Plus Two Physics Notes Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction is part of Plus Two Physics Notes. Here we have given Plus Two Physics Notes Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Physics Notes |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 |
| Chapter Name | Electromagnetic Induction |
| Category | Plus Two Kerala |
Kerala Plus Two Physics Notes Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
Introduction
In this chapter we are going to discuss the laws governing electromagnetic induction; how energy can be stored in a coil, the generation of ac, the relation between voltage and current in various circuit components, and finally the working of the transformer.
The Experiments Of Faraday And Henry
Faraday and Henry conducted a series of experiments to develop principles of electromagnetic induction.
Experiment – 1
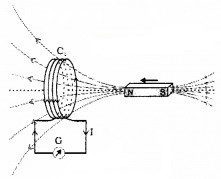
Connect a coil to a galvanometer G as shown in the figure. When the north pole of a bar magnet is pushed towards the coil, galvanometer shows deflection. The deflection indicates that a current is produced in the coil.
The galvanometer does not show any deflection when the magnet is held stationary. When the magnet is pulled away from the coil, the galvanometer shows deflection in the opposite direction.
Conclusion of experiment 1:
The relative motion between magnet and coil produces an electric current in the first coil.
Experiment 2
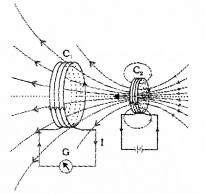
Connect a coil C1 to a galvanometer G. Take another coil C2 and connect it with a battery. A steady current in the coil produces a steady magnetic field. When the coil C2 is moved towards the coil C1, the galvanometer shows a deflection. This deflection indicates that the electric current is induced in the coil G.
When the coil C2 is moved away, the galvanometer shows a deflection in the opposite direction. When the coil C2 is kept fixed, no deflection is produced in the coil C1.
Conclusion of Experiment – 2:
The relative motion between two coils induces an electric current in the first coil.
Experiment – 3
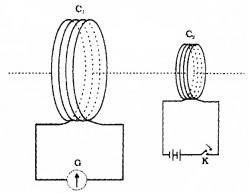
In this experiment coil C1 is connected to galvanometer G. The second coil C2 is connected to a battery through a key K.
When the key K is pressed, the galvanometer shows a deflection. If the key is held pressed continuously, there is no deflection in the galvanometer. When the key is released, a momentary deflection is observed again, (but in opposite direction).
Conclusion of experiment – 3:
The change in current in second coil induces a current in the first coil.
Magnetic Flux
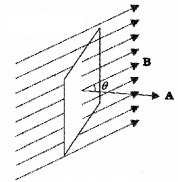
Magnetic flux through a plane of area A placed in uniform magnetic field B can be written as
![]()
Φ = BAcosθ
Faraday’S Law Of Induction
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction states that the magnitude of the induced emf in a circuit is equal to the time rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.
Mathematically, the induced emf is given by
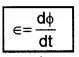
If the coil contain N turns, the total induced emf is given by,
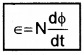
Lenz’S Law And Conservation Of Energy
Lenz’s law:
Lenz’s law states that the direction emf (or current) is such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux which produces it,
Mathematically the Lenz’s law can be written as
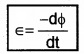
The negative sign represents the effect of Lenz’s law. The magnitude of the induced emf is given by Faraday’s law. But Lenz’s law gives the direction induced emf.
Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law of conservation of energy.
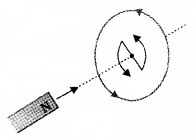
When the north pole of the magnet is moved towards the coil, the side of the coil facing north pole becomes north as shown in above figure. (Current is produced in the coil and flows in an anticlockwise direction).
So work has to be done to move a magnet against this repulsion. This work is converted into electrical energy.
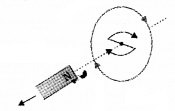
When the north pole of the magnet is moved away from the coil, the end of the coil facing the north pole acquires south polarity. So work has to be done to overcome the attraction. This work is converted into electrical energy. This electrical energy is dissipated as heat produced by the induced current.
Motional Electromotive Force
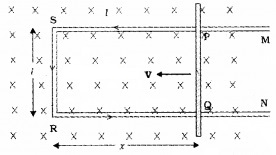
Consider a rectangular frame MSRN in which the conductor PQ is free to move as shown in figure. The straight conductor PQ is moved towards the left with a constant velocity v perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. PQRS forms a closed circuit enclosing an area that change as PQ moves. Let the length RQ = x and RS = I.
The magnetic flux Φ linked with loop PQRS will be BIx.
