 5th nitrogen bases, what will be its effect on transcription?
Answer:
a) AUG / CUC / AAU / AUA / UAU / GUA
OR
TAC / GAG / TTA / TAT / ATA / CAT
b) Frame shift mutation / point mutation/Mutation / Entire amino acid sequence changed / incorrect protein produced / change in protein structure / incorrect transcription and translation /abnormal protein.
Question 3.
In a paternity dispute, the VNTR DNA samples of parent and child were DNA finger printed. The diagrammatic representation of the DNA fingerprint is shown below. (MAY-2010)
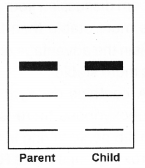
a) What is your opinion about the paternity of child? Substantiate your opinion.
b) List down any four major steps of molecular biological procedures adopted for this.
Answer:
a) Paternity is confirmed
VNTR bands / finger print bands / bands are similar.
b) Steps of DNA finger printing techniques are
i) Isolation of DNA
ii) Digestion of DNA by restriction endo nuclease
iii) Seperation of DNA fragment by Electrophoresis,
iv) Plotting of DNA fragment into Nitro cellulose
v) Ditection of hybridised DNA by Auto radiography
Question 4.
A transcriptional unit is given below. Observe it and answer the questions. (MARCH-2012)
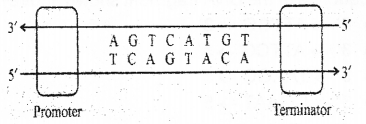
a) How can you identify the coding strand?
b) Write the sequence of RNA formed from this unit?
c) What would happen if both strands of the DNA act as templates for transcription?
Answer:
a) Coding strand has 5′ end at the promoter or 5’TCAGTACA3′
b) 5′ UCAGUACA 3′
c) The two RNA will be complimentary and may form double stranded RNA and it prevents the translation.
Question 5.
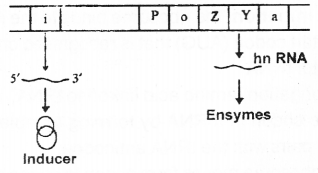
In E.coli lactose catabolism is controlled by Lac operon. Lac operon in the absence of inducer (lactose) is given below. (MARCH-2012)
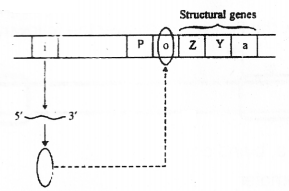
a) What is ‘P’?
b) Name the enzymes produced by the structural genes ‘Z’, ‘Y’ and ‘a’?
c) Redraw the diagram in the presence of an inducer.
Answer:
a) Promoter
Z-Bgalactosidase
b) Y – Permease
a-Transacetylase
c)
Question 6.
Following are the first two steps in Griffith transformation experiment: (MAY-2012)
1) S strain 2 Inject into mice 2 mice live
2) R strain 2 Inject into mice 2 mice die
a) If there is any mistake correct it.
b) Write the remaining steps.
Answer:
a) 1. S strain -> inject into mice -> mice die
2. R strain inject into mice -> mice live
b) When Griffith was injected heat-killed S strain into mice, bacteria did not kill them. But he injected a mixture of heat-killed S and live R bacteria, the mice died .
Question 7.
DNA is better genetic material than RNA. Do you agree with this statement ? Substantiate. (MAY-2012)
Answer:
The 2-OH group present at the nucleotide in RNA is a reactive group and makes RNA labile and easily degradable. Hence DNA is less reactive and structurally more stable when compared to RNA. Therefore, among the two nucleic acids, the DNA is a better genetic material.
Question 8.
Given below is the diagrammatic representation of first stage of a process in bacteria. (MAY-2012)
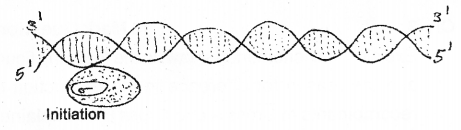
a) Identify the process.
b) Name the enzyme catalyses this process.
c) What are the additional complexities in Eukaryotes for this process?
