Kerala Plus Two Computerised Accounting Notes Chapter 5 Accounting Software Package – GNUKhata
GNUKhata – Introduction
GNUKhata is an accounting software based on Double Entry Book Keeping system. It is a Free and Open Source Software (FOSS).
GNUKhata is developed by Digital Freedom Foundation in association with International Centre for Free and Open Source Software (ICFOSS). It is a free and flexible software for accounting and inventory management.
Features of GNUKhata
- It is free and open source accounting software.
- It is based on double-entry bookkeeping
- All financial reports can be prepared
- Display of dual ledger facility
- Attachment of source document to vouchers is possible
- Linking of sales and purchase transactions to invoice.
- Export or import of data from spread sheet is possible.
- It ensures password security and data audit facility.
Installing GNUKhata
GNUKhata is Free and Open Source Software (FOSS). It can be legally downloaded and copied without having to pay anything to anyone. It is very simple to install GNUKhata in Linux. The installer file can be downloaded from the website www.anukhata.in. When we open GNUKhata for the first time, we can see a welcome screen.
Create Organisation
The first step in GNUKhata is to create an the organisation. To create a new organisation, click on “Create organisation” or press shift + control + R. While creating an organisation, the following details are to be given.
- Organisation Name: enter the name of the organisation and press Enter Key.
- Case: Choose the appearance of the organisation name, the options are As -is, Upper case, Lower Case or Title Case.
- Organisation Type: Select the organisation type either Profit Making or Not for Profit.
- Financial year: Enter the opening date of financial year then press enter key, closing date will show automatically which can be edited.
- Inventory: Tick the box of Inventory for maintaining inventory accounts.
1. Create Admin and log in:
There are Four levels of users in GNUKhata. They are Admin, Manager, Operatorand internal Auditor. Each has different authorities. Only one user can log in as “Admin”. There may be any number of users in the role of manager, operator and internal auditor.
“Create Admin” is mandatory. After creating an organisation, the next step is “Create Admin”. Fill all the fields in the Create Admin window and Enter/click on create and login. Now we can see a Menu bar at the top. Click Menu items to activate the Keyboard shortcuts.
2. Organisation Particulars:
We can enter the organisation details like Address, Country, State, city, etc through Edit Organisation Particulars in Master menu. Enter or click on Save to save the details and click on Reset to clear the fields, if necessary.
3. Change Organisation:
Select Change Organisation from Sign Out menu to exit the active organisation. To change the user, select Logout from Sign Out menu.
4. Selecting Organisation:
To select the existing organisation, click on Select Existing Organisation tab and select Organisation name from the drop down menu.
5. Deleting Organisation:
After login as “Admin” user, select Delete Organisation from Administration menu. Confirm the decision to delete the organisation, the organisation will be deleted.
Groups and Sub-Groups
Grouping of account is a method of organising the large number of ledger accounts into sequential arrangement for recording and summarisation of accounting data. GNUKhata has predefined Groups and Sub-Groups.
They are:
- Balance Sheet Groups
- Profit & Loss / Income & Expenditure Account Group
1. Balance sheet Groups in GNUKhata:
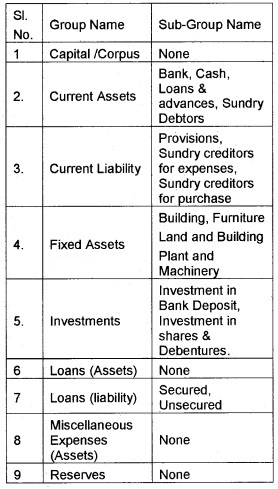
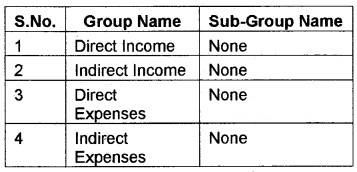
2. 
3. Description of the Groups and Sub Groups:
(i) (a) Capital: Amount contributed by proprietor, partners and share holders are recorded in this group.
(b) Corpus: Amount Contributed by the members of a non profit organisation (capital fund) are recorded in this group.
(ii) Current Assets: The assets which are consumed in operations are known as current assets. Accounts of such assets generated in the course of doing business are recorded in this group. The sub groups are
- Bank-(Deposits)
- Cash – (in hand, at factory, petty cash)
- Inventory-(closing stock)
- Loans and Advances-(temporary advance to Staff)
- Sundry Debtors – (Credit sales)
(iii) Current Liability: The liabilities which are to be paid with in a short period (less than one year) are called current liabilities. The sub groups of current liabilities are.
- Provisions: (PF, ESI, TDS dues, etc.)
