Kerala Plus Two Zoology Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 Human Reproduction
Question 1.
Given below is the diagrammataic representation of human blastocyst. Observe the diagram and answer the following questions: (MARCH-2010)
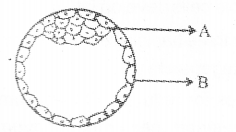
a) Identify A and B
b) Write the functions of A and B.
Answer:
a) A – Inner cell mass, B – Trophoblast
b) A – Differentiate into embryo germ layers/gastrula B – Attachment to endometrium / form different embryonic membranes/ placenta formation/ nutritional supply.
Question 2.
When the urine sample of a lady is tested, presence of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is detected. (MARCH-2010)
a) What does the presence of HCG indicate?
b) Which is the source of HCG?
Answer:
a) Pregnancy
b) Placenta
Question 3.
The graph shown below shows the levels of LH and FSH at various stages of menstrual cycle. (MAY-2010)
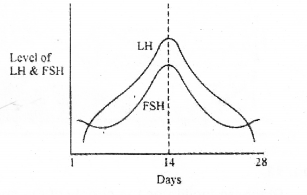
a) Name the source of LH and FSH.
b) The level of LH is maximum during the middle day of the cycle. Mention its effect.
c) Note the function of LH in males.
Answer:
a) Pituitary gland
b) Helps for ovulation
c) Stimulates the synthesis of horrnones (androgens)
Question 4.
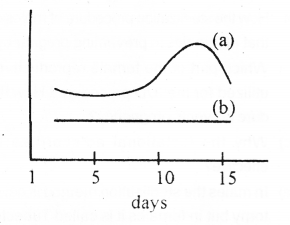
The above graph shows the level of ovarian hormones in a normally menstruacing woman during the follicular phase. (MARCH-2011)
a) Name ‘a’ and ‘b’
b) Mention the role of pituitary hormones in maintaining this condition.
c) Reconstruct the graph for Luteal phase.
Answer:
a) i) Estrogens
ii) Progesterone
b) FSH / Follicle stimulating Hormone, LH / Luteinizing Hormone
OR
Gonadotropins
One function each of FSH and LH.
c)
Question 5.
Some stages of the embryonic development are given below. Observe these diagrams and answer the questions. (MAY-2011)
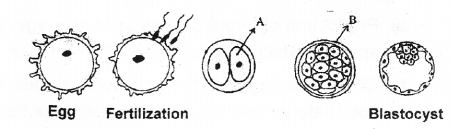
a) What is A & B?
b) Name thetwo types of cells found in the blastocyst.
c) Which layer of blastocyst is attached to the endometrium? And name that process.
Answer:
a) A – Blastomere B – Morula
b) Trophoblast and inner cell mass
c) Trophoblast, Implantation
Question 6.
Observe the diagram provided (Do not copy the picture) (MARCH-2012)
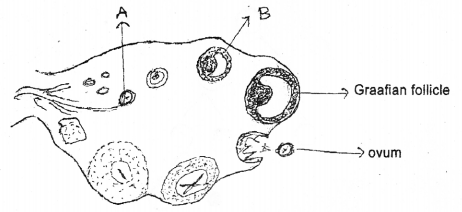
a) Label A and B
b) On which day of menstrual cycle Graafian follicle rupture.
c) Name the process induces the rupture of Graafian follicle.
d) Write the name and function of the structure forming inside the ovary after the rupture of Graafian follicle.
Answer:
a) A – Primary follicle B – Tertiary follicle
b) 14th day
c) The rupture of Graafian follicle and the release of ovum is called ovulation.
d) The corpus luteum secretes large amounts of progesterone which helps in the maintenance of the endometrium.
Question 7.
The following statements compares the process of oogenesis and spermatogenesis. Which one is not true? (MAY-2012)
a) Production of ovum ceases at certain age, but sperm production continues even in old men.
b) Oogenesis begins in the embryonic stages, but spermatogenesis starts at the onset of puberty.
c) Meiotic arrest occurs both in Oogenesis and spermatogenesis.
d) Polar bodies are formed in oogenesis.
Answer:
a) Replication
b) Transcription
c) Translation
d) Reverse transcription
Question 8.
The diagram represents a process of gametogenesis. Closely observe it and answer the following (MARCH-2013)
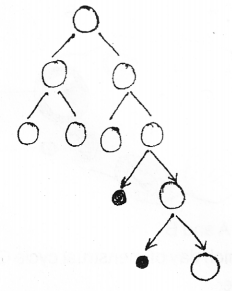
Is it spermatogenesis or Oogenesis?
What does the smaller shaded circle represent? Write down two significance of production of the same.
Answer:
a) oogenesis
b) polar bodies
c) Retention of cytoplasm in ovum Maintaining one functional haploid ovum
Question 9.
Though one ovum is produced from a primary oocyte it can result into a male or female child after fertilization. But in the case of spermatocyte though 4 sperms are produced only two of them can result to a female child after fertilization”. Justify. (MARCH-2013)
Answer:
Two types of sperms are produced one with x chromosomes and other withy chromosome. Sperm with x chromosome after fertilization results in the formation of female baby
Question 10.
Sterilization and IUDS are effective birth control measures, but lactational amenorrhea may not be so effective. (MAY-2013)
a) How the sterilization procedure of males differ from that of females in preventing pregnancy?
b) Which part of the female reproductive organ is utilized for the IUD procedure? How this procedure prevents pregnancy?
c) Why the lactational amenorrhea is not so effective?