Answer:
a) Prokaryotic transcription
b) RNA polymerase
c) In eukaryotes hnRNA undergo additional processing called as splicing, capping and tailing.
In splicing the introns are removed and exons are joined together. In capping methyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5-end of hnRNA. In tailing, adenylate residues are added at 3-end in a template.The fully processed hnRNA, called as mRNA, that is transported out of the nucleus for translation.
Question 9.
The flow of genetic information is shown below. (MARCH-2013)
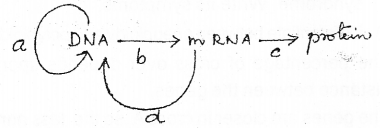
Name the processes a, b, c
Answer:
a) Replication
b) Transcription
c) Translation
d) Reverse transcription
Question 10.
RNA is not an ideal molecule as genetic material because ________. (MARCH-2013)
a) 2’OH group of ribose is reactive and make it labile
b) It is catalytic and hence reactive
c) Both (a) and (b)
d) None of the above
Answer:
c) Both a and b
Question 11.
Presence of lactose enhances the production of (3 galactosidase and other enzymes in bacteria, how will you explain this phenomenon? (MAY-2013)
Answer:
In lac operon,lactose is the inducer.Inducer binds with repressor protein but repressor cannot bind to op-erator gene,the free operator gene induces the RNA polymerase to bind with promoter and initiates tran-scription Three structural genes synthesise three mRNAs to produce enzymes.
Question 12.
A DNA sequence needed for coding a peptide is given below. (MAY-2013)
CAAGTAAATTGAGGACTC
(Hint: Codons and Aminoacids)
CAAGTAAATTGAGGACTC
UUA-Leu
CCU – Pro
CAU – His
ACU-Thr
GUU-Val
GAG-Glu
a) Write the complementary mRNA coding sequence for this.
b) Find out the amonoacid sequence of the peptide chain using the codons given in the hints.
c) If a mutation cause a change in the sixth codon CTC to CAC. It leads to a mendelian disorder. Identify the disease and write the specific characteristics of the diseasie.
Answer:
a) GUUCAUUUAACUCCUGAG
b) Val,His,Leu,Thr,Pro,Glu
c) Sickle cell anaemia, RBC become sickle shaped and unable to take oxygen .These are destroyed more rapidly leading to anaemia.
Question 13.
Draw a flow chart showing the steps of southern blot hybridization using radio labelled VNTR. (MAY-2013)
Answer:
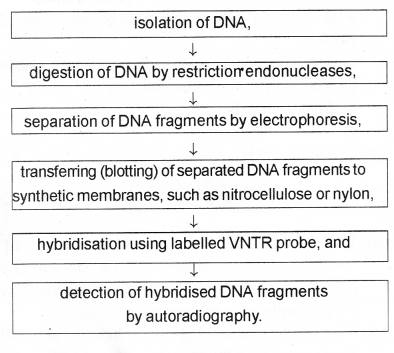
Question 14.
“Prediction of the sequence of amino acids from the nucleotide sequence in mRNA is very easy, but the exact prediction of the nucleotide sequence in m RNA from the sequence of amino aids coded by mRNA is difficult”.(MARCH-2014)
a) Which properties of the genetic code is the reason for the above condition? Explain.
b) Which are the stop codons in DNA replication?
Answer:
a) Degeneracy – A single aminoacid is represented by many codons (degenerate codons)
b) Stop codons are UAA,UAG,UGA
Question 15.
Diagrammatic representation of Central dogma’ is given below: Observe the diagram carefully and redraw it making appropriate corrections. (MARCH-2014)
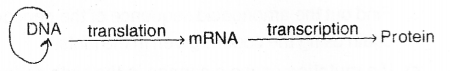
Answer:
Question 16.
