Kerala Plus Two Political Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 4 India’s External Relations
Question 1.
Write true’ or ‘false’ against each of these statements.
a) Non- alignment allowed India to gain assistance both from USA and USSR.
b) India’s relationship with her neighbours has been strained from the beginning.
c) The cold war has affected the relationship between India and Pakistan.
d) The treaty to peace and Friendship in 1971 was the result of India’s closeness to USA.
Answer:
a. true b. false c. true d. false
Question 2.
Match the following.
| A | The goal of India’s foreign policy in the period 1950 -1964 | i | Tibetan spiritual leader who crossed over to India |
| B | Panchsheel | ii | Preservation of territorial integrity, sovereignty and economic development |
| C | Bandung Conference | iii | Five principles of peaceful coexistence |
| D | Dalai Lama | iv | Led to the establishment of NAM |
Answer:
a – ii
b – iii
c – iv
d – i
Question 3.
One Article in the Indian constitution gives it an international character. It declares our commitment to protect international peace and security. Identify the Article.
a) Article 32
b) Article 21
c) Article 51
d) Article 72
Answer:
c) Article 51
Question 4.
The first Non-Aligned summit was held in 1961 at (Bandung, Belgrade, Beijing)
Answer:
Belgrade
Question 5.
We had signed some important treaties with China and Pakistan. Arrange the data provided in the following table.
| Treaty | Leader of India | Leader of Pakistan / China |
| Panchseel | Indira Gandhi | Ayub Khan |
| Tashkent Agreement | Jawaharlal Nehru | Zulphikar Ali Bhutto |
| Shimla Agreement | Lai Bahadur Sastri | Chou En Lai |
Answer:
| Treaty | Leader of India | Leader of Pakistan / China |
| Panchseel | Jawaharlal Nehru | Chou En Lai |
| Tashkent Agreement | Lai Bahadur Sastri | Ayub Khan |
| Shimla Agreement | Indira Gandhi | Zulphikar Ali Bhutto |
Question 6.
The friendship among three international personalities led to the formation of NAM. Identify them.
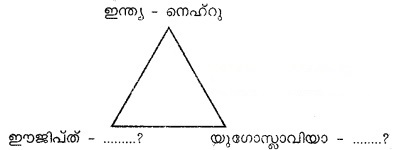
Answer:
Egypt – Nasser
Yugoslavia-Tito
Question 7.
The five legs of the following star represent ‘Big Five’ countries. Try to fill the blanks
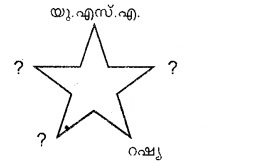
Answer:
China, France, England
Question 8.
In 1957 the Tibetan spiritual leader crossed the Chinese border and came to India. It was a landmark in the Indo Sino relation. Identify the Person.
Answer:
Dalai Lama
Question 9.
The following are the major revolutions that took place in different countries of the world. Chronologically arrange them.
| a | 1688 | 1 | Chinese Revolution |
| b | 1773 | 2 | American Revolution |
| c | 1789 | 3 | Glorious Revolution |
| d | 1917 | 4 | Russian Revolution |
| e | 1949 | 5 | French Revolution |
Answer:
a. Glorious Revolution
b. American Revolution
c. French Revolution
d. Russian Revolution
e. Chinese Revolution
Question 10.
After colonial administration, India was divided into India and Pakistan. In 1971 Pakistan was further divided into Pakistan and Bangladesh. These three countries consider three persons as the fathers of these countries. Identify them.
Answer:
India – Mahatma Gandi
Pakistan – Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Bangladesh – Mujibur Rehman
Question 11.
India conducted two nuclear explosions during 1974 and 1998. identify the code names given to these explosions.
| Year | Code Name |
| 1974 | |
| 1998 |
Answer:
1974-Buddha Laughs
1998 – Operation Shakti
Question 12.
Two personalities are associated with the concept of cold war. One person is Bernard Baruch, and then who is the other person?
Answer:
Walter Lippmann
Question 13.
The boundary line between India and Pakistan is . ‘Radcliffe Line’. Identify the boundary line between India and China?
a) Durand Line.
b) 17th Parallel
c) Mac Mohan Line
d) Demarcation Line
Answer:
c) Mac Mohan Line
Question 14
Match the columns.
| A | B | C |
| Bharathiya Kisan union | Caste system | Mahendra Singh Tilkayat |
| Chipko movement | Sardar Sarovar project | Maharastra |
| Narmada Bhachao Andolan | Meerut Agitation | Sundar Lai Bhahuguna |
| Dalit Panthers | Uttarakhand | Medha Patkar |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Bharathiya Kisan union | Meerut Agitation | Mahendra Singh Tilkayat |
| Chipko movement | Uttarakhand | Sundar Lai Bhahuguna |
| Narmada Bhachao Andolan | Sardar Sarovar project | Medha Patkar |
| Dalit Panthers | Caste system | Maharastra |
Question 15.
