Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Matrices are part of Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Chapter 3 Matrices.
Kerala Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Matrices
Plus Two Maths Matrices 3 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
Write A as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix. A=[14−1254−1−63] (March – 2010)
Answer:
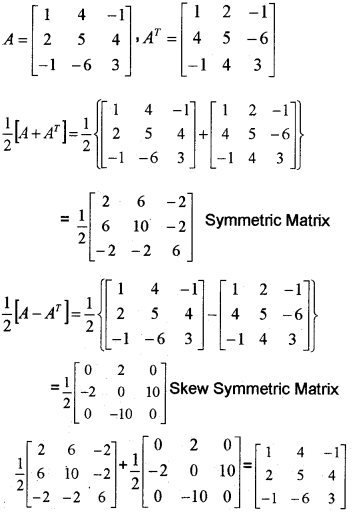
Question 2.
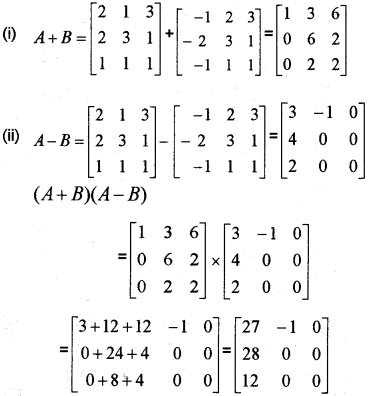
Consider the matrices
A=[213231111] and B=[−123−231−111]
(i) Find A+B
(ii) Find (A + B) (A-B) (May -2010)
Answer:
Question 3.
Given P=[2−3−12] Find the inverse of P by elementary row operation. (March 2011)
Answer:
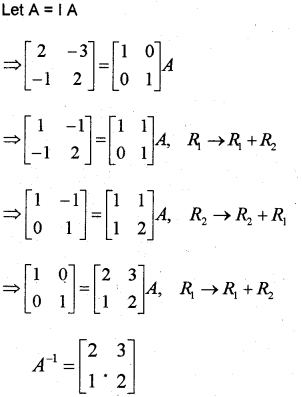
Question 4.
Let A=[365678] and C=[12−3456]
(i) Find 2A
(ii) Find the matrix B such that 2A + B = 3C (May 2011)
Answer:
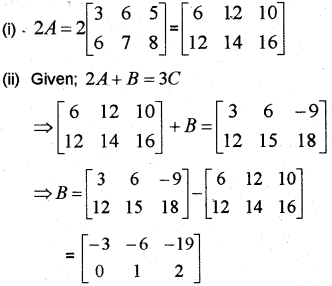
Question 5.
Let A=[24−11]
(i) Apply elementary transformation R → R R1/2 in the matrix A.
(ii) Find the inverse of A by the elementary transformation. (May 2011)
Answer:
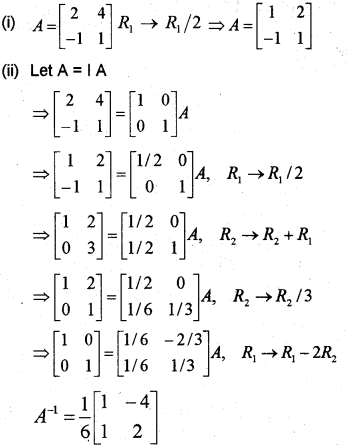
Question 6.
Consider the matrix A=[31−12]
(i) Find A2
(ii) Find ksothat A2 = kA – 7I (March – 2012)
Answer:
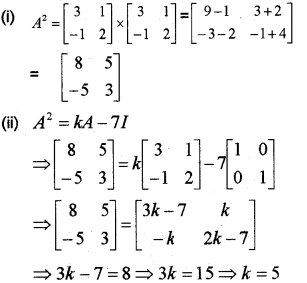
Question 7.
Consider a 2×2 matrix
A=[aij]$where$aij=|2i−3j|
(i) Write A
(ii) Find A + AT (March – 2012)
Answer:
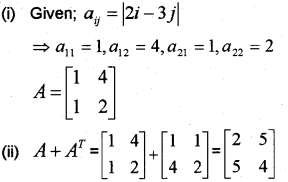
Question 8.
