Kerala Plus Two Computer Science Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 8 Database Management System
Plus Two Computer Science Database Management System One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Select the property which is desirable for a database.
(a) Redundancy
(b) Inconsistency
(c) Integrity
(d) Complexity
Answer:
(c) Integrity
Question 2.
Pick the odd man out.
Answer:
(a) Create
(b) Select
(c) Update
(d) Insert
Answer:
(a) Create
Question 3.
______ is the ability to modify a schema definition in one level without affecting the schema definition in the next higher level.
Answer:
Data Independence
Question 4.
For accessing data from a database, provides an interface with programming languages.
Answer:
SQL(orDML)
Question 5.
Give an example for RDBMS package.
Answer:
Packages such as Oracle, My SQL, etc.
Question 6.
Name the key that acts as a candidate key but not a primary key.
Answer:
Alternate key
Question 7.
With the help of ______ the process of storing, retrieving and modifying data are greatly simplified.
Answer:
DBMS
Question 8.
If _____ is controlled , DBMS can guarantee that database is never inconsistent.
Answer:
Redundancy.
Question 9.
The property of a DBMS that guarantees that the database is never inconsistent.
Answer:
Redundancy.
Question 10.
_____ and ______ are the two types of integrity checks.
Answer:
Range checks, Value checks.
Question 11.
Which component of DBMS provides interfaces with programming Languages ________.
Answer:
DML
Question 12.
The level of database abstraction that describes how the data is actually stored in the storage medium.
Answer:
Physical level.
Question 13.
The level of database abstraction that describes what data are stored in the database.
Answer:
Logical level.
Question 14.
Database Administrators (DBA) are more concerned with level ____ of Abstraction.
Answer:
Logical level
Question 15.
The programmers are connected with ______ .level of abstraction.
Answer:
Logical level.
Question 16.
The teller at a bank sees only that part of the database that has information on customer accounts. Which level of Database abstraction he is at?
Answer:
View level.
Question 17.
As part of project work, Ashish defines the type of data and the relationship among them. He is at _____ level of database abstraction.
Answer:
Logical.
Question 18.
_____ is the other name for logical level
Answer:
Conceptual level
Question 19.
if the modifications made on storage format does not affect the structure of data, then we achieve ___ data independence.
Answer:
Physical data independence.
Question 20.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) network model
(b) hybrid model
(c) relational model
(d) hierarchical model
Answer:
(b) hybrid model
Question 21.
“I am a data model. My records can have more than one parent record” Who am I?
Answer:
Network model.
Question 22.
Name the language that enables user to access or manipulate data as organized by RDBMS.
Answer:
DBML
Question 23.
A Database Administrator is able to modify the structure a programmer changes data types and length of a database without affecting certain fields in a database of a bank and the program. Identify the data independence associated in it.
Answer:
Logical data Independence
Question 24.
Name the language that used to define a database scheme.
Answer:
DDL
Question 25.
Name the person who has central control over the database and programs in DBMS
(a) Naive user
(b) Programmer
(c) Database Administrator
(d) System Analyst
Answer:
(c) Database Administrator
Question 26.
Oracle DBMS package is based on _____ model.
Answer:
Relational
Question 27.
Match the following.

Answer:
a – ii
b – iii
c – i
Question 28.
Name the Relational operation which selects certain columns from the table while discarding others.
Answer:
Project.
Question 29.
How to define the Domain of a column ‘subject 1’of MARKS relation.
Answer:
Range of values from 0 to 100
Question 30.
State whether true or False.
A view is a kind of table whose contents are taken from other tables.
Answer:
True.
Question 31.
State True or False.
A view can be queried, inserted into, updated and deleted from.
Answer:
True.
Question 32.
Name an efficient way to provide only required data to users hiding other data from the database.
Answer:
View.
Question 33.
Pick the key which can not be used to uniquely identify a tuple on a relation:
(Candidate Key, Primary Key, Alternate Key, Super Key, None of these)
Answer:
None of these.
Question 34.
π (pi) Greek letter is used to denote ______ operation in relational algebra.
Answer:
Project.
Question 35.
Which relational Algebra operation returns all possible combinations of tuples from two relations.
Answer:
Cartesian product.
Question 36.
Pick the odd one out.
(Select, Cartesian product, Union, intersection)
Answer:
Select – unary operator.
Question 37.