“Foreign policy means the policy which a nation follows while maintaining her relation with other nations”. So the foreign policy of any country is influenced by international environment. India’s foreign policy was also influenced by the international environment in which India got independence. Can you identify the international conditions in which we evolved our foreign policy?
Answer:
The world was going through very difficult circumstances when India got her freedom. This situation has influenced our foreign policy. Five factors have influenced our foreign policy in a greater measure.
- The II World War and the rebuilding after that.
- The efforts to form an international organization.
- The emergence of many small nations at the end of colonialism.
- The challenges the new Nations faced for democracy and welfare.
- The Cold War between America and Russia because of ideological differences.
Question 16.
The Directive Principles of State Policy provided Indian constitution an international character. As a student who learned Directive Principles of State Policy, can you mention the provisions of Directive Principles of State policies that gave our constitution an international character?
Answer:
Article 51 of our Constitution gives importance to international peace and security. It states that India Government:
- will encourage international peace and security.
- will maintain cordial relations between nations.
- will respect all the international laws, treaties and organizations.
- will try to solve international disputes through mediation.
Question 17.
Jawaharlal Nehru is the architect of India’s foreign policy. He played a major role in fostering Afro Asian unity. Find out the important contributions of India to Afro-Asian Unity.
Answer:
Nehru was a chief spokesperson of Afro-Asian unity. Under his leadership, in March 1947, there was an Asian Relations Conference. It supported the freedom struggle of Indonesia. India made great efforts to free Indonesia from the hands of the Dutch. For this purpose in 1949 an international conference was summoned.
India was also against the apartheid policy of South Africa. The Conference that held in the Indonesian city of Bandung, is known as the Bandung Conference. The intervention of India helped many African and Asian nations to get their freedom from their colonial masters. This Conference later proved to be the starting point of the Non-Aligned Policy.
Question 18.
“A country without material, men or money-the three means of power is now fast coming to be recognized as the biggest moral power in the civilized world…. Her word is listened to with respect in the councils of the great’. So India is developed as a major power in international politics. Can you give a brief note about the development of India’s foreign policy?
Answer:
The Indian National Movement was a protest against colonialism and imperialism. It helped other Asian and African nations to fight for their freedom and against colonialism and imperialism. Our leaders got into contact with the leaders of other Afro-Asian nations and together they formulated a policy against colonial rule.
The foreign policy of a country depends on the internal and external factors prevalent in the country. The ideas and goals of the Freedom Movement have influenced our foreign policy. India got freedom when the Cold War was going on between Russia and America at the political, economic and military levels. It was around this time that the United Nations was born. The use of atomic weapons began just a little before this period. Therefore it was necessary to formulate a foreign policy in keeping with the interests of the nation. The following 3 things were important in formulating such a policy.
a. The role of Nehru:
Nehru was the Prime Minister and Foreign Minister of India from 1946 to 1964. He had a big role in the formulation of our foreign policies. He followed a policy which was conducive to the maintenance of our sovereignty, protection of our boundaries, our unity and our economic growth. It was with all these in his mind, he became one of the chief architects of the Non-Aligned Policy.
b. Keeping equidistance from both the superpowers. As the Cold War was going between the superpowers, we wanted world peace. For that we:
- continued with our non-aligned policy.
- tried to reduce the tension of the Cold War.
- supplied manpower for the peaceful missions of the United Nations.
As a newly independent country, India could not claim any big political power. Therefore India decided to keep away from the on-going Cold War between the superpowers. The Non-Aligned Policy helped us to do that It was difficult for India to maintain this non-aligned stance always. When the British attacked Egypt and Russia attacked Hungary, we could not stick with our non-aligned stand. But in many international problems India maintained an independent stand. India received help both from the USA and also Russia on different occasions.
c. Afro-Asian Unity:
Another factor that influenced the foreign policy of India was Afro-Asian Unity. Nehru maintained good relations with different Asian and African leaders. In March’1947, the Asian Relations Conference was summoned. Through this, India raised her voice against colonialism and apartheid. The Bandung Conference paved the way for the formulation of the Non-Aligned Movement. Indo-China Relations: In the beginning the relations between India and China were cordial. There is a
historical and cultural background.to that. Nehru played a big role in maintaining the good relationship. India was the first country to recognize China after the Chinese Revolution. Nehru did his best to help China to come out of the Western shadow. He helped China in many international matters. Because of the cordial relations, on the borders between India and China only paramilitary personnel, not army, were deployed.