Since x is changing with time the rate of change of flux Φ will induce an e.m.f. given by
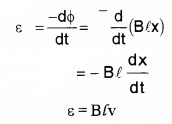
Energy Consideration: A Quantitative Study
Let ‘r’ be the resistance of arm PQ. Consider the resistance of arm QR, RS, and SP as zero. When the arm is moved,
The current produced in the loop,
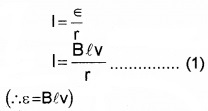
This current flows through the arm PQ. The arm PQ is placed in a magnetic field. Hence force acting on the arm,
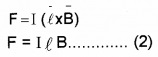
Substituting eq. (1) in eq. (2)
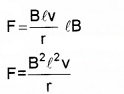
If this arm is pulling with a constant velocity v, the power required for motion P = Fv
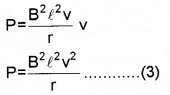
The external agent that does this work is mechanical. Where does this mechanical energy go?
This energy is dissipated as heat. The power dissipated by Joule law,
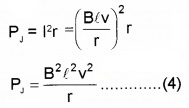
From eq. (3) and (4), we can understand that the workdone to pull the conductor is converted into heat energy in conductor.
Relation between induced charge and magnetic flux:
We know
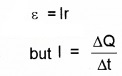
so the above equation can be written as
![]()
We also know magnitude of induced emf
![]()
Comparing (1) and (2), we get
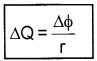
Eddy Currents
Whenever the magnetic flux linked with a metal block changes, induced currents are produced. The induced currents flow in closed paths. Such currents are called eddy currents.
Experiment to Demonstrate Eddy Currents
Experiment -1
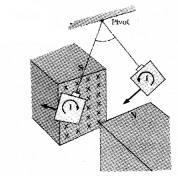
Allow a rectangular metal sheet to oscillate in between the pole pieces of strong magnet as shown in figure. When the plate oscillates, the magnetic flux associated with the plate changes. This will induce eddy currents in the plate. Due to this eddy current the rectangular metal sheet comes to rest quickly.
Experiment – 2
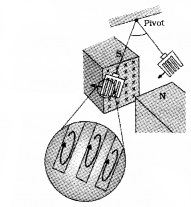
Make rectangular slots on the copper plate. These slots will reduce area of plate. Allow this copper plate to oscillate in between magnets. Due to this decrease in area, the eddy current is also decreased. Hence the plate swings more freely.
Some important applications of Eddy Currents:
1. Magnetic braking in trains:
Strong electromagnets are situated above the rails. When the electromagnets are activated, eddy currents induced in the rails. This eddy current will oppose the motion of the train.
2. Electromagnetic damping:
Certain galvanometers have a core of metallic material. When the coil oscillates, the eddy currents are generated in the core. This eddy current opposes the motion and brings the coil to rest quickly.
3. Induction furnace:
Induction furnace can be used to melt metals. A high frequency alternating current is passed through a coil. The metal to be melted is placed in side the coil. The eddy currents generated in the metals produce heat, that melt it.
4. Electric power meters:
The metal disc in the electric power meter (analogue type) rotates due to the eddy currents. This rotation can be used to measure power consumption.
Inductance
An electric current can be induced in a coil by two methods:
- Mutual induction
- Self-induction
1. Mutual inductance:
Mutual induction:
The phenomenon of production of an opposing e.m.f. in a circuit due to the change in current or magnetic flux linked with a neighboring circuit is called mutual induction.
Explanation
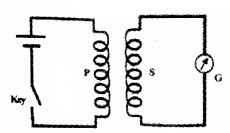
Consider two coils P and S. P is connected to a battery and key. S is connected to a galvanometer. When the key is pressed, a change in magnetic flux is produced in the primary.
This flux is passed through S. So an e.m.f. is produced in the ‘S’. Thus we get a deflection in galvanometer. similarly, when key is opened, the galvanometer shows a deflection in the opposite direction.
Mutual inductance or coefficient of mutual induction:
The flux linked with the secondary coil is directly proportional to the current in the primary
i.e. Φ α I Or Φ = MI
Where M is called coefficient of mutual induction or mutual inductance.
If I = 1, M = Φ
Hence mutual inductance of two coils is numerically equal to the magnetic flux linked with one coil, when unit current flows through the other.
(i) Mutual inductance of two coils:
Expression for mutual inductance:
Consider a solenoid (air core) of cross-sectional area A and number of turns per unit length n. Another coil of total number of turns N is closely wound over the first coil. Let I be the current flow through the primary. Flux density of the first coil B= µ0nI
Flux linked with second coil, Φ = BAN
Φ = µ0nIAN _____(1)
But we know Φ = MI _______(2)
From eq(1) and eq(2), we get
∴ MI = µ0nIAN
M = µ0nAN
If the solenoid is covered over core of relative permeability µr
then M = µrµ0nAN
Relation between induced e.m.f. and coefficient of mutual inductance:
Relation between induced e.m.f and mutual inductance
We know induced e.m.f
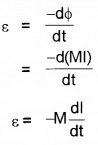
2. Self-inductance:
Self-induction
The phenomenon of production of an induced e.m.f in a circuit when the current through it changes is known as self-induction.