Answer:
a) In males the sterilization method is called vasectomy but in females it is called Tubectomy
b) uterus, lUDs suppresses sperm motility and fertilizing capacity of sperm or they make uterus unsuitable for implantation.
c) During intense lactation, menstrual cycle does not occur. Therefore the chance of conception is almost nil. But the method is effective only upto six months following delivery
Question 11.
Observe the diagram, and answer the questions: (MARCH-2013)
a) Identify A and B.
b) What is the function of C ?
c) In which of the marked part reduction division takes place? What is the significance of it?
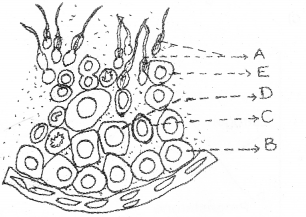
Answer:
a) A – Spermatozoa, B-Primary spermatocyte
b) Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
c) Primary spermatocyte, chromosome number reduced to half
Question 12.
Diagram of a mammalian sperm’is given. Label the parts marked. (MAY-2014)
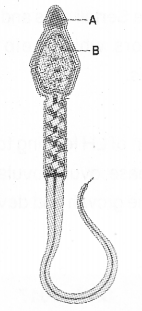
Answer:
A – Acrosome
B – Nucleus containing chromosomal material
Question 13.
Schematic representation of gametogenesis is given below. Identify A. Write one difference between A& B. (MARCH-2015)
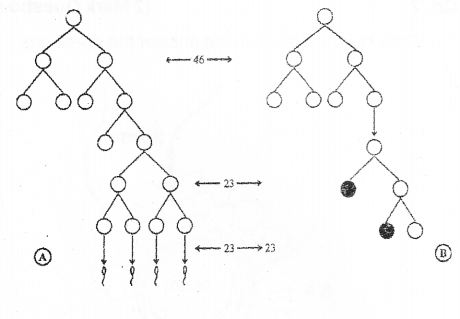
Answer:
A) Spermatogenesis – It results 4 spermatozoa
B) Oogenesis – It results one ovum and polar body
Question 14.
1) In which part of the human reproductive system the following events occur? (MARCH-2015)
a) Fertilisation
b) Implantation
2) Diagram of a human biastocyst is given below. Identify A & B.
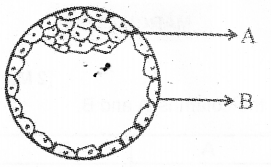
Answer:
a) ampullary-isthmicjunction
b) Endometrium of the uterus
A – inner cell mass
B – trophoblast
Question 15.
Choose the odd one from the following and write the common feature of others; (MAY-2015)
a) Estrogen
b) Androgen
c) Relaxin
d) Progesterone
Answer:
Androgen.
Others are ovarian hormones.
Question 16.
Complete the flow chart showing spermatogenesis by filling A and B and answer the questions: (MAY-2015)
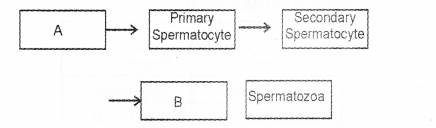
a) What is the chromosome number of primary spermatocyte
b) What is the significance of reduction division in spermatocyte?
Answer:
A- Spermatogonia
B- Spermatids
a) Primary spermatocyte-Diploid number, in man it is 23 pair, spermatids-haploid number, in man it is 23
b) Reduction division helps to reduce chromosome number as half in gametes (haploid).
It helps keep chromosome number species as constant for many generations.
Question 17.
Match the columns A and B: (MARCH-2016)
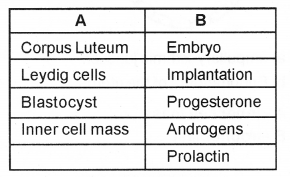
Answer:
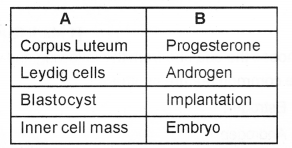
Question 18.
The process of fusion of a sperm with ovum is called _______. (MAY-2016)
Answer:
Fertilisation
Question 19.
Match columns A and B. (MAY-2016)
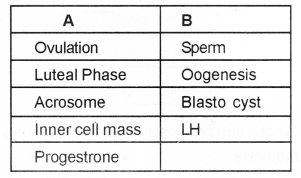
Answer:
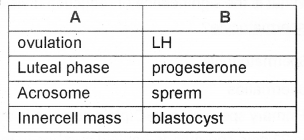
Question 20.
LH and FSH are gonadotrophins. Distinguish their roles in males and females. (MARCH-2017)
Answer:
LH acts at the Leydig cells and stimulates synthesis and secretion of androgens.
Androgens stimulate the process of spermato-genesis.
FSH acts on the Sertoli cells and stimulates secretion of some factors which help in the process of spermiogenesis.
Female Rapid secretion of LH leading to rupture of Graafian follicle and release ovum (ovulation). FSHhelpsinthe growth and development of ovarian follicle.
Question 21.
Human female possess 44 + XX chromosome number. The chromosome number of secondary oocyte is (MAY-2017)
a) 44 + X
b) 22 + X
c) 44 +XX
d) 22 +XX
Answer:
b) 22 + X
Question 22.
Observe the diagram and answer the questions: (MAY-2017)
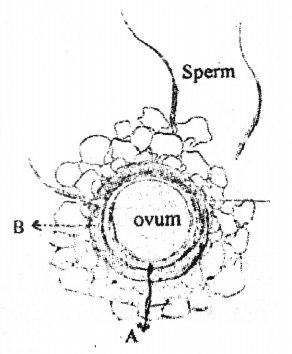
a) Identify A and B
b) Write the function of B.
Answer:
a) A – peri vitelline space
B- zona pellucida
b) Prevent the entry of further sperms after fertilization