If A=[31−12] then
(i) Find A2
(ii) Hence show that A2 – 5A + 7I = 0. (March 2013)
Answer:
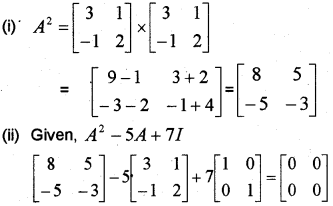
Question 9.
If a matrix A=[3xx−x2x] is a solution of the equation x2 – 5x + 7 = 0, find any one value of X. (May 2013)
Answer:
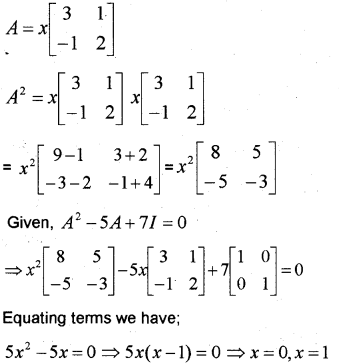
Question 10.
Consider the matrices A=[1−2−13]$and$B=[abcd]$ AB=[2956], find the values of a,b,c,d (March – 2014)
Answer:
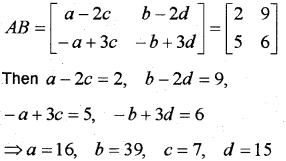
Question 11.
Consider a 2 x 2 matrix A=[aij] Where aij=(i+2j)22
(i) Write A
(ii) Find A + AT (March – 2014)
Answer:
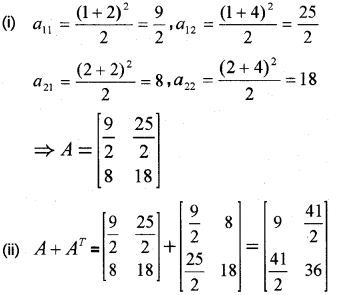
Question 12.
If X + Y = [7025] and X – Y = [3003] then
(i) Find X and Y.
(ii) Find 2X + Y. (May – 2014)
Answer:
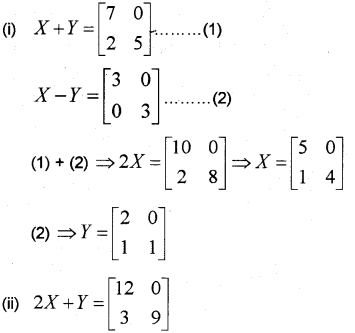
Question 13.
i) If A, B are symmetric matrices of same order then AB – BA is always a ………….
A) Skew-Symmetric matrix
B) Symmetric matrix
C) Identity matrix
D) Zero matrix
(ii) For the matrix A=[2456], verify that A + AT is a symmetric matrix. (March – 2015)
Answer:
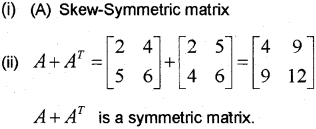
Question 14.
Consider the matrix A=[3−24−2]
(i) Find A2
(ii) Find k so that A2 = kA – 21 (May – 2015)
Answer:
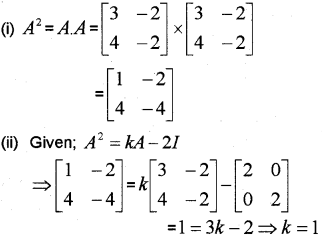
Plus Two Maths Matrices 4 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
(i) Find the value of x and y from the equations a[x57y−3]+[3−412]=[761514]
(ii) Given A=[123−142],B=[−14−5210] Show that AB ≠ BA (March – 2011)
Answer:
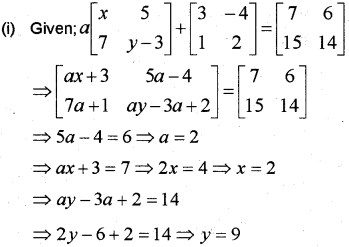
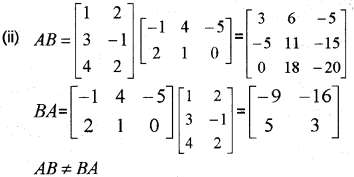
Question 2.