Explanation
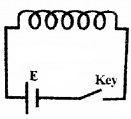
Consider a coil connected to a battery and a key. When key is pressed, current is increased from zero to maximum value. This varying current produces a changing magnetic flux around the coil. The coil is situated in this changing flux, so that an e.m.f. is produced in the coil.
This induced e.m.f. is produced in the coil. This induced e.m.f is opposite to applied e.m.f (E). Hence this induced e.m.f is called back e.m.f.
Similarly, when key is released, a back e.m.f is produced which opposes the decay of current in the circuit.
Thus both the growth and decay of currents in a circuit is opposed by the back e.m.f. This phenomenon is called self – induction.
Mathematical expression for self-inductance:
Consider a solenoid (air core) of length /, number of turns N and area cross-section A. let ‘n’ be the no. of turns per unit length (n = N/l)
The magnetic flux linked with the solenoid,
Φ = BAN
Φ = µ0nIAN (since B = µ0nI)
but Φ = LI
∴ LI = µ0nIAN
L = µ0nAN
If solenoid contains a core of relative permeability µr the L = µ0µrnAN.
Definition of self-inductance:
We know NΦ = LI
If I = 1, we get L = NΦ
Self-inductance (or) coefficient of self-induction may be defined as the flux linked with a coil, when a unit current is flowing through it.
Note: Physically, self-inductance plays the role of inertia.
The relation between induced emf and coefficient of self-induction:
When the current through a coil is varied, a back emf produced in the coil. Using Lens law, emf can be written as,
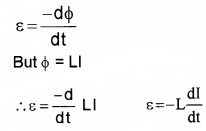
4. Energy stored in an inductor:
When the current in the coil is switched on, a back emf (ε = -Ldt/dt) is produced. This back emf opposes the growth of current. Hence work should be done, against this e.m.f.
Let the current at any instant be ‘I’ and induced emf
E = \(\frac{-\mathrm{d} \phi}{\mathrm{dt}}\)
i.e., work done, dw= EIdt
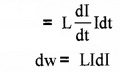
Hence the total work done (when the current grows from 0 to I0 is)
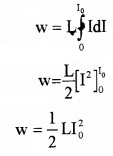
This work is stored as potential energy.
V = \(\frac{1}{2}\)LI2
Ac Generator
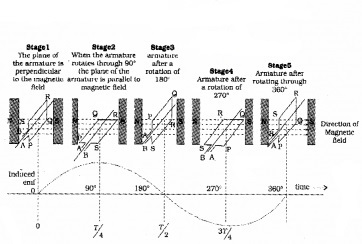
An ac generator works on electromagnetic induction. AC generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
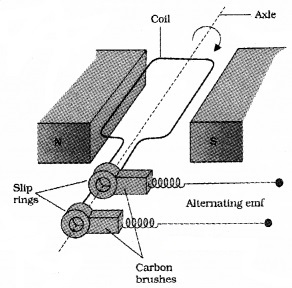
The structure of an ac generator is shown in the above figure. It consists of a coil. This coil is known as armature coil. This coil is placed in between magnets. As the coil rotates, the magnetic flux through the coil changes. Hence an e.m.f. is induced in the coil.
1. Expression for induced emf:
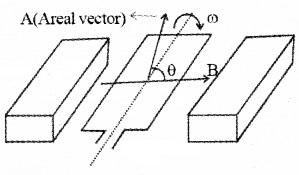
Take the area of coil as A and magnetic field produced by the magnet as B. Let the coil be rotating about an axis with an angular velocity ω.
Let θ be the angle made by the areal vector with the magnetic field B. The magnetic flux linked with the coil can be written as
![]()
Φ = BA cosθ
Φ = BA cosωt [since θ = ωt)
If there are N turns
Φ = NBA cosωt
∴ The induced e.m.f. in the coil,
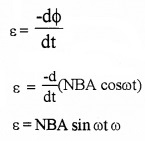
Let ε0 = NAB ω,
then s = ε0 sin ωt.
Expression for current:
When this emf is applied to an external circuit .alternating current is produced. The current at any instant is given by
I = \(\frac{V}{R}\)
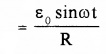
(V = ε0 sin ω)
I = I0 sin ωt
Where I0 = ε0/R, it gives maximum value of current. The direction of current is changed periodically and hence the current is called alternating current.
Variation of AC voltage with time:
We hope the Plus Two Physics Notes Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction help you. If you have any query regarding Plus Two Physics Notes Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