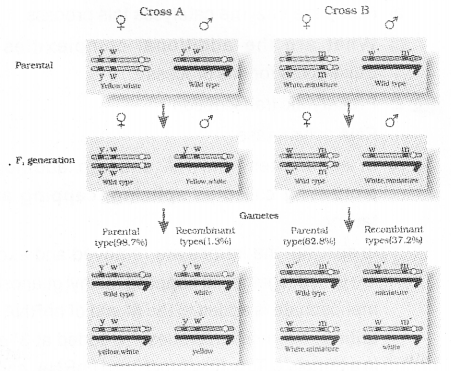
Explain the phenomenon shown in the following figure and the reason for difference in the production of II recombinants in Cross A and Cross B as explained by morgan. (MARCH-2014)
Difference in chromosome number of some human beings A, B. C and D are given below:
A) 22 pairs of Autosomes
B) 22 pairs of Autosomes+XO
C) 22 pairs of Autosomes + 1 Autosome
D) 22 pairs of Autosomes+XXY
OR
a) Identify the person who suffers from Klinefelter’s syndrome. Write its symptoms.
b) Differentiate between aneuploidy and polyploidy.
Answer:
The percentage of cross over depends upon the distance between the genes.
The genes are closer in cross A,so the less number of recombinants are produced. This is called link-age.
In cross B, genes are distantly located so more number of recombinants are produced.
OR
a) 22 pairs of autosomes+XXY, Sterile male, poorly developed testis and mental retardation
b) Aneuploidy-failure of separation of chromosomes during cell division results in-the gain or loss of chromosome.
Polyploidy – Failure of cytokinesis aftertelophase results in the increase in a whole set of chromosome
Question 17.
Correct the amino acid sequence of sickle cell haemoglobin. (MAY-2014)
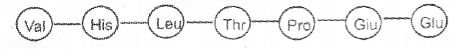
Answer:
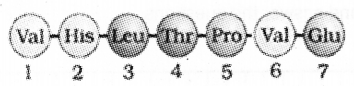
Question 18.
Diagram of components of DNA are given below: Identify and differentiate the two diagrams I and II. (MAY-2014)
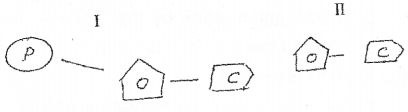
Answer:
I- Nucleotide II- Nucleoside
Question 19.
a) Identify the diagram and explain. (MAY-2014)

b) In same cases DNA is produced from RNA. Name this process and give example.
Answer:
a) Central Dogma in molecular biology
b) Reverse transcription
Question 20.
a) Define mutation. (MAY-2014)
b) What are the different types of mutation?
Answer:
a) Mutation is a phenomenon which results in alteration of DNA sequences and consequently results in changes in the genotype and the phenotype of an organism
b) physical mutation and chemical mutation
Question 21.
a) Paternity or maternity can be determined by certain scientific methods. What is it? Define. (MAY-2014)
b) Briefly write the* methodology involved in the technique.
c) Comment on its other applications.
Answer:
a) DNA fingerprinting. DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence
b) i) isolation of DNA
ii) digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases
iii) separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis
iv) transferring (blotting) of separated DNA fragments to synthetic membranes, such as nitrocellulose or nylon
v) hybridisation using labelled VNTR probe
vi) detection of hybridised DNA fragments by autoradiography
c) It is also used in forensic science
Question 22.
Fill in the blanks: (MARCH-2015)
a) _________is a metabolic disorder that occurs due to the lack of an enzyme, that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine.
b) _______is a disease caused by the substitution of Glutamic acid by valine at 6th position.
Answer:
a) Phenylketonuria
b) Sickle-cell anaemia
Question 23.
The flow of genetic information is shown below. Name the process of (a) and (b). (MARCH-2015)

Answer:
a) Trancription
b) Translation
Question 24.
Explain transcription. A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by three regions. Write the names of any two regions. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
Information contained in DNA is copied down to mRNA is called Transcription – Promoter and structural gene.
Question 25.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions: (MAY-2015)
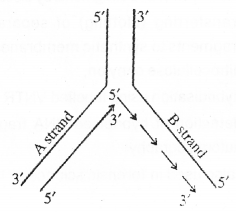
a) What is the difference in the replication processes in A strand and B strand?
b) What is the role of DNA ligase in the replication process in B strand?
c) What is meant by Replication fork?