What will be the cardinality of the resultant table if after the following operation if the cardinality of STUDENT is 5 and INSTRUCTOR is 3?
Student × Instructor
Answer:
15.
Question 38.
Consider two relations FOOTBALL AND CRICKET, How to get the names of players play only cricket not also FOOTBALL.
Answer:
CRICKET – FOOTBALL.
Question 39.
Why we call a Foreign Key so?
Answer:
it is a candidate Key in another table, A foreigner.
Question 40.
______ is range of values from which actual values are appearing in a given column are drawn.
Answer:
Domain
Question 41.
Name the table that does not contain data of its own, but is derived from a base table.
Answer:
View
Question 42.
Name a way to uniquely identify a tuple in a relation.
Answer:
By using primary key.
Question 43.
Give two Unary operations performed on a relation in Relational Algebra.
Answer:
Select, Project.
Question 44.
Data redundancy is not a desirable property. But All redundancy can not or should not be eliminated. Do you agree with this statement? Justify.
Answer:
Yes. Because sometimes there can be technical or business reasons for maintaining several distinct copies of same data.
Question 45.
Anju is able to do all the internal operations in a DBMS. What type of user is she? What are the other type of users?
Answer:
DBA, Other type users are Appl Programmer and Naive users.
Question 46.
Which of the following statements are true?
(1) DBMS facilitates storage, retrieval, and management of databases.
(2) We must keep more copies of the same data in databases.
(3) Data inconsistency is eliminated in DBMS.
(4) DBMS allows sharing of data but does not ensure security.
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) Both (1) and (3) are true
(b) Statements (1), (3) and (4) are true
(c) Statements (1), (2) and (4) are true
(d) All statements are true
Answer:
(a) Both (1) and (3) are true
Question 47.
Which of the following refers to duplication of data in files?
(a) Data redundancy
(b) Data inconsistency
(c) Data integrity
(d) Data security
Answer:
(a) Data redundancy
Question 48.
The following are some responsibilities of database users. Which of them belongs to Database Administrator?
(1) Design the conceptual schema of the database.
(2) Develops programs to interact with the database.
(3) Interacts with the database through queries.
(4) Ensures authorised and secured access of data
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) Both (1) and (3)
(b) Except (2) and (3)
(c) (1), (2) and (4)
(d) All four
Answer:
(b) Except (2) and (3)
Question 49.
Which of the keys in a relation do not allow null values? Choose the most appropriate option from the following.
(a) Primary key
(b) Candidate key
(c) Both primary key and candidate key
(d) Either primary key or candidate key
Answer:
(c) Both primary key and candidate key
Question 50.
Choose the level of database abstraction that describes what data is stored in the database and what relationships exist among them,
(a) External
(b) Logical
(c) Physical
(d) View
Answer:
(b) Logical
Question 51.
Which of the following operations can extract the specified columns of a table?
(a) Selection
(b) Projection
(c) Intersection
(d) Set Difference
Answer:
(b) Projection
Plus Two Computer Science Database Management System Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The schema of a table is EMPLOYEE (emp_code, emp_name, designation, salary). Write down the relational expressions for the following:
a) To get the name and designation of all employees.
b) To get the details of employees whose salary is above 25000.
c) To get the names of employees who designation is Manager.
d) To get the details of Managers with salary less than 25000.
Answer:

Question 2.
Data sharing is an essential feature of DBMS. How data sharing reduces the data inconsistency in a database? Data sharing is an essential feature of DBMS. How data sharing reduces the data inconsistency in a database?
Answer:
Instead of storing more than one copy of the same data, it stores only one copy. This can be shared by several users. If redundancy occurs there is a chance to inconsistency. If redundancy is removed then in-consistency cannot occur.
Question 3.
Pick the odd one out and justify your answer:
(a) Column
(b) Attribute
(c) Field
(d) Tuple
Answer:
(d) Tuple. The other three terminologies indicate the same characteristic of a table.
Question 4.
Suppose a table (relation) contains the details of customers in a bank. Which attribute of the customer will be set as primary key for the table? Give reason for your opinion.
Answer:
Account number can be set as primary key since account number is different. different customers. That is it is unique hence it can be set as primary key.
Question 5.
How many distinct tuples and attributes are there in relation with cardinality 22 and degree 7.
