Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Question 1.
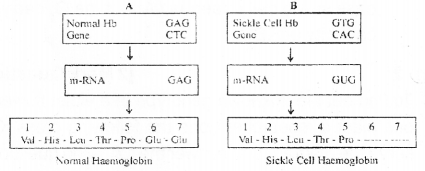
Polypeptide chains of two haemoglobin molecules are shown below. One of the chains shows an abnormality. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions. (MARCH-2010)
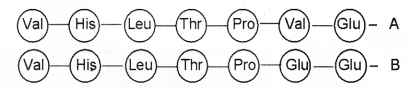
a) Which of the polypeptide chain in haemoglobin is abnormal leading to a disease?
b) What is the reason for this abnormality?
c) What will be the effect of this change in polypeptide chain?
Answer:
a) A
b) Substitution of glutamic acid by valine in the 6th position of polypeptide chain.
c) The RBC become sickle shaped causing a disease sickle cell anaemia / Affect the o2 carrying capacity of RBC.
Question 2.
To find out the unknown genotype of a violet flowered pea plant a researcher done the following cross. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions: (Hint: Violet flower colourin pea plant is dominant over white). (MARCH-2010)
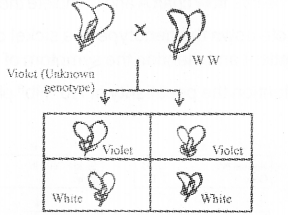
a) What would be the above cross called?
b) Can you determine the unknown genotype of violet flowered parent by drawing Punnet square?
Answer:
a) Test cross
b)
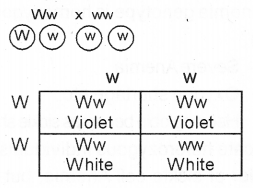
Genotype of unknown parent Ww/ Heterozygous.
Question 3.
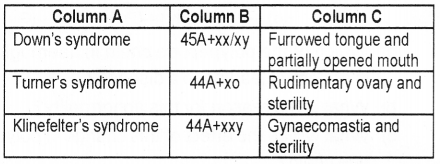
Some genetic abnormalities, their genotypes and features are distributed in columns A, B and C respectively. Match them correctly. (MAY-2010)

Answer:
Question 4.
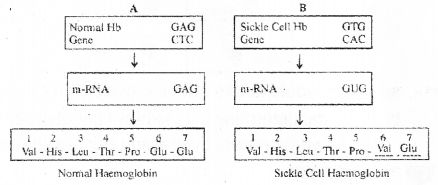
The flow charts A and B given below represents the inheritance of normal haemoglobin and sickle cell haemoglobin: (MAY-2010)
a) Observe flow chart A and complete the flow chart B.
b) Note down the genotype of a sickel cell anaemia patient and mention the symptom of the disease.
c) Mention the peculiarity of HbA Hbs phenotype.
Answer:
a)

b) Sickle cell Anemia genotype is homozygous for Hbs (HbsHbs).
Symptoms
SevereAnemia
Oxygen shortage etc.
Haemoglobin becomes sickle shaped.
c) HbA Hbs indicate heterozygous individuals, who are the carrier of sickle cell Anemia, but unaffected ones.
Question 5.
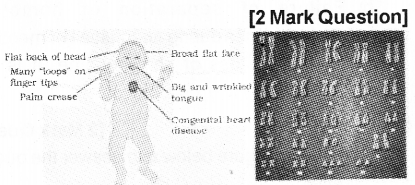
After analyzing’the karyotype of a short statured round headed person with mental retardation, a general physician noticed an addition of autosomal chromosome. (MARCH-2011)
Answer the following questions.
a) Addition or deletion of chromosome generally results in ______
b) What may be the possible syndrome or disorder of the above person should suspected to be?
c) Suggest two / more morphological peculiarities to confirm the chromosome disorder in that person.
Answer:
a) Aneuploidy / Chromosomal disorders/ Chromo-somal abberrations/Chromosomal mutations.
b) Down’s syndrome / Mongolism / Trisomy 21st / 45A + xx / xy.
c) Furrowed tongue, partially opened mouth, Broad palm, Skin fold at the corner of the eye.
Two correct points.
Question 6.
The frequency of occurrence of Royal disease or . haemophilia is high in the pedigree of royal families of Queen Victoria. Which of the following cannot be generally inferred from this? (MARCH-2011)
a) Queen Victoria was not homozygous forthe disease.
b) Many heterozygous females were there in the Royal families.
c) Non-Royal families were not affected with haemophilia.
d) There is less possibility to become a female diseased.
e) Generally a diseased female cannot survive after the first menstruation.
f) Pedigreee analysis is the study of inheritance patterns of traits in human females.