Answer:
a) In A, replication is continuous and form leading strand but in B replication is discontinuous and form lagging strand.
b) In B, short stretch of Okazaki fragments are connected with the help of DNA ligase and form continuous strand
c) The replication occur within a small opening of the DNA helix, referred to as replication fork. It appears as Y shaped forked structure.
Question 26.
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions: (MAY-2015)
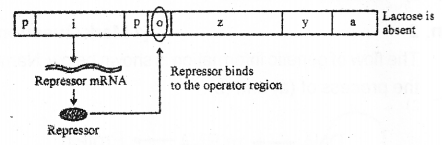
a) Diagrammatically represent the changes take place when lactose is added to the medium.
b) What is the role of z, y and a genes in this metabolic pathway?
Answer:
a)
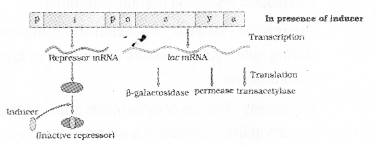
b) The z gene codes for beta-galactosidase which is responsible for the hydrolysis of the disaccharide, lactose into galactose and glucose. The y gene codes for permease, which increases permeability of the cell to beta-galactosides.The a gene encodes a transacetylase
Question 27.
Read carefully the sequence of codons in the mRNA unit and answer the questions. (MARCH-2016)

a) What change in needed in the first codon to start the translation process?
b) If translation starts by that change, till which codon it can continuous? Why?
Answer:
a) AUG is needed
b) UGA, Termination of translation occurs
Question 28.
Schematic representation of DNA fingerprints are shown below: (MARCH-2016)
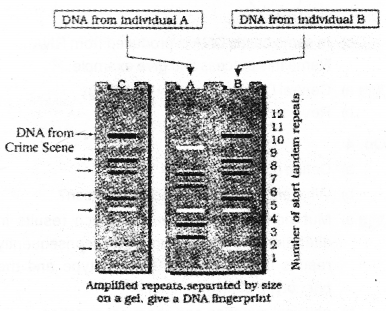
[Hints : C is a sample taken from a crime scene, A and B from two suspected individuals]
a) Which one of the suspected individual may involved in the crime?
b) Write any other use of DNA fingerprinting.
Answer:
a) suspected person is B
b) disputed parentage determining population and genetic diversities.
Question 29.
Observe the figure of mRNA and answer the questions: (MAY-2016)

a) Find the start and stop codons.
b) How many amino acids will be present in the protein translated from this mRNA?
c) The additional sequences that are not translated in mRNA are called _______.
Answer:
a) Start codon – AUG
Stop codon – UAG
b) 4
UTR- Untranslated region
Question 30.
a) The hints of the lac operon is given below: (MAY-2016)
Hints:
Inducer, Repressor,
Structural genes, operator Regulatory gene
i) Which substance is acting as inducer in this operon?
ii) Explain the working of operon in presence of the inducer.
OR
b) With the help of the figure given, explain the processing of hnRNA to mRNA in eukaryotes.
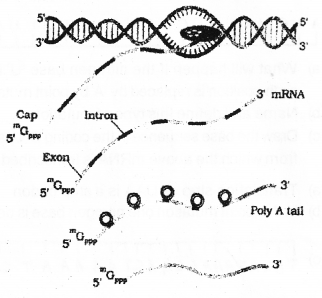
Answer:
a) i) lactose inducer
ii) If lactose is present in a medium, it has to be breakdown into glucose and galactose,for this positive control of operon works and structural genes transcribe. The switch on condition of operator gene is due to the binding of RNA polymerase with promotersite. In +ve control, repressor from regulator gene is inactivated due to the presence of lactose.
OR
b) 1) Splicing-the introns are removed and exons are joined together.
2) capping -methyl guanosine triphosphate is added to the 5-end of hnRNA.
3) Tailing- adenylate residues (200-300) are added at 3-end in a template
After these three process, fully processed mRNA is released from nucleus into cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
Question 31.
Examine the following fragment of beta globin chain in human haemoglobin and identify the hereditary disease with reason. (MARCH-2017)
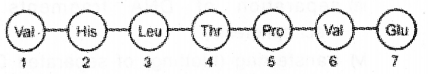
Answer:
Sickle cell anaemia
The defect is caused by the substitution of Glutamic acid by Valine at the sixth position of the beta globin chain of the haemoglobin molecule The mutant haemoglobin molecule under low oxygen tension causing the change in the shape of the RBC from biconcave disc to elongated sickle like structure.
Question 32.
Which of the following combinations do not apply to DNA? (MARCH-2017)
a) Deoxyribose, Guanine
b) Ribose, Adenine
c) Deoxyribose, Uracil
d) Guanine, Thymine
1) (a) and (b)
2) (b) and (c)
3) (c) and (d)
4) (a) and (d)
Answer:
2) b) and c)
Question 33.
Examine the diagram of mRNA given below. Mark the ‘5’ and ‘3’ ends of the mRNA by giving reasons. (MARCH-2017)
![]()
Answer:
Polyadynilation always at 3′ end of m RNA ,so the other must be 5′ end.
Question 34.
A small fragment of skin of a different person was extracted from the nails of a murdered person. This fragment of skin led the crime investigators to the murderer. Based on this incident answer the following questions: (MARCH-2017)
1) What technique was used by the investigators?
2) What is the procedure involved in this technique?
OR
In an E. coli culture lactose is used as food instead of glucose. If so, answer the following questions:
1) How do the bacteria respond to the above situation at genetic level?
2) If lactose is removed from the medium what will happen?
Answer:
1) DNA finger printing
2) The technique, is based on following procedure
i) isolation of DNA,
ii) digestion of DNA by restriction endonucleases,
iii) separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis,
iv) transferring (blotting) of separated DNA fragments to synthetic membranes, such as nitrocellulose or nylon,
v) hybridisation using labelled VNTR probe, and vi) detection of hybridised DNA fragments by autoradiography
OR
In this closely associated genes function as unit called operon If lactose is present in a medium, it has to be breakdown into glucose and galactose ,for this positive control of operon works and structural genes transcribe with the help of switch on condition of operator gene. This is due to binding of RNA polymerase on promoter site of DNA.
Question 35.
Find the odd one and write the common feature of others. (MAY-2017)
Cytidine, Adenine, Thymine, Guanine.
Answer:
Cytidine, All others are nitrogen bases.
Question 36.
Observe the diagram: (MAY-2017)
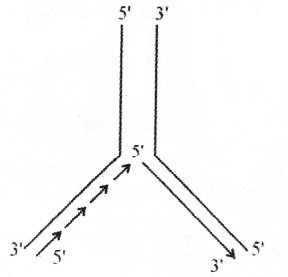
a) Redraw the diagram correctly if any mistake is there.
b) What does the diagram indicate?
c) What is the function of DNA ligase in this process?
Answer:
a)
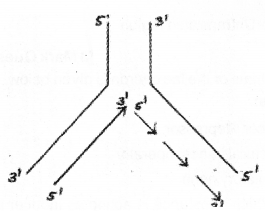
b) Replication fork.
c) Discontinuously synthesised fragments of DNA are joined by DNA ligase.
Question 37.
Read the codon sequence in the mRNA unit which is undergoing translation. (MAY-2017)
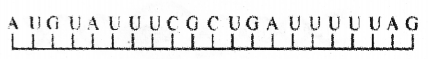
a) What will happen if the nitrogen base ‘U’ in the sixth position is replaced by ‘A’ by point mutation?
b) Name and define this type of mutation.
c) Draw the base sequence in the coding DNA strand from which the above mRNA is transcribed.
Answer:
a) Translation stop as UAA is a stop codon.
b) In this point mutation one nitrogen base is deleted.
c)