The Panchsheel Agreement (25 April 1954) between the PMs of India and China were a big landmark. The PMs exchanged visits and received the love and respect from the people. Nehru had cordial relations with China. But people like Vallabhbhai Patel were not sure if the Chinese could be trusted so much. But Nehru never thought the Chinese would attack India. But in 1962, Nehru was proved wrong when the Chinese attacked us.
Chinese Attack in 1962:
Two things spoiled the good relationship between India and China. One was the Tibetan Issue and the other was boundary dispute. Even in the 1950s, when India had good relations with China the boundary disputes existed. China was not ready to accept our views and suggestions regarding the boundaries. The main dispute was about the boundary in the West and East. China claimed the Ladakh Region of Jammu and Kashmir and many areas of Arunachal Pradesh.
Between 1957-59, the Chinese occupied the Aksai-Chin sector and built the Karakoram Highway. There were letters between leaders, but nothing positive happened. The second issue was Tibet. In 1950, China annexed Tibet. It was a breach of trust. In the beginning India did not object to it. But it could not continue to maintain its silence as the Chinese tried to impose their culture on the Tibetans. In 1959, the Dalai Lama, the spiritual leader of the Tibetans, sought refuge in India. Then the Chinese started accusing us of anti Chinese activities. In October 1962, the Chinese army infiltrated into areas of dispute.
The attacks lasted a week. The Chinese army occupied some important places in Arunachal Pradesh. The next series of attacks came the following month. But the Indian Army stopped the Chinese on the western side of Ladakh. But in the East they were able to come up to4he Assam Plain. Then they announced a unilateral ceasefire and retreated from the occupied lands.
After-effects of the Indo-Chinese war:
During The War, Russia kept neutrality. So India had to seek military help from the USA and Britain. The war was a shame to the country. But it fortified our national feeling. After the war, many top military officers resigned. Nehru’s close friend and the then Defence Minister V.K Krishna Menon, had to resign. Nehru was criticized for his blind faith in China and for not being militarily ready to counter the attacks.
A No Confidence Motion was brought against him. Many discussions took place in the Parliament. Congress was defeated in many by elections to the Lok Sabha The War affected even the Opposition. In 1964, the Communist Party split as Pro-Chinese and Pro- Russian. The group that leaned towards Congress was CPI and the group with the Pro-China stand was CPI(M).
The War brought caution among the leaders The north Eastern areas were backward. The War forced the country to embark upon projects to protect its unity and also to make economic progress in the country.
Indo-Pak Relations:
It can be said that Pakistan is the closest, and at the same time, the farthest neighbour of India. Pakistan is close to India historically, geographically and culturally. But when it comes to democracy, outlook on religion, and mutual understanding, Pakistan is the farthest neighbour.
The good aspects of Indo-Pak Relations:
Both countries worked together to rehabilitate the women kidnapped during the division of the country. An understanding was negotiated through the mediation of the World Bank for sharing river water. The leaders of both countries cooperated in the Agra Summit. Although it proved to be a failure in the end, it gave some hope for the future.The cricket diplomacy reduced the tension between the two countries.
During the time of Atal Bihari Bajpai in India and Musharaf in Pakistan, there were bus and train services between the two countries. Although the above things are good, for quite some time serious disputes have been going on between the two neighbours. The first dispute is in the case of Kashmir. Even in 1947 itself there was a clash between Indian and Pakistani soldiers.
Since was Impugn wefore the United Nations, it did not develop into a full-scale war. With that Pakistan became a decisive factor in our relations with America and China.In 1965, Pakistan madean armed attack in the Rann of Kutch in Gujarat. Later in August arid September, Pakistani army attacked Kashmir.
The Pakistan government expected the Kashmiri people to support them but it did not happen. Then Lai BhadurSastri ordered the Indian army to attack Pakistan from the Punjab border. The army came close to Lahore. Then, there was a treaty between India and Pakistan, signed by Satri of India and Ayub Khan of Pakistan. This was the Tashkent Agreement. For Pakistan this war caused a huge military loss. Our financial situation also went bad.