Answer:
‘C’ and ‘f ’ c1 non royal families were not affected with haemophilia.
f2 Pedegree analysis is the study of inheritance pattern of traits in human females.
Question 7.
A couple have two daughters. The blood group of husband and wife is ‘O’ (MARCH-2011)
a) What is the possible blood groups of the children should have?
b) Whether any change in blood group will occur if they have two sons instead of daughters.
Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
a) O group
b) No.
There is no sex specificity in blood group alleles / Co-dominance / Homozygous recessive . Not related to sex chromosomes or autosomes /
Question 8.
Complete the table using suitable terms. (MARCH-2012)
Turner’s syndrome (a) ______ Sterile female
(b) __________44A + XXY (c) _________
(d) __________ Trisomy 21 Mental retardation
Answer:
a) 44A + X0
b) Klinefelters Syndrome
c) Sterile male
d) Down’s Syndrom
Question 9.
In pea plant the gene for yellow seed colour is dominant over green and round seed shape is dominant over wrinkled. Write the four types of gametes formed in a heterozygous pea plant with yellow and round seeds. (Yy Rr).
Answer:
YR Yr yR yr
Question 10.
The first child of a couple is affected with phenylketonuria. During the second pregnancy they visited a genetic counsellor and he prepared a pedigree chart of their family. (MARCH-2012)
a) What is pedigree analysis?
b) Draw the symbols for
i) Affected female.
ii) Sex unspecified.
iii) Consanguineous mating.
Answer:
a) It is the study of inheritance of a trait for several generation of a family.
b)

Question 11.
Diagrammatic representation of chromosome map of Drosophila is given below: (MARCH-2012)
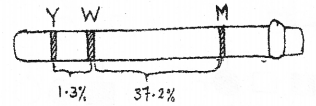
Y – Yellow
W – White
M – Miniature
a) Which genes are more linked?
b) Who mapped the chromosome firstly?
c) Tightly linked genes show low recombination. Why?
Answer:
a) y and w
b) Alfred Sturtevant
c) Crossing over rarely takes between genes
Question 12.
Work of a student is given below: (MAY-2012)
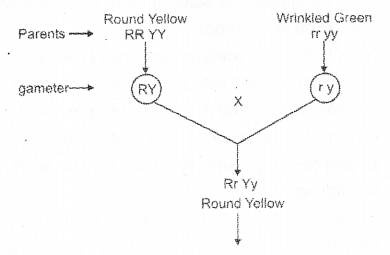
a) From the above give an example for genotype and phenotype.
b) Complete the work’using punnett square and find out the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation.
Answer:
a) First filial generation Genotype-RrYy,Phenotype- round yellow

Question 13.
Identify the traits from the pedigree chart. Give one example each. (MAY-2012)
Answer:
a) Autosomal dominant trait
Eg. Muscular dystrophy
b) Autosomal recessive trait
Eg. Sickle cell anaemia
Question 14.
A poultry farm manager was cursing his hens for producting lion share of cocks in its progeny. Hearing this, Kumar – farm attender starts to blame his wife for delivering consecutive girl children. Analyze the situtations scientifically and state whether you agree with kumar. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
No, During spermatogenesis two types of gametes are produced of which 50 per cent carry the X- chromosome and the rest 50 per cent has Y- chromosome besides the autosomes. Females produce only one type of ovum with an X- chromosome.
In case the ovum fertilises with a sperm carrying X- chromosome the zygote develops into a female (XX) and with Y-chromosome results into a male offspring. Thus the genetic makeup of the sperm that determines the sex of the child.
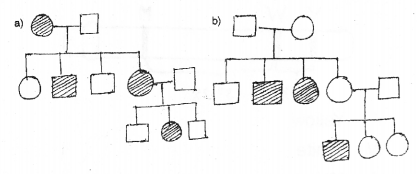
Question 15.
In the given pedigree the shaded figures denote individuals expressing a specific trait. (MARCH-2013)
Which of the following is the most probable mode of inheritance of this trait.
Answer:
Principles of inheritance & Variation
A – Simple Mendelian Recessive
B – Co dominant relationship of a single pair of alleles.
C- X – linked recessive transmission
D – X- linked dominant transmission
E – Polygenic inheritance.
X-Linked recessive transmission
Question 16.
“Gopalan argues that if father is of A’ blood group, mother is of ‘B’ blood group. Their children can only be A’ group, B group or AB’ group.” (MARCH-2014)
a) Do you agree with Gopalan’s Argument ?
b) Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
a) No ,All groups are possible including O group
b) 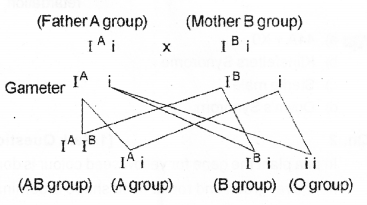
Question 17.
Identify the syndrome from the genotype given below: (MAY-2014)
1) 44 Autosomes + XXY
2) 44 Autosomes + XO
Answer:
1) Klinefelters syndrome
2) Turners syndrome
Question 18.
The family of Queen Victoria shows a number of haemophilic descendants as she was the carrier of the disease. Name the pattern of inheritance of this royal disease. (MAY-2014)
Answer:
Sex linked inheritance .
The heterozygous female (carrier) for haemophilia may transmit the disease to sons.
(Criss cross inheritance)
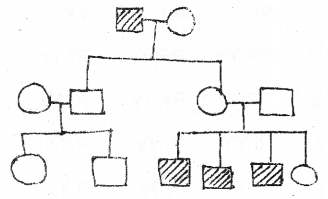
Question 19.
a) Identify the syndrome from the diagram, and write the genotype. (MARCH-2015)
b) It occurs in both sexes (male and female)? Write the reason.
Answer:
a) Downs syndrome , 45 A+XX or 45A+XY
b) The cause of this genetic disorder is the presence of an additional copy of the chromosome number 21 (trisomy of 21).
Question 20.
It is evident that, it is the genetic make up of the sperm that determine the sex of the child in human beings. Substantiate. (MARCH-2015)
Answer:
During spermatogenesis among males, two types of gametes are produced. 50% of the total sperm produced carry the X-chromosome and the rest 50 per cent has Y-chromosome besides the autosomes. In case the ovum fertilises with a sperm carrying X- chromosome the zygote develops into a female (XX) and the fertilisation of ovum with Y-chromosome carrying sperm results into a male offspring. Hence the genetic makeup of the sperm that determines the sex of the child.
Question 21.
Diagrammatic representation of the pedigree analysis of the inheritance of sickle cell anaemia is shown below: (MAY-2015)
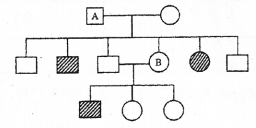
a) Name the type of inheritance shown in the figure.
b) Write the genotype of A and B.
(Hint: Disease is controlled by a pair of alleles HbA & Hbs)
Represent pedigree analysis of an X-linked recessive inheritance diagrammatically.
Answer:
a) Mendalian inheritance
b) A-HbA Hbs B- HbA Hbs
Question 22.
Observe the inheritance shown in A (MAY-2015)
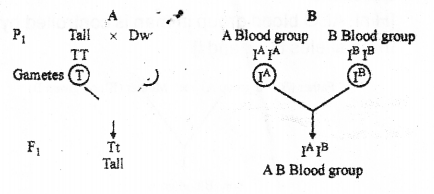
a) Name the type of inheritance shown in A and B.
b) What is the difference between the two types of inheritance.?
Answer:
a) A- Dominance B-Co dominance
b) In dominance , dominant gene mask the expression of recessive gene and tall character in F1 progenies but in co dominance both dominant gene express together and shows AB blood group.
Question 23.
Results of a famous experiment is given in the figure. Answer the questions. (MARCH-2016)
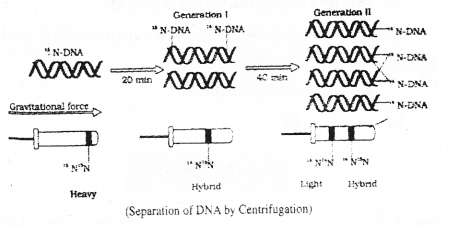
a) Identify the experiment.
b) Which property of the DNA is proved by this experiment?
Answer:
a) Semiconservative DNA replication experiment
b) During DNA replication one parent strand is conserved
Question 24.
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder? (MARCH-2016)
i) Colourblindess
ii) Down’s syndrome
iii) Haemophilia
iv) Thalassemia
Answer:
ii) Down’s syndrome
Question 25.