Answer:
- Cardinality is the number of rows (tuples)
- Hence number Of tuples is 22
- Degree is the number of columns (attributes)
- Hence number of attributes 7
Question 6.
Distinguish primary key and alternate key.
Answer:
- Primary key: It is a set of one or more attributes used to uniquely identify a row.
- Alternate key: A candidate key other than the primary key.
Question 7.
Write an example for relational data model.
Answer:

Question 8.
Observe the following table and choose the correct match from the following options.
Column A | Column B |
| 1. Cardinality 2. Degree 3. Relation 4. Tuple | A. Row of a table B. Table C. Number of rows D. Number of columns E. Attribute |
(a) 1 → B, 2 → D, 3 → E, 4 → C
(b) 1 → C, 2 → D, 3 → E, 4 → A
(c) 1 → C, 2 → D, 3 → B, 4 → A
(d) 1 → D, 2 → C, 3 → B, 4 → E
Answer:
(c) 1 → C, 2 → D, 3 → B, 4 → A
Question 9.
Consider the table with the following fields Name, RollNumberand Mark for a set of students. Suggest a field among them, which is suitable for primary key. Justify your answer.
Answer:
field RollNOmber is suitable for the primary key. The name and mark can have same values so they are not suitable for the primary key.
Question 10.
Raju is confused with the statement ‘logical data independence is more difficult to achieve than physical data independence. How can you help Raju to understand the statement?
Answer:
Because Appl. Programs heavily dependent on the logical structure of data. So any change in structure means chance of rewriting Appl. Programs.
Question 11.
Match the following.
A | B |
| a. DBA | i. querying and updating |
| b. Application programmer | ii. ensures consistency |
| c. Naive users | iii. defines conceptual view |
Answer:
a – ii
b – iii
c – i.
Question 12
Match the following.
| A | B |
| a. The hierarchical model | i. data as tables |
| b. Network model | ii. Network as storage medium |
| c. Relational model | iii. Child record can have more than one parent |
| iv. Tree structure |
Answer:
a – iv
b – iii
c – i.
Question 13.
Your friend tells you that only relational model is used nowadays as DBMS. Will you agree with that? Justify.
Answer:
Yes. Other two models are complex. In.RDMS, no redundancy, and relationships can be formed easily.
Question 14.
The telephone number of Gokul is entered in Library file as 802111 and in admission register file as 802171.
- Can you correlate this problem with a concept in DBMS?
- Can you propose a solution to avoid this?
Answer:
Consistency problem, Remove data redundancy
Question 15.
What is DBMS?
Answer:
A DBMS is used to store large volumes of data and it is used to retrieve data whenever needed, edit the existing data, update the data and it is possible to delete also.
Question 16.
“View provides an excellent way to access data from data.” Do you agree with this statement? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes. Views can have data from more than one table, view can be queried, inserted into, deleted from and updated like a normal table.
Question 17.
A relation is given below
STUDENT
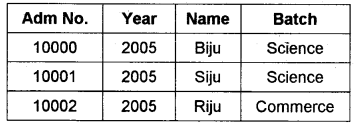
Mark the following:
Tuple, Attributes, Cardinality, Degree
Answer:
- Tuple – It is the Rows
- Attributes – It is the columns
- Cardinality – 3 (Number of Rows)
- Degree – 4 (Number of Columns)
Question 18.
State whether true or False.
- Primary key cannot be composite key.
- Only a candidate key can become a Primary Key.
- Foreign key of a table js a candidate key in another table.
- A super key uniquely identifies a row in a relation.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- True
Question 19.
Explain the meaning of following operations.
Answer:
select the tuples whose department is sales and who have salary > 5000.
Question 20.
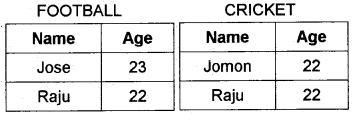
Is it possible to find the players who play both FOOTBALL AND CRICKET by applying any of the Relational Algebra Operations? Explain.
Answer:
Intersection operation.
FOOTBALL ∩ CRICKET
Question 21.
How will you differentiate Primary key and Super Key?
Answer:
- primary key – one of the candidate keys chosen to uniquely identify the rows of a table.
- Super key – Combination of a Primary key with any other attribute or group of attributes.
Question 22.
Cardinality of a table T1 is 10 and of table, T2 is 8 and the two relations are union compatible. If the cardinality of