In 1970, Pakistan faced a lot of internal problems. During the first election in West Pakistan the Party of Zulfikar AN Bhutto got the majority. But in East Pakistan, the Awami League led by MujiburRehman got the majority. The East Pakistanis wanted to be free from West Pakistan. They thought that they were treated as second class citizens. The rulers of West Pakistan were not willing to recognize the Awami League or respect the verdict of the people.
In 1971, the West Pakistani army arrested Mujibur Rehman and threatened the people of East Pakistan. The people there wanted their own separate country called Bangladesh. Because of the repressive measures by the Pakistani government, India had to accommodate some 80 lakh refugees. India . supported the demand for Bangladesh. Pakistan accused India of aiding East Pakistan.
In the circumstances, America and China supported . Pakistan and thus the three countries were against India. In 1971, India signed a Peace arid Friendship Treaty for 20 years with the Soviet Union. According to this Treaty, if India was attacked by any country, Russia would come to her assistance.
In 1971 Pakistan attacked Punjab, Rajasthan and Jammu-Kashmir. Indians attacked Pakistan from the East and West simultaneously. With popular support, the Indian army surrounded Dhaka from three sides. In 10 days the Pakistani army surrendered. With the freedom of Bangladesh, India declared a unilateral ceasefire. The war ended. Indira Gandhi and Zulfikar AN Bhutto signed the Shimia Agreement on 3 July 1972.
Another big problem was the Kargil Issue. The Indian army reported that many parts of the Line of Control were occupied by Mujahidins, India felt that Pakistan had a hand in this and it also started behaving in that manner. This resulted in a controversy between the two countries. On 26 July 1999, India recaptured some of the places occupied by the Mujahidins. As both countries had atomic weapons, this issue captured world attention. But the dispute limited itself to the Kargil area. General Musharaf recalled the Pakistani army from there.
There are still many disputes between India and Pakistan. One of them is regarding terrorist attacks. The attacks on the Parliament and Mumbai worsened the relations between the two countries. Recently Pakistan made some moves against the terrorists there. It is hoped that such actions will bring peace to the Asian mainland.
Question 19.
India is always against armament race particularly nuclear armament race. But at the very same time India refused to sign NPT or CTBT Is it found contradictory? Mention your opinion about India’s Nuclear policy.
Answer:
India supports non-proliferation of atomic weapons. It believes that atomic power should be used only for peaceful purposes. In 1974, India tested its first atomic device.Nehru believed that what modern India wanted was scientific and technological growth, in 1940, under Homi. J. Bhabha India embarked on an atomic scheme. India wants atomic power only for peaceful purposes. Nehru was against atomic weapons. Therefore he requested the big powers to disarm.
But the collection of atomic weapons was increasing. In 1968, the five major atomic powers tried to bring a treaty which prohibited the use of atomic weapons. It is called the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT). But India refused to sign it saying that it was discriminatory in nature. When India tested its first atomic device, its intention was peaceful. India asserts that atomic power should be used only for peaceful purposes. whereas it denies non-atomic powers to make any tests, thus preventing them from developing atomic power even for peaceful purposes.
Additional Question
Question 1.
What is Kargil war? What were its consequences?
Answer:
in the early years of the 1990s, a group calling itself Mujahidins forcefully occupied many parts of the Line of Control. The areas they ocupied included Dras, Kaksara and Batalik. In India it was believed that this occupation was with the knowledge of the Pakistani authorities. So India reacted and this brought about the Kargil War.
This happened in May-June 1999. By 26 July, 1999, the Indian Army was ableto take control of ail the illegally occupied places by the Mujahidin. Following this war, the Pak Commander-in-Chief of the Army, General Parvez Musharaf, staged a coup d’etat and became the ruler of Pakistan.
Question 2
Describe the difference between Neutrality and Non Alignment.
Answer:
There are some major differences between Neutrality and
Non-Alignment.
- Neutrality is relevant only when there is a war. But Non-Alignment is relevant both in the times of war and also peace.
- Neutrality is used in international laws. But the term Non-Alignment is used in the mutual relations between countries. Neutrality would mean keeping away. But Non-Alignment does not mean keeping away from something. There is inclusion in Non-Alignment.
Question 3.
India conducted first nuclear explosion in
Answer:
May 1974
Question 4.
Write a short note on India’s Nuclear Policy.
Answer:
India is against the testing of atomic weapons for warlike purposes. India stands for complete disarmament within the framework of the United Nations. Even then India refuses to sign the NPT. It is so because India thinks NPT is discriminatory. It allows the atomic powers to make further tests.