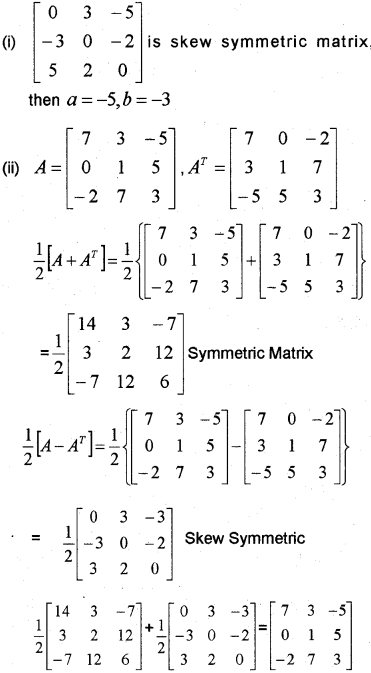
(i) Find a, b matrix [03ab0−2520] is skew symmetric matrix.
(ii) Express A=[73−5015−273] sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix. (May – 2012)
Answer:
Question 3.
Consider the matrices A=[2−612]$and$A+3B=[5−3−2−1]
(i) Find matrix B
(il) Find matrix AB.
(iii) Find the transpose of B. (May – 2013)
Answer:
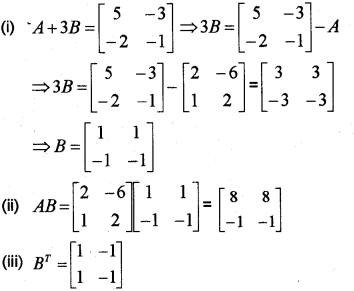
Question 4.
(i) The value of k such that matrix [1k−k1] is symmetric if
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) – 1
(d) 2
(ii) If A=[cosθsinθ−sinθcosθ] then prove that A2=[cos2θsin2θ−sin2θcos2θ]
(iii) if A=[1341], then find |3AT| (March – 2017)
Answer:
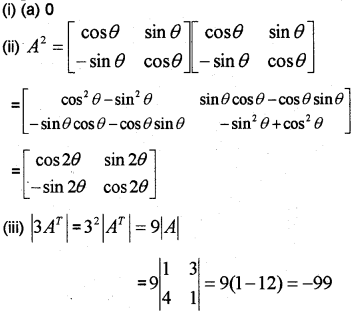
Plus Two Maths Matrices 6 Marks Important Questions
Question 1.
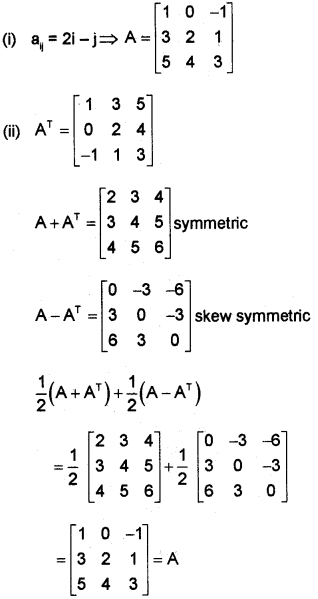
Let A be a matrix of order 3 x 3 whose elements are given by aij = 21 – j
(i) Obtain the matrix A.
(ii) Find AT Also express A as the sum of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix. (March – 2010)
Answer:
Question 2.
Consider a 2 x 2 matrix A=[aθ] with aij = 2i + j
(i) Construct A.
