Kerala Plus Two Microeconomics Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Introduction
Plus Two Economics Introduction Microeconomics One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
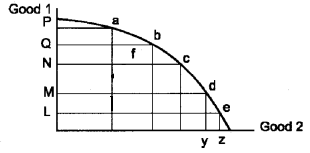
The diagram shows:
(a) A movement from ‘a’ to ‘b’ has no opportunity cost.
(b) A movement from ‘f’ to ‘b’ has an opportunity cost.
(c) Higher is the production of good 2 greater is the opportunity cost of reducing its production.
(d) Higher is the production of good 2 lesser is the opportunity cost of reaching its output.
Answer:
The concave shape of PPC shows that higher the production of goods 1 and 2. Goods 2 higher will be the opportunity cost of reducing production.
Question 2.
State economic terms. The allocations of scarce resources and the distribution of the final goods and services.
Answer:
The central problem of an economy.
Question 3.
As a result of liberalisation policy, the inflow of foreign capital has increased. What is its impact on production possibility frontier?
Answer:
PPC shifts upward as a result of the increase in the availability of capital resources.
Question 4.
What is the shape of a production possibility curve?
(i) Convex to origin
(ii) Concave to origin
(iii) Horizontal
(iv) Vertical
Answer:
(ii) Concave to origin
Question 5.
How does a market economy solve central economic problems?
(i) Central planning
(ii) Price mechanism
(iii) Both (i) and (ii)
(iv) None of the above
Answer:
(ii) Price mechanism
Question 6.
Scarcity definition was given by:
Answer:
(i) Adam Smith
(ii) Alfred Marshall
(iii) Lionel Robbins
(iv) Samuelson
Answer:
(iii) Lionel Robbins
Plus Two Economics Introduction Microeconomics Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
Answer:
Question 2.
Classify the following statement into two branches of economics.
- Indian economy grew by 9.2% GDP in the financial year 2006.
- An unexpected lorry strike caused the price of vegetables to rise.
- Recently the RBI reduced the Cash Reserve Ratio to 5.5%.
- Madras Cement LTD is planning to add 40 lakh tonne to its existing production capacity of 60 lakh tonnes.
Answer:
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
Question 3.
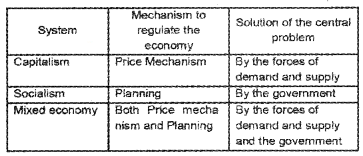
Distinguish between centrally planned economy and a market economy.
Answer:
In a centrally planned economy, the government or the central authority plan all the important activities in the economy. All important decisions regarding production, exchange, and consumption of goods and services are made by the government.
On the other hand in a market economy, all the important decisions are made on the basis of demand and supply conditions. The central problems regarding what and how much to produce are solved through the coordination of economic activities brought about by the price signals.
Question 4.
Give two examples of underutilization of resources.
Answer:
- Improper distribution of scarce resources leads to underutilisation of capacities,
- Due to technological backwardness, industrial workers’ capacity is underutilized.
Question 5.
Give a few examples of resources in economics.
Answer:
By the term ‘resources’, we mean land, labour, tools, machinery, etc. in economics.
Question 6.
The government should increase tax on tobacco products. Explain whether the statement is positive or normative.
Answer:
This is a normative statement because it says how the government should tax. It is only an opinion. This cannot be proved. Since it contains a value judgment it is a normative statement.
Question 7.
“Study of aggregates is equally important to study individual units.”
Substantiate the above statement by distinguishing the two branches of Economics. Give two examples for each.
Answer:
- Microeconomics which is the study of individual units is helpful in analysing a micro-economy, whereas macroeconomics is helpful in under-standing the working of macroeconomy.
- Microeconomics – Individual income, price of apple Macroeconomics – Inflation, national income.
Plus Two Economics Introduction Microeconomics Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
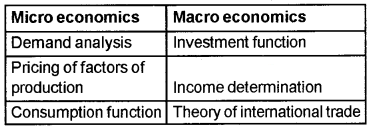
Classify the following into Microeconomics and Macroeconomics.
Answer:
Demand analysis, Consumption function, Theory of international trade, Income determination, Pricing of factors of production, Investment function.
Question 2.
Match Column B and C With Column A.
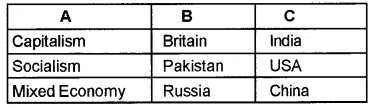
Answer:
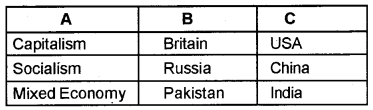
Question 3.
