Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Alternating Current is part of Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Alternating Current.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Physics Chapter Wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | Alternating Current |
| Category | Kerala Plus Two |
Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Alternating Current
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A 100Ω resistor is connected to a 220V, 50 Hz ac supply.
- What is the RMS value of current in the circuit?
- What is the net power consumed over a full cycle?
Answer:
Given R = 100Ω, Eν = 220V, ν = 50 Hz.
1. Since lν = Eν12
So lν = 220100 = 2.2 A
2. Paν = Eν Iν = 220 × 2.2
or Paν = 484 W.
Question 2.
- The peak voltage of an ac supply is 300V. What is the RMS voltage?
- The RMS value of current in an ac circuit is 10A. What is the peak current?
Answer:
1. Given E0 = 300 V, Eaν = ?
Since Eν = E0√2 = 0.707 × 300
or Eν = 212.1V.
2. Given Iν = 10A, I0=?
Since l0 = √2 Eν = 1.414 × 10
or I = 14.14 A.
Question 3.
A 44 mH inductor is connected to 220V, 50 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
Answer:
Given L = 44 mH = 44 × 10-3H
Eν = 220V, ν = 50Hz, Iν = ?
Since Iν = EνxL=220ωL
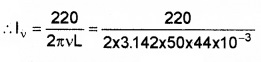
or Iν = 15.9A.
Question 4.
A 60µF capacitor is connected to a 110V, 60 Hz ac supply. Determine the RMS value of the current in the circuit.
Answer:
Given C = 60µF = 60 × 10-6F, Eν = 110V, ν = 60 Hz.
Since Iν = Eνxc
∴ Iν = ωCEν
= 2pνCEν = 2 × 3.142 × 60 × 60 × 10-6 × 110
= 2.49A or
Iν = 2.49V.
Question 5.
In Exercises 7.3 and 7.4, what is the net power absorbed by each circuit over a complete cycle. Explain your answer.
Answer:
In both cases, the net power consumed is zero because in both cases.
Net power consumed P = Eν lνcosΦ
and Φ =90°
∴ P = 0 (in each case).
Question 6.
Obtain the resonant frequency of a series LCR circuit with L=2.0H, C=32µV and R = 10?. What is the Q-value of this circuit?
Answer:
Given L = 2.0H, C = 32µF = 32 × 10-6F
R = 10Ω, Q = ?, ω0 = ?
Resonant frequency
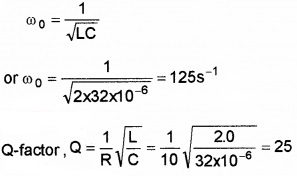
Question 7.
A charged 30µF capacitor is connected to a 27mH inductor. What is the angular frequency of free oscillations of the circuit?
Answer:
Given C = 30µF=30 × 10-6F,L = 27mH = 27 × 10-3H
ω0 = ?
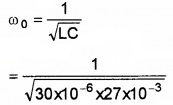
or ω0 = 1.1 × 10-3S-1.
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which type of transformer do you use to operate the coffee maker at 220 V?
Answer:
Step down transformer.
Question 2.
In an A C. circuit, Irms and Io are related as.

Answer:
(d) Irms = I0√2
Question 3.
A capacitor of capacitance C has reactance X. If capacitance and frequency become double then reactance will be
(a) 4X
(b) X/2
(c) X/4
(d) 2X
Answer:
(c) Explanation
![]()
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks
- Impedance: admittance
- ……………..: conductance
Answer:
Resistance
Question 5.
Why it is better to use an inductor rather than a resistor to limit the current through the fluorescent lamp?
Answer:
No power is developed across the inductor as heat.
Question 6.
In an a.c circuit with phase voltage V and current I, the power dissipated is
(a) V.l
(b) Depends on phase angle between V and I
(c) 12 × V.I
(d) 1√2
Answer:
(b) Depends on phase angle between V and I
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
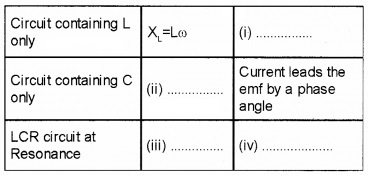
Answer:
(i) Current lags by π/2
(ii) Xc = 1/cω
(iii) R
(iv) Phase difference is zero.
Question 2.
A.C. adaptor converts household ac into low voltage dc. A stepdown transformer is an essential part of ac adapter.
- What is the use of a step-down transformer?
- What is the principle of a transformer? Explain.
Answer:
- To decrease voltage
- It works on the principle of mutual induction.
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match the following
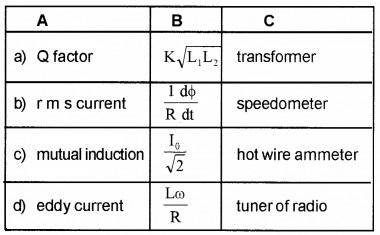
Answer:
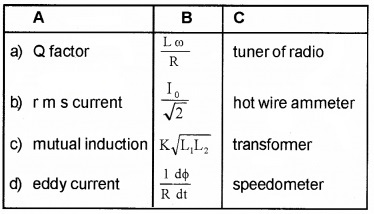
Question 2.
The following figure is a part of a radio circuit.
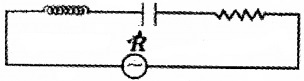
- Identify the circuit.
- What happens to this circuit if XL = XC
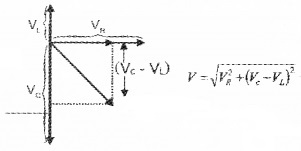
- lf XC > XL draw the phaser diagram.
Answer:
1. LCR circuit.
2. When XL = XC, the impedance of circuit becomes minimum and the current corresponding to that frequency is maximum.
3.
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Figure below shows a bulb connected in an electrical circuit.
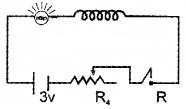
1. When the key is switched ON the bulb obtains maximum glow only after a shorter interval of time which property of the solenoid is responsible for the delay?
- Self-induction
- Mutual Induction
- Inductive reactance
- None of the above
2. If the flux linked with the solenoid changes from 0 to 1 weber in 2 sec. Find the induced emf in the solenoid.
3. If the 3v battery is replaced by an AC source with the key closed, what will be observed? Justify your answer.
Answer:
1. Self-induction.
2. dϕdt=12 = 0.5V.
3. When AC has connected the brightness of the bulb will be decreased. This is due to the back emf in the circuit.
Question 2.
A graph connecting the voltage generated by an a.c. source and time is shown.
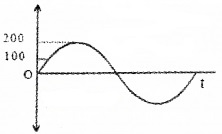
- What is the maximum voltage generated by the source?
- Write the relation connecting voltage and time
- This a.c. source, when connected to a resistor, produces 40J of heat per second. Find the equivalent d.c. voltage which will produce the same heat in this resistor.
Answer:
- 200v.
- V = V0sin ωt
- Vmax=V0√2=200√2 = 141.8v.
Question 3.
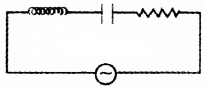
An inductor, capacitor, and resister are connected in series to an a.c. source V = V0sin ωt.
- Draw a circuit diagram of L.C.R. series circuit with applied a.c. voltage.
- Find an expression for impedance of L.C.R. series circuit using phasor diagram.
- What is impedance of L.C.R. series circuit at resonance?
Answer:
1.
2.
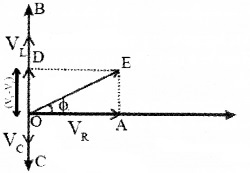
For impedance of LCR circuit.
From the right angled triangle OAE,
Final voltage, V = √v2n+(vL−vc)2
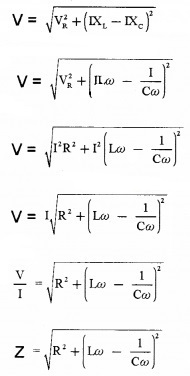
Where Z is called impedance of LCR circuit
3. Impedance, Z=R.
Question 4.
A voltage source is connected to an electrical component X as shown in the figure.
