Kerala Plus Two Microeconomics Notes Chapter 6 Non-Competitive Markets
Introduction
There are three types of non-competitive markets such as:
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
ആമുഖം
മത്സര രഹിത വിപണികൾ മൂന്ന് വിധമുണ്ട്. അവ താഴെ പറയുന്നവ യാണ്.
- കുത്തക കമ്പോളം
- കുത്തക മത്സര കമ്പോളം
- ഒലിഗോപോളി
Price and output determination under non-competitive markets
Under inperfect competition price and output determination of a fim can be analysed in two different method
a) Total revenue and total cost approach
b) Marginal revenue and marginal cost approach
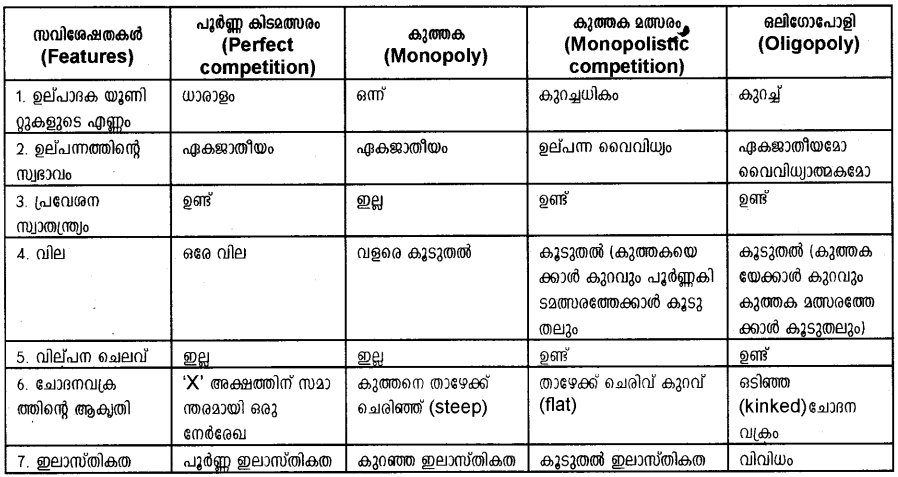
a) Under inperfect competition the relation between TR, MR and AR is given in the diagram below.
Firms under inperfect competition are price makers. In contrast to perfect competition they can sell more units only if they reduce the price. So total revenue which increases initially starts falling after reducing the maximum.
- When TR increases MR is positive and AR is price elastic.
- When TR is maximum MR is zero and the price elasticity of AR is -1.
- When TR is falling MR is negative and AR is price inelastic.
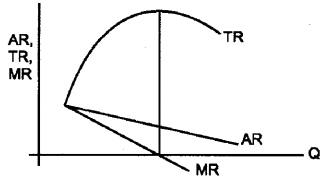
The profit of the firm will be maximised when the gap between TR and TC is maximum as shown in the diagram.
At q1 level of output the difference between TR and TC is maximum.
b) Marginal revenue and marginal cost approach. Just like in the case of perfect competition under unperfect competition firm will maximise their profit when MR = MC.
മത്സരരഹിത വിപണികളിൽ വില, ഉല്പാദനം എന്നിവയുടെ നിർണ്ണയം
മത്സരരഹിത വിപണികളിൽ ഉല്പാദന യൂണിറ്റുകളുടെ വില, ഉല്പാദന നിർണയം താഴെ പറയുന്ന രണ്ട് രീതിയിൽ, മൊത്തവ രവ്, മൊത്തച്ചെലവ് വകങ്ങൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച് അപഗ്രഥിക്കാം. അപൂർണ കിടമത്സരങ്ങളിലെ മൊത്ത വരവ്, സീമാന്ത വരവ് ശരാശരി വകങ്ങളും അവ തമ്മിലുള്ള ബന്ധവും ഡയഗ്രത്തിൽ കൊടുത്തിരിക്കുന്നു.
അപൂർണ കിടമത്സരത്തിലെ ഉല്പാദന യൂണിറ്റുകൾ വില നിർണ യിക്കുന്നവരാണ്. പൂർണ്ണ കിടമത്സരത്തിൽ നിന്നും വിഭിന്നമായി ഇവിടെ. ഉല്പാജന യൂണിറ്റുകൾക്ക് ഒരു യൂണിറ്റ് അധികം വിൽക്കണമെങ്കിൽ വില കുറച്ചേ മതിയാകു. അതിനാൽ ആദ്യം വർധിക്കുന്ന മൊത്ത വരവ് പരമാവധിയിലെത്തിയ ശേഷം കുറ യാൻ തുടങ്ങുന്നു.
- മൊത്തവരവ് വർധിക്കുമ്പോൾ സീമാന്ത വരവ് പോസിറ്റീവ് ആണ്. ചോദനം വില ഇലാസ്തികമാണ്.
- മൊത്ത വരവ് പരമാവധിയാകുമ്പോൾ സീമാന്ത വരവ് പൂജ്യവും ചോദന വകത്തിന്റെ ഇലാസ്തികത -1 ഉം ആണ്.
- മൊത്ത വരവ് കുറയുമ്പോൾ സീമാന്ത വരവ് നെഗറ്റീവാണ്. ‘ശരാശരി വരവ് (ചോദനം) കുറഞ്ഞ ഇലാസ്തികതയെ കാണി ക്കുന്നു.
ഉല്പാദന യൂണിറ്റുകളുടെ ലാഭം പരമാവധിയാക്കപ്പെടുന്നത് മൊത്ത വരവും മൊത്ത ചെലവും തമ്മിലുള്ള അകലം ഏറ്റവും കൂടുതൽ ഉള്ളിടത്താണ്.
ഒരു ഉല്പ്പാദന യൂണിറ്റ് q1 ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കും. കാരണം ആ ഉല്പന്നം ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കുമ്പോഴാണ് ഒരു ഉല്പാദന യൂണിറ്റിന്റെ ലാഭം പര മാവധിയാകുന്നത്.
b) സീമാന്ത വരവ്, സീമാന്തച്ചെലവ് വൃകങ്ങൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച്. പൂർണ്ണ കിടമത്സരത്തിലേതുപോലെതന്നെ അപൂർണ കിടമ ത്സരത്തിലും ഉല്പ്പാദന യൂണിറ്റുകൾ ലാഭം പരമാവധിയാ ക്കുന്നത് MR = MC ആകുമ്പോഴാണ്. ഇത് പിന്നീട് ചർച്ച ചെയ്യാം
Monopoly Market
Monopoly may be defined as a market situation in which there is only a single seller. He controls the entire market. The term monopoly has derived from two Greek words such as ‘mono’ means single and poly means ‘seller’. The meaning of the combined term is single seller. In a boarder sense, a monopolist is single seller of a commodity which does not have close substitutes. E.g. KSEB
Features of Monopoly Market:
Some of the salient features of monopoly are as follows:
- There is only a single firm producing the product
- There is no close substitute for the product
- Entry is denied for other producers
- Since there is only one seller, the firm and the industry are same
- The firm under monopoly is the price maker
കുത്തകമത്സരം
ഒരു വിൽപ്പനക്കാരൻ മാത്രം നിയന്ത്രണാധികാരമുള്ള കമ്പോള അവസ്ഥയാണ് കുത്തക കമ്പോളം (Monopoly market). ‘മോണോ ‘ (Single – ഒന്ന്), “പോളി’ (Seller – വിൽപ്പനക്കാരൻ) എന്നീ രണ്ട് ഗ്രീക്ക് പദങ്ങളിൽ നിന്നാണ് മോണോപോളി (Monopoly) അഥവാ കുത്തക എന്ന വാക്കുണ്ടായത്. ഇതി നർത്ഥം “ഒറ്റവിൽപ്പനക്കാരൻ” (Single seller). അതായത് ഒരു ഉല്പാദകൻ മാത്രമുള്ളതും, ഉല്പന്നങ്ങൾക്ക് അടുത്ത പ്രതിസ്ഥാ പന വസ്തുക്കളില്ലാത്തും കമ്പോളത്തിൽ പൂർണനിയന്ത്രണം (വി ല, ഉല്പ്പന്ന അളവ്) ഉള്ളതുമായ കമ്പോള അവസ്ഥയാണ് കുത്തക കമ്പോളം (Monopoly market) എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്നത്. ഉദാ: കെ.എസ്.ഇ.ബി.
സവിശേഷതകൾ:
- ഒരു ഉല്പ്പന്നത്തിന് ഒരു ഉല്പാദകൻ മാത്രമേ ഉണ്ടാകുക യുള്ളൂ.
- അടുത്ത പ്രതിസ്ഥാപന വസ്തുക്കൾ ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കുകയില്ല. (no close substitutes)
- പുതിയ സ്ഥാപനങ്ങൾക്ക് കമ്പോളത്തിൽ പ്രവേശിക്കാൻ സാധിക്കില്ല. (entry is denied)
- കുത്തക കമ്പോളത്തിൽ ഒരു ഉല്പാദന യൂണിറ്റ് മാത്രമുള്ള – തിനാൽ ഉല്പ്പാദന യൂണിറ്റും, വ്യവസായവും ഒന്നുതന്നെയാണ്. (firm and industry are same)
- ഉല്പാദകൻ വില നിർണയിക്കുന്നവൻ (price maker) ആണ്.
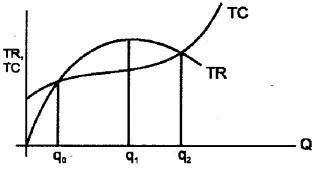
Comparison Of Monopoly And Perfect Competition
Comparison of monopoly and perfect competition can be summarised in the following table.
| Perfect competition | Monopoly |
| Firm is a price taker | Firm is a price maker |
| Large number of firms | Single producer |
| Homogenous products | No close substitutes |
| Free entry | Entry is denied |
| The demand curve is horizontal and perfectly elastic | The demand curve is steep and less elastic |
| MR curve will be a straight line parallel to X axis | As output increases, MR declines. The MR curve will be under AR curve |
| TR curve is starting from the origin and upward sloping straight line | TR curve takes the shape of inverted parabola |
കുത്തകയും പൂർണ്ണമത്സരവും തമ്മിലുള്ള താരതമ്യം
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a market characterized by the elements of perfect competition and monopoly. It is a market situation characterized by large number of firms producing various kinds of goods and services. The products of a firm will be different from the products of other firms in terms of size, shape, smell, colour, etc.
Features:
The salient features of perfect competition are as follows:
- Large number of buyers and sellers: Under monopolistic competition, there exists large number of buyers and sellers. But the number of sellers will be less compared to perfect competition.
- Product differentiation: One of the most important characteristic of monopolistic competition is the existence of product differentiation. Each firm has its own product with unique brand names. The products of one firm will be different from the products of other firms in terms of size, shape, smell, colour, etc.
- Freedom of entry and exit: Under monopolistic competition there is the freedom of entry and exit.
- Selling cost: The cost incurred for sales promotion such as advertisement, coupons, gifts, etc. are known as selling cost. Under monopolistic competition, the selling costs would be relatively high.
കുത്തകമത്സര കമ്പോളം
പൂർണ മത്സരത്തിലേയും കുത്തക കമ്പോളത്തിന്റേയും സവി ശേഷതകൾ ചേർന്ന കമ്പോളമാണ് കുത്തകമത്സര കമ്പോളം. ധാരാളം വില്പനക്കാർ ‘ഡിഫറൻഷിയേറ്റഡ്’ ഉല്പന്നങ്ങൾ വിൽക്കുന്ന കമ്പോളമാണിത്. സാധനങ്ങൾ തമ്മിൽ നിറം, മണം, ആകൃതി എന്നിവയിൽ മാറ്റങ്ങൾ ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കും.
സവിശേഷതകൾ:
- ധാരാളം വിൽപ്പനക്കാരും വാങ്ങുന്നവരും
- വ്യത്യസ്തതയുള്ള ഉല്പന്നങ്ങൾ
- പ്രവേശന നിഷ്ക്രമണ സ്വാതന്ത്യം
- വില്പന ചെലവ്
Oligopoly
The term oligopoly has derived from two terms oligo (small) and poly (seller). Thus oligopoly is a market situation characterized by a competition among few sellers. In simple terms, it is a competition among few sellers in the market selling either homogneous or differentiated product. The industries manufacturing car, motor cycle, scooter, etc. are some of the examples for oligopolistic competition.
Features:
The main features of oligopolistic competition are as follows:
- Few sellers: The number of sellers or producers would be few under oligopolistic competition.
- Homogenous or differentiated products: The products sold under oligopolistic competition would be either homogneous (e.g.gas, petrol) or differentiated (e.g. car, scooter)
- Free entry and exit: Free entry and exit persist under oligopolistic competition.
- Selling cost: Firms spend on advertisement and sales promotion.
- Interdependence of the firms: Since the number of firms under oligopoly are few, they are highly interdependent. The action of one firm will certainly have impact on other firms in terms of price, quality of the product, etc.