“Since resources are limited, they should be properly used”. Comment on this statement in the light of utilization of energy resources in Kerala.
Answer:
This statement relates to the problem of scarcity of resources and thus connected to the scarcity definition of Lionel Robbins. According to this statement, the scarcity of resources forces the economy to choose the most urgent need that is to be satisfied.
Since energy resource in Kerala is limited in supply, it has to be judiciously utilized. Control over the utilization of energy is necessary in states like Kerala so that this scarce resource can be protected.
Question 4.
Classify the following features under the title centrally planned economy and market economy. Price mechanism, comprehensive planning, welfare motive, profit motive, public sector, private sector.
Answer:
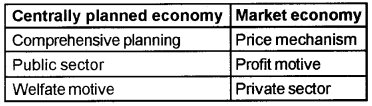
Question 5.
“Labour intensive technique is the best technique of production”. Give arguments in favour of and against this statement.
Answer:
Arguments in favour of:
- Labour intensive technique provides more employment opportunities.
- Labour intensive technique needs less capital.
- Labour intensive technique requires less skill only.
Arguments against:
- Labour intensive technique is less productive.
- Labour intensive technique prevents development
- Labour intensive technique makes the economy less productive.
Question 6.
Given below a Production Possibility Curve of an economy. Compare the points in the context of production possibilities of the economy.
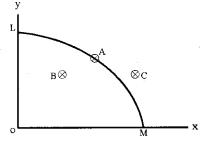
Answer:
The Production Possibility Curve is an analytical tool presenting the alternative production possibilities of an economy. It is used to explain the central problems of an economy and how they are solved.
In the diagram:
1. Point A indicates the efficient utilization of available resources.
2. Point B shows that the available resources of the economy are not fully utilized. In other words, it is an indication of the underutilization of resources.
3. Point C is outside the Production Possibility frontier. This means that the economy cannot produce at this point using the available resources.
Question 7.
Suppose there is growth of resources in an economy. How does it affect the PPC?
Answer:
When there is growth of resources the PPC shifts outwards as shown, below.
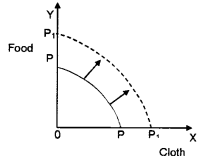
The PPC shifts from PP to P due to growth of resources in the economy. Therefore, economy produces more of food and cloth.
Question 8.
With the ₹500 cash award received by a student prepares a list of goods. She writes to have each of the goods priced @₹500.
- An Economics textbook.
- A movie with her friends.
- An outing.
- A dinner with her parents.
Explain opportunity cost. Identify the opportunity cost of buying one economic textbook.
Answer:
Opportunity cost is the next best alternative forgone. The opportunity cost of buying an economic textbook is the foregone movie with friends.
Question 9.
Different economic systems solve basic economic problems using different mechanisms. Complete the following table by writing the basic economic problems as well as the mechanisms used. Also, give one example for each economic system.
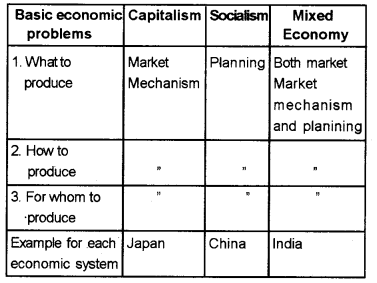
Answer:
Question 10.
Read the following statements and write the terms used in economics.
Answer:
- The curve representing various combinations of any two goods the economy can produce with the available resources and technology.
- An investigation in economics concerned with it is rather than what ought to be.
- An economic system in which basic problems are solved through planning.
Answer:
- PPC
- Positive economics
- Socialism
Plus Two Economics Introduction Microeconomics Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following statements into positive and normative statements.
- Statement I: India introduced a new economic policy in 1991.
- Statement II: Globalization badly affected India’s agricultural sector.
- Statement III: The number of people living below poverty line has to be reduced from the present level of 21%.
- Statement IV: Mean, median and mode are the measures of central tendency.
Answer:
- Statement I: positive statement
- Statement II:normative statement
- Statement III:normative statement
- Statement IV:positive statement.
Question 2.
“The implementation of Vizhinjam project will shift our PPC rightward”. Suggest two points in favour and against this statement.
Answer:
A production Possibility Curve is an analytical tool presenting the alternative production possibilities of an economy.
Points in favour of:
- Since the Vizhinjam project needs abundant skilled manpower, it would shift our PPC rightward.
- Kerala has abundant skilled manpower. They will get more employment and hence ppc will shift rightward.
Points against:
- The abundant skilled labour available in Kerala is lying unutilized only partially.
- The project need not be a continuous success as it will badly affect environment.
Question 3.