- Sundry CreditorsforExpenses: (Outstanding expenses)
- Sundry Creditors for Purchase: (Amount payable to suppliers)
(iv) Fixed Assets: Accounts of all fixed assets (life span more than one year) are recorded in this Group. The subgroups are
- Building
- Furniture
- Land
- Plant and Machinery
(v) Investments: Contains accounts of investment made by the organit#ation. The subgroups are
- Investment in Bank Deposits
- Investment in shares and Debentures
(vi) Loan (Assets): Includes accounts of long term loans given
(vii) Loans (Liability): Amount borrowed from financial institutions. The sub Groups are
- Secured: (Loan against Security)
- Unsecured: (No Security)
(viii) Miscellaneous Expenses (Assets): This includes preliminary and preformation Expenses to the extent those are not written off.
(ix) Direct Income: Income from sale of goods, included in this group. If it is a service organisation, income from fees will come under this group.
(x) Indirect Income: All incomes which is not a direct income come under this group.
Eg: rent received, discount received, dividend received etc.
(xi) Direct Expenses: Expenses of purchase or manufacturing of goods are included in this group.
Eg. Wages, carriage inward, consumables etc. GNUKhata opens Opening Stock Account under this group.
(xii) Indirect Expenses: All office, administration sellng and distribution expenses are coming under this group.
Eg: Salary, Interest, depreciation, etc.
(xiii) Reserves: Contains retained earnings reserves and surplus.
System Generated Ledger Accounts in GNUkhata
GNUkhata has 29 predetermined Groups and subGroups. Out of these 13 are Groups and 16 are sub Groups. 25 Predefined Groups and subgroups are related with Balance sheet. Out of these 9 are Groups and 16 are Sub Groups. 4 Groups are related with Profit and Loss Account/ Income and Expenditure Account.
In GNUkhata, there are 4 system generated ledger accounts. We can neither change the name nor delete these accounts. Do not create accounts with similar names. These are.
Creating Ledger Accounts in GNUKhata
A ledger account contains record of all transactions relating to Assets, Capital, Liabilities, Expenditure and Revenues. A ledger account is to be created under any of the above five groups. Based on the group under which a ledger account is created, the “ balance of the ledger account will be appeared either in Trading, Profit and loss account or in Balance sheet.
1. Steps for Creation of Ledger Accounts:
- Step 1: Click on Master Menu or Press Shift + Control + M or Press F2
- Step 2: Select Create Account option. Then a dialogue box appears. Enter all the details.
- Group Name: Select the name of the group from the drop down list.
- Sub group name: Select the name of sub gorup from the drop down list depending on the group we selected. A new subgroup can also be created.
- Account name: Enter the name of account which we want to create
- Step 3: Click on Save button
2. Display Ledger Accounts:
To display Ledger accounts, select List of Accounts from Report menu. Now we can see a table containing a list of all ledger accounts along with its group name and sub group name.
3. Editing a ledger account:
To edit a ledger account, select Edit Account from Master menu. Here we can change Account name and opening balance. But we can not change the name of Group and sub Group.
4. Deleting a ledger account:
To delete a ledger account, select Edit Account from Master menu. Select the ledger account – we want to delete, click on Delete Button and confirm the deletion. System generated account and the ledger account already used in voucher cannot be deleted.
Types of Vouchers
GNUKhata has the following pre defined voucher types. We can not create a new voucher type.
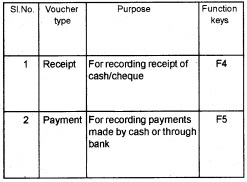
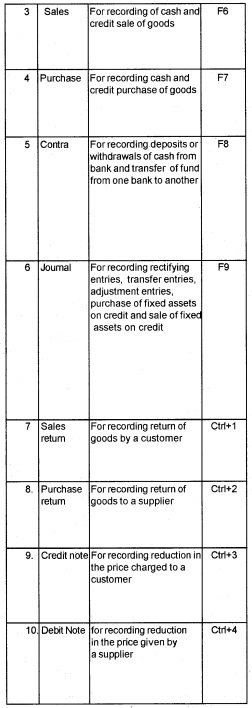
Voucher Entry
Recording a transaction through voucher is called voucher entry. While recording a voucher the debit part of the transaction recorded first and there after credit part. We can add any number of debits and credits in a voucher.
1. Finding and Editing a Voucher Entry:
To edit a voucher entry, it must be found out first. For this, the given steps are to be followed.
- Step 1: Select Find/ Edit voucher from voucher menu.
- Step 2: Select any one Criteria and press Enter key. All transactions fulfilling the criteria will be displayed.