- Price leadership: Some of the firms may emerge as price leaders under oligopoly. The price leader could be the first firm in the industry or the firm with largest number of consumers. The price leader takes the important decisions regarding the vital decisions such as the price of the product or number of units to be produced in the market, etc.
അല്പാധീശത്വകമ്പോളം (Oligopoly Market)
‘ഒലിഗോ’ (oligo-കുറച്ച്), “പോള് (Poly-വില്പനക്കാരൻ) എന്നി രണ്ട് പദങ്ങളിൽ നിന്നാണ് ഒലിഗോപോളി എന്ന പദം ഉണ്ടായത്. “കുറച്ച് വിൽപ്പനക്കാർക്കിടയിലെ മത്സരം” എന്നാണിതിനർത്ഥം. ഒരേ തരത്തിലുള്ള അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വ്യത്യസ്ത തരത്തിലുള്ള ഉല്പന്ന ങ്ങൾ ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കുന്ന കുറച്ച് വിൽപ്പനക്കാർ തമ്മിലുള്ള മത്സര കമ്പോളമാണ് ഒലിഗോപോളി കമ്പോളം. ഉദാഹരണമായി കാർ, മോട്ടോർ സൈക്കിൾ, സ്കൂട്ടർ തുടങ്ങിയവ ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കുന്ന അൽപം സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളാണ് ഉള്ളത്.
സവിശേഷതകൾ:
- കുറച്ച് വില്പനക്കാർ മാത്രമേ ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കുകയുള്ളൂ.
- ഉല്പന്നം ഏകജാതീയമോ വ്യത്യസ്തമോ ആയിരിക്കും.
- പ്രവേശന നിഷ്ക്രമണ സ്വാതന്ത്യം ഉണ്ട്.
- വില്പന ചെലവ് ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കും.
- സ്ഥാപനങ്ങൾ തമ്മിൽ പരസ്പരാശ്രയത്വം ഉണ്ട്.
- വില നേതൃത്വം ഉണ്ട്.
Duopoly
Duopoly is an integral part of oligopoly. It is characterized by two sellers. It is assumed that the two firms produce homogneous products and there are no close substitutes for their products. Imagine that there TATA motors and Ashok Leyland are the only two manufacturers of heavy vehicles. It is the case of duopoly. In India, in reality we have more than two manufacturers of heavy vehicles.
ഡുവോപോളി (Duopoly) ദ്വിവ്യാപാരാധീശത്വം
അല്പാധീശത്വ കമ്പോളത്തിന്റെ തന്നെ ഒരു സുപ്രധാന ഭാഗ മാണ് ഡുവോപോളി (Duopoly). ഇവിടെ രണ്ട് വില്പനക്കാർ മാത്രമാണുള്ളത്. രണ്ട് ഉല്പാദകരും ഉല്പാദിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സാധന ങ്ങൾ ഏകജാതീയമാണെന്ന് (Homogeneous) സങ്കൽപ്പിച്ചിരി ക്കുന്നു. കൂടാതെ പകരം വയ്ക്കാനുള്ള (substitute) സാധന ങ്ങൾ ഇല്ലായെന്നും സങ്കൽപ്പിക്കുന്നു. ഉദാ. പാരമ്പര്യമായി ഇന്ത്യ യിൽ ഹെവി വാഹനങ്ങൾ നിർമ്മിക്കുന്നത്. പ്രധാനമായും രണ്ട് ഉല്പാദകരാണ്. ടാറ്റാ മോട്ടോഴ്സസും, അശോക് ലൈലാന്റും.
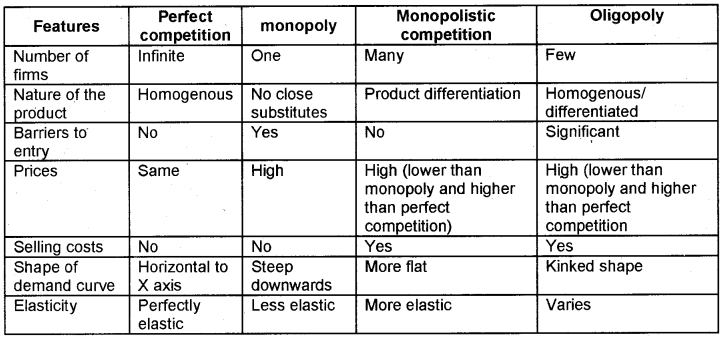
Comparison of Various Market Forms
(വിവിധ കമ്പോളങ്ങൾ – ഒരു താരതമ്യ പഠനം)