Study the following cross and answer the questions. (MARCH-2016)
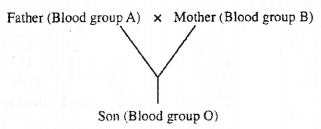
[Hint: ABO blood group in man is controlled by three alleles IA, IB, and i]
a) Write the geno types of Father, Mother and Son.
b) The type of dominance of human blood group inheritance is ________.
Answer:
Father-IA i or i i Mother-IB or i i Son-i i
Question 26.
Observe the figures and answer the questions. (MARCH-2016)
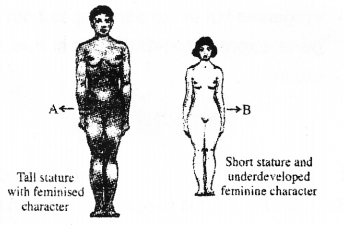
a) Identify the syndromes A and B.
b) What is the chromosome numbers in A and B?
Answer:
a) A-KlinefelterSyndrome;
B- Turner’s Syndrome
b) A-47 B-45
Question 27.
a) Complete the flow chart of chromosomal disorder by filling the blank boxes (A and B). (MAY-2016)
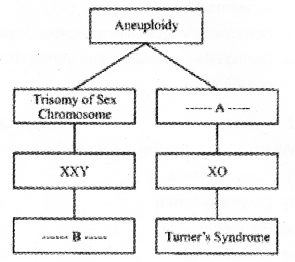
b) What is an euploidy?
Answer:
a) A-monosomy of sex chromosome B – Klinefelters syndrome
b) Failure of separation of homologous chromosomes during anaphase I of meosis lead to gain or loss of chromosome, it is called aneupoidy.
Question 28.
Observe the figure below and answer the questions following: (MAY-2016)
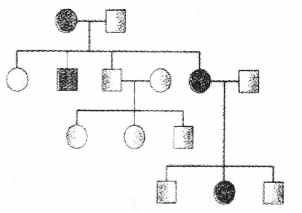
a) Identify the figure
b) What shows the shaded symbols used?
Answer:
a) Pedigree analysis or Autosomal dominant trait
b) Individuals with genetic disorder (male and female)
Question 29.
The following table shows the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross, identify the ‘Phenotype’ with homozygous recessive genotype.(MARCH-2017)
Find out A : B : C : D.
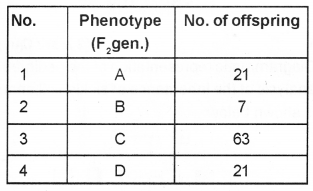
Answer:
B , Genotype A: B:C:D: = 3:1:9:3 OR 9:3:3:1
Question 30.
Which of the following do not have similar sex chromosomes? (Homogametic) (MARCH-2017)
a) Human female
b) Drosophila female
c) Bird female
d) Bird male
Answer:
c) Bird female
Question 31.
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions: (Hint: Steps in making a cross in pea plant) (MAY-2017)
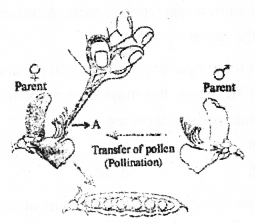
a) Name the process marked as A and write its significance.
b) Diagrammatically represent a monohybrid cross between Tall and dwarf pea plants.
Answer:
a) Removal of anthers from female plants
Significance –It prevents self pollination and fertilization
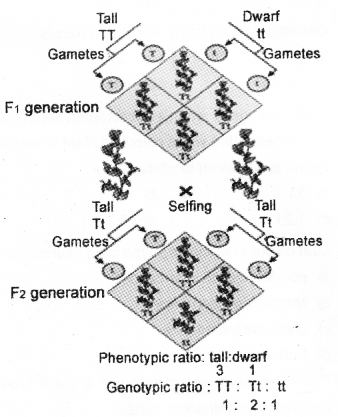
Question 32.
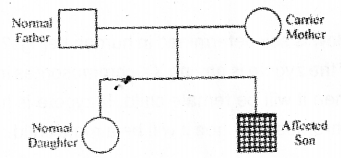
Observe the diagrammatic representation of the following pedigree analysis and answer the questions (MAY-2017)
a) Describe the type of inheritance shown in the diagram.
b) Distinguish between Mendelian disorder and chromosomal disorder with example.
Answer:
a) Sex linked inheritance
b) Mendelian disorder is determined by mutation in the single gene.
These disorders are transmitted to off springs in the same line as the principles of inheritance.