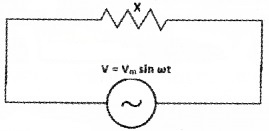
1. Identify the device X.
2. Which of the following equations can represent the current through the circuit?
- i = im sin(ωt + π/2)
- i = im sin(ωt – π/2)
- i = im sin ωt
- i = im sin(ωt + π/4)
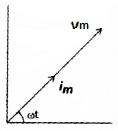
3. Draw the phasor diagram for the circuit. (2)
Answer:
1. Resistor
2. i = im sin ωt
3.
Question 5.
A friend from abroad presents you a coffee maker when she visited you. Unfortunately, it was designed to operate at 110V line to obtain 960W power that it needs.
- Which type of transformer you use to operate the coffee maker at 220V? (1)
- Assuming the transformer you use as ideal, calculate the primary and secondary currents. (2)
- What is the resistance of the coffee maker? (1)
Answer:
1. Step down transformer.
2. Since the transformer is ideal
VpIp = Vs Is = 960W, Vp = 220v, Vs = 110v
VpIp =960
![]()
3.
![]()
Plus Two Physics Alternating Current Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The voltage-current values obtained from a transformer constructed by a student is shown in the following table.
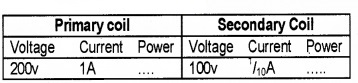
- Identify the transformer as step up or step down.
- How much power is wasted by the transformer?
- What are the possible energy losses in a transformer?
- If the input voltage is 48v and input current is 1 A, is it possible to light 240v, 100w bulb using the above transformer. Justify.
Answer:
1. Step down transformer.
2. Power loss = 200w -10w = 190w
3. The possible energy losses in a transformer:
- Eddy current loss
- Copper loss
- Hysterisis loss
- Flux leakage
4. In this case input power = VI = 48 × 1 = 48W.
If the transformer does not waste energy, input power = output power.
Hence maximum output power 48W. But bulb requires 100w. Hence the bulb does not glow with this low input power.
Question 2.
The current through fluorescent lights are usually limited using an inductor.
- Obtain the relation i = im sin(ωt – π/2)for an inductor across which an alternating emf v = vm sin ωt is applied. (2)
- Why it is better to use an inductor rather than a resistor to limit the current through the fluorescent lamp? (1)
- When 100 V DC source is connected across a coil a current of 1 A flows through it. When 100V, 50 Hz AC source is applied across the same coil only 0.5 A flows. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the coil. (2)
Answer:
1. AC voltage applied to an Inductor
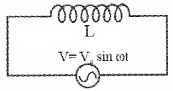
Consider a circuit containing an inductor of inductance ‘L’ connected to an alternating voltage. Let the applied voltage be
V = V0 sinωt…………(1)
Due to the flow of alternating current through coil, an emf, LdIdt is produced in the coil. This induced emf is equal and opposite to the applied emf (in the case of ideal inductor).
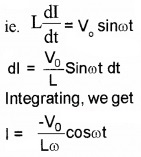
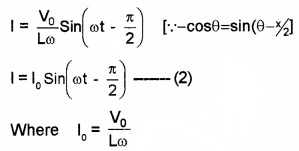
2. No power is developed across the inductor as heat.
3. Resistance of the coil R = vI=1001 = 100Ω. Current through the coil when ac source is applied.
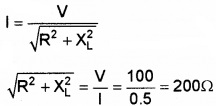
R2 + X2L = 2002
X2L = 2002 – 1002
XL = 173.2Ω
Lω = 173.2
![]()
Question 3.
An alternating voltage is connected to a box with some unknown circuital arrangement. The applied voltage and current through the circuit are measured as v = 80 sinωt volt and i = 1.6 sin(ωt + 45°) ampere.
- Does the current lead or lag the voltage?
- Is the circuit in the box largely capacitive or inductive?
- Is the circuit in the box at resonance?
- What is the average power delivered by the box?
Answer:
1. Leads.
2. Capacitive
3. No Hint: Current and voltage are not in the same phase.
4. P = VrmslrmsCosΦ, Vm = 80v, im = 1.6A
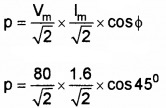
p = 45.25W
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Alternating Current help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 7 Alternating Current, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