- Step 3: Select the transaction that we want to edit and press Enter key
- Step 4: Click Edit button to open the transaction in edit mode make necessary changes.
- Step 5: Click on Save button to save changes.
2. Deleting a voucher entry:
To delete a voucher, First find it and click on Delete, after confirmation, the record will be deleted. Deleted vouchers cannot be restored.
3. Add account while in voucher entry:
While recording transactions in voucher entry mode, we can add a ledger account by clicking on Add Account, select the Group, sub Group, enter the account name and opening balance, if any. Click on Save Button and return to Voucher entry mode.
Reports
One of the tabs in the menu bar is Reports. From the Report menu, we will enable to view reports such as Ledger, Trial Balance, Balance sheet, Profit and Loss Account, List of accounts and List of deleted vouchers. For all these reports, we have to specify the periods.
1. Display Ledger Account:
- Step 1: Click on Report tab from the menu bar
- Step2: Select Ledger option from the list, Now view Ledger screen appears
- Step 3: Select the name of ledger account we want to display
- Step 4: Enter from date and to date
- Step 5: Click on view button to view the ledger
2. Display Trial Balance:
- Step1: Click on Report tab from the menu bar
- Step 2: Select Trial balance from the menu
- Step 3: Enter From date and To date
- Step 4: Select the Trial Balance Type
- Step 5: Click on view button to view the Trial Balance
3. Display Profit and Loss Account/Income and Expenditure Account:
- Step 1: Click on Report tab from the menu bar
- Step 2: Select Profit and loss or Income and Expenditure from the list
- Step 3: Enter From date and To date.
- Step 4: Click on view button
4. Display Balance sheet:
- Step 1: Click on Report Tab from the menu bar
- Step 2: Select Balance sheet from the list
- Step 3: Select Balance sheet type
- Step 4: Click on View button
Bank Reconciliation statement (BRS)
Bank Reconciliation statement is prepared by an account holder to reconcile cash book balance and pass book balance on a specific date. It is prepared for bank accounts opened under the Sub Group Bank of the Group Current Assets. To open Bank Reconciliation Statement, select Bank Reconciliation statement from the Master menu.
1. Causes of Difference between Cash Book Balance and Pass Book Balance:
- Cheque issued; but not presented for payment
- Cheque deposited; but not collected
- Direct payment by a customer to the bank
- Interest on deposit credited by the bank
- Dividend, rent, etc collected by the bank
- Payment made on behalf of the customer
- Bank charges as per pass book
- Bills receivables discounted, but dishonored
- Interest on overdraft debited in the pass book
2. Terms associated with BRS:
- Transaction Date: The date of the transaction
- Clearance date: The date on which a particular transaction appears in a pass book
- Reconciliation period: The period for which Bank Reconciliation is done is called Reconciliation period.
- Statement of uncleared items: When the clearance date and Transaction date of a transaction falls with in the Reconciliation period, that transaction is said to be cleared. Otherwise it is uncleared item.
Short cut keys in GNUKhata
| Use | Keys |
| 1. Activate Toolbar Tab | F1 |
| 2. Create Ledger Account | F2 |
| 3. Find/Edit Ledger Account | F3 |
| 4. Receipt Voucher | F4 |
| 5. Receipt Voucher | F5 |
| 6. Sales voucher | F6 |
| 7. Purchase Voucher | F7 |
| 8. Contra Voucher | F8 |
| 9. Journal Voucher | F9 |
| 10. Find/ Edit voucher | F10 |
| 11. View Ledger Account | F11 |
| 12. Display Trial Balance | F12 |
| 13. Sales Returns voucher | Ctrl + 1 |
| 14. Purchases Returns voucher | Ctrl + 2 |
| 15. Credit Note voucher | Ctrl + 3 |
| 16. Debit Note voucher | Ctrl + 4 |
| 17. Cost centre statement | Ctrl + 5 |
| 18. Cash Flow statement | Ctrl + 6 |
| 19. List of Accounts | Ctrl + 7 |
| 20. Create/ Edit cost centre | Alt + P |
| 21. Bank Reconciliation statement | Alt + R |
| 22. Manual | Alt + M |
| 23. Master Tab | Ctrl + M |
| 24. Inventory Tab | Ctrl + I |
| 25. Transaction Tab | Ctrl + T |
| 26. Report Tab | Ctrl + R |
| 27. Administration Tab | Ctrl + D |
| 28. Help Tab | Ctrl + H |
| 29. Sign out Tab | Ctrl + S |
| 30. Sign out Tab | Ctrl + L |