(ii) Find A + AT, A – AT
(iii) Express A as sum of a symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix. (May -2015)
Answer:
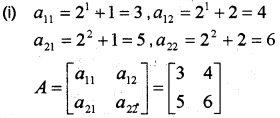
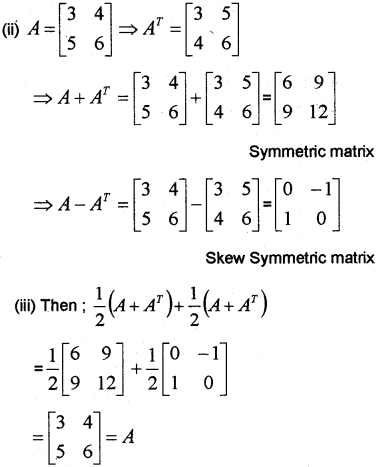
Question 3.
(i) A=[0100],B=[1000] then BA = _____
(a) [1001] (b) [0110] (c) [0100] (d) [0000]
(ii) Write A=[351−1] as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix.
(iii) Find the inverse of A=[2−61−2] (March 2016)
Answer:
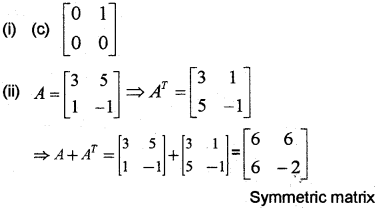
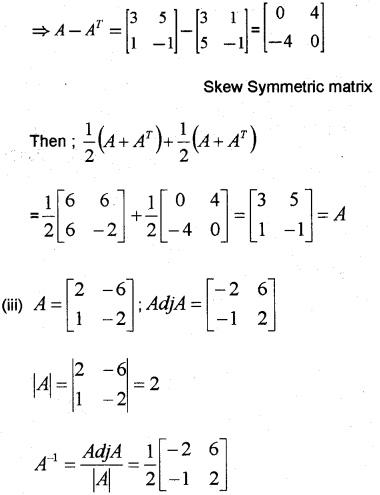
Question 4.
(i) If the matrix A is both symmetric and skew-symmetric, then A is a
(a) diagonal matrix
(b) zero matrix
(c) square matrix
(d) scalar matrix
(ii) If A=[13−24], then show that
(iii) Hence find A-1 (May 2016)
Answer:
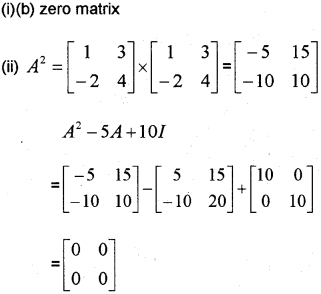
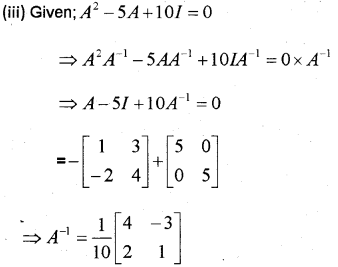
Question 5.
(i) The number of all possible 2 x 2 matrices with entries O or 1 is
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 16
(d) 25
(ii) If the area of a triangle whose vertices are (k,0), (5,0), (0,1) is 10 square units the find k.
(iii) Using elementary transformations find the inverse of the matrix [2111] (May 2017)
Answer:
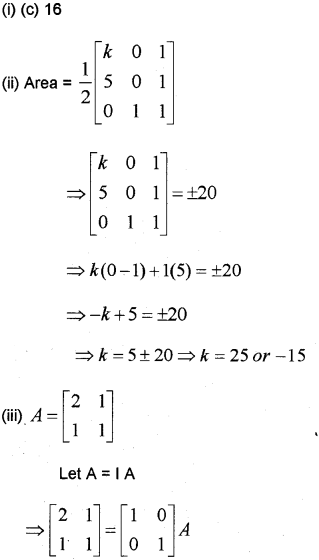
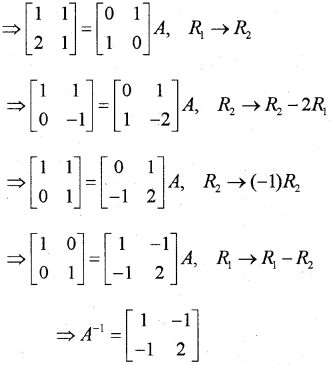
We hope the Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Matrices help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Maths Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 3 Matrices, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