Prepare a production possibility schedule showing constant marginal opportunity cost.
Answer:
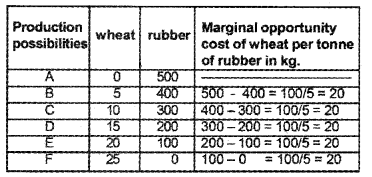
It is clear from the tables that in each production possibility to increase the production of wheat by one tonne, 20 kgs of rubber have to be sacrificed. This shows that there is constant marginal opportunity cost operating in this case. In this case, the PPC of rubber and wheat becomes a straight line.
Question 4.
Differentiate between microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Answer:
| Microeconomics | Macroeconomics |
| Deals with individual units | Deals with aggregates |
| Provides worms’ eye view | Provides bird’s eye view |
| Deals with partial equilibrium analysis | Deals with general equilibrium analysis |
| Known as price theory | Known as income theory |
Question 5.
A few statements are given below. Classify them under two branches of economics.
- RBI formulated its new monetary policy.
- National Income recorded the highest growth last year.
- Shyam purchased a new mobile phone.
- Inflation adversely affects the fixed income of people.
- Total Fixed Cost of a firm remains constant even if output increases.
Answer:
- Macroeconomics
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
Plus Two Economics Introduction Microeconomics Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Suppose a country uses its entire resources to provide educational and health facilities required for the people. Given the resources, the country can provide various combinations of number of schools and hospitals as shown in the table below.
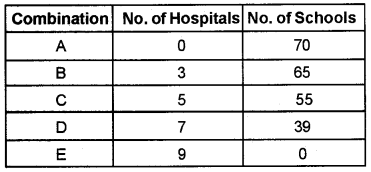
a. Define PPC and represent the above schedule on a diagram.
b. Suppose the country has already attained near-total literacy. If so, will the country prefer points on upper portion of PPC or points on the lower portion of PPC? Substantiate your answer.
c. Which mechanism will you advice to utilise the resources to provide more health facilities planning or market? Give reasons.
Answer:
a. Production Possibility Curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of all possible combinations of two goods or services that can be produced in an economy with given level of resources and technology. It is also known as production possibility frontier (PPF). The shape of PPC is concave to the origin.
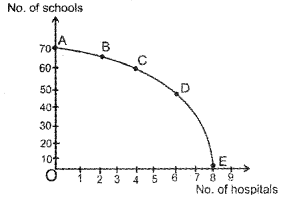
b. Combination D. Because more resources will be spent for health and less on education.
c. Planning. Because only the government can ensure public services.
Question 2.
Prepare a seminar paper on “central problems of an economy.
Answer:
Respected teachers and dear friends,
The topic of my seminar paper is “central problems of an economy”. As we know the central problems arise due to the fact that the human wants are unlimited and the means to satisfy those wants are limited. In this seminar paper, I would like to present the central problems such as what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce.
Introduction:
The resources available to the consumer are limited but their wants are unlimited. Due to scarcity of resources, the economy faces the problem of choice. It is this mismatch between unlimited wants and the limited resources that gives rise to three central problems faced by every economy.
Contents:
a. What to produce and in what quantities?
An economy faces the problems of what to produce because the resources available to an economy are scarce. As resoruces are scarce, an economy cannot produce all those goods and services the society needs. Therefore, society has to take the crucial decision of what goods and services to be produced in an economy.
For example, the resources of an economy can be used for the production of food, defense equipment or luxury goods. It can also be used for education, health or entertainment. A national society has to make a priority list of items to be produced and allocate the available resources accordingly.
Once the decision regarding what to produce is taken, the next problem is to decide in what quantities the goods and services are to be produced. It is important because the production of one good may lead to the withdrawal of the production of some other goods.
b. How to produce?
After taking the decision regarding the type and quantity of goods to be produced, the next question is ‘how to produce goods arid services’. This problem is related to the method or technology of production. Goods can be produced using different technologies.
There are mainly two technologies for producing goods, viz., labor-intensive technology and capital intensive technology. Labour intensive technology uses more labour compared to capital. On the other hand, capital intensive technology uses more caiptal compared to labour. The choice of technique depends upon various factors like the availability of labour force and capital resources and its prices.
c. For whom to produce?
The goods and services produced once should be distributed among the people of the economy. Whether it should be distributed equally among the people? Should the distribution of the goods be in such a way that at least minimum consumption level has to be attained by everyone in the economy? Should everyone get primary health and education?
Conclusion:
Thus it can be concluded that every economic system faces three basic problems. The solution to these economic problems depends upon the nature of the economic system.
