Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 Wave Optic is part of Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions and Answers Kerala. Here we have given Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Wave Optic.
Kerala Plus Two Physics Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 10 Wave Optic
Question 1.
Brewster’s law gives a relationship between angle of polarization and refractive index of the material, (March – 2010)
a) State Brewster’s law.
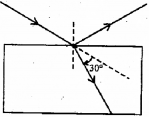
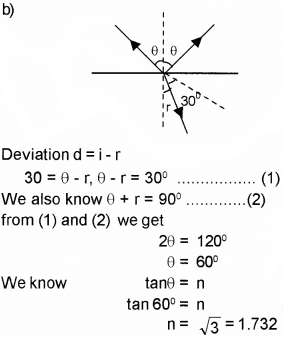
b) A ray of light is allowed to incident on the surface of a glass plate and it is found that the reflected and refracted rays are mutually perpendicular as shown in the figure. The refracted ray is deviated from its initial path by an angle of 30°.
Determine the refractive index of the glass plate.
Answer:
a) Tangent of polarising angle is equal to the refractive index of the material of the reflector,
Question 2.
a) What do you observe when a soap bubble or thin layer of oil on water is illuminated by white light? Why? (March – 2009)
b) When a tiny circular obstacle is placed in the path of light from a distance source, a bright spot is seen at the centre of the shadow of the obstacle. Explain why.
Answer:
a) Coloured fringes are observed. This is due to the interference of light waves reflected from the upper and lower layer surface of the thin film.
b) Waves diffracted from the edge of the circular obstacle interfere constructively at the centre of the shadow. This causes a bright spot.
Question 3.
In interference and diffraction of light, dark and bright bands are seen on the screen. (March – 2011)
a) Do these phenomena violate the law of conservation of energy? Explain.
b) In an interference pattern, the ratio of maximum intensity to minimum intensity is 36:9. Find the ratio of amplitudes and intensities of the two interfering waves.
Answer:
a) No. The energy lost in the dark band appears at bright band.
Maximum intensity lmax = (a – a2)2

Question 4.
Match the following : (March – 2012)
| A | B | C |
| i) Doppler ii) Maxwell iii) Rayleigh | Scattering Red shift Polarization Diffraction Electromagnetic waves | Theory of light Coherent sources Astigmatism Speed of Galaxies Blue colour of sky |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| i) Doppler ii) Maxwell iii) Rayleigh | Red shift EM waves Scattering | Speed of Galaxies Theory of light Blue colour of sky |
Question 5.
Wave nature of light is essential to explain phenomena like diffraction, interference etc. (Say – 2012)
a) What are the conditions to obtain a sustained interference pattern?
b) Obtain an expression for fringe width in Young’s double slit experiment.
Answer:
a) i) The two sources of light must be coherent.
ii) The amplitude of waves from two sources should preferably be equal.
iii) The two sources should preferably be monochromatic.
b) Refer 10.5 under the heading ‘Expression for bandwidth’.
Question 6.
Various phenomena exhibited by light can be explained using the wave theory of light (March – 2013)
a) Name the phenomenon which proves the transverse nature of light.
b) What are the differences between interference and diffraction?
Answer:
a) Polarisation
b) Interference
- Interference is due to the superposition of waves coming from two wavefronts.
- Interference bands are of equal width.
- Minimum intensity regions are perfectly dark.
- All the bright bands are of equal intensity.
Diffraction
- Diffraction is due to the superposition of waves coming from different parts of the same wave front.
- Diffraction bands are of unequal width.
- Minimum intensity regions are not perfectly dark.
- All bright bands are not of the same intensity.
Question 7.
Match the following: (Say – 2013)
| A | B | C |
| i) Thomas Young ii) Lord Rayleigh iii) Charles K Kao iv) Christian Doppler | Scattering Redshift Interference Polarisation Optical fibre Diffraction | Astronomy Communication Myopia Rainbow Coherent sources Colour of sky |
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| i) Thomas Young ii) Lord Rayleigh iii) Charles K Kao iv) Christian Doppler | Interference Scattering Optical fibre Red shift | Coherent sources Colour of sky Communication Astronomy |
Question 8.
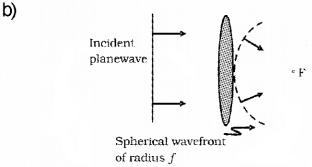
Wave front is a concept introduced by Huygens to explain various optical phenomena. (Say – 2013)
a) What type of wave front will emerge from
i) A point source and
ii) Distant souce of light?
b) A plane wave front is incident normally on a convex lens. Sketch the refracted wave front.
Answer:
a) (i) Spherical
(ii) Plane
Question 9.
a) Describe Young’s experiment in interference with necessary theory. (March – 2014)
b) Mention the shape of wave front for the portion of wave front of light from a distant star intercepted by the earth.
Answer:
a) Refer 10.5
b) Plane wave front
Question 10.
We obtained alternate dark and bright regions if we look at the shadow by an obstacle closed to geametrical shadow. (March – 2014)
a) Mention the phenomenon behind it.
b) Differentiate the interference pattern with a coherently illuminated single slit diffraction pattern.
Answer:
a) Diffraction
b) Refer March 2013, Question 1.b
Question 11.
Figure given below shows the arrangement to test the polarization of light wave (Say – 2014)
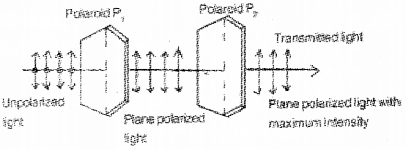
Draw a graph showing angular dependance of intensity of transmitted plane polarized light with second polaroid P2.
Answer:
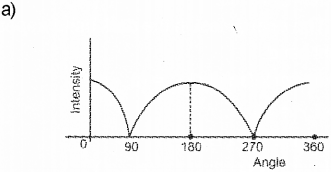
Question 12.
A) Interference of light from two sources can be observed if (March – 2015)
a) the sources are independent
b) the sources are different frequencies and random phases
c) the sources are of different frequency
d) the sources are coherent
B) Draw Young’s arrangement to produce interference pattern.
C) Derive an expression for the fringe width of interference pattern formed on the screen.
D) Write the condition to produce good interference bands.
Answer:
A) d
C) Refer 10.5 under the heading ‘Expression for band width’.
D) 1) Sources must be coherent.
2) Screen must be at large distance.
3) Sources must be close to each other.
Question 13.
A) The following questions has choice: (March – 2016)
a) Unpolarized light is incident on a plane glass surface. What should be the angle of incidence so that the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other? (Given n = 1.5)
OR
B) Light waves from two coherent sources having intensities I and 21 cross each other at a point with a phase difference of 600. What ¡s (he resultant intensity at the point?
Answer:

Question 14.
A) An interference and diffraction of light waves produce alternate dark and bright regions called fringes. (Say – 2016)
a) Regarding the fringe width choose the correct statement.
i) Interference fringes are of unequal width.
ii) Diffraction fringes are of same width.
iii) Interference fringes are of equal width and dif-fraction fringes are of different width.
iv) Both interference and diffraction fringes are of different width.
b) Using a schematic diagram derive an expression for the fringe width in Young’s double slit experiment.
B) Huygen’s principle help us to find the shape of a wave front emanating from a source.
a) The shape of the wave front originating from a tubelight is
(i) Plain
(ii) Circular
(iii) Cylindrical
(iv) Spherical
b) Give Huygen’sprincipIe with the help of a ray diagram. Prove the law of reflection.
Answer:
A) a) Diffraction fringes are of same width.
b) Refer 10.5 underthe heading ‘Expression for band width’.
B) a) Cylindrical
b) Referlo.3.2
Question 15.
Choose the wrong option. (March – 2017)
i) interference
ii) diffraction
iii) polarisation
iv) reflection
Answer:
v) Volt = Weber x Second
Question 16.
a) Sound waves do not exhibit (March – 2017)
i) interference
ii) diffraction
iii) polarisation
iv) reflection
b) Describe Young’s double-slit experiment to determine bandwidth of the interference pattern.
Answer:
a) (iii) Polarisation
b) Refer 10.5 under the heading ‘Expression for band width’.
Question 17.
Young’s double slit experiment is used to demonstrate interference of light. (Say – 2017)
a) In Young’s double slit experiments, 1 mm slit separation cwoduces a bandwidth of 0.6 mm on a screen placed at a certain distance away from the slits. When the screen is moved further away from the slits through 0.25 m, the bandwidth becomes 0.75 mm. Find the initial separation between slits and screen.
b) If one of the slits is closed still dark and bright bands are observed on the screen. This is due to
i) Interference
ii) Polarisation
iii) Reflection
iv) Diffraction
Answer:

We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Wave Optic help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Wave Optic, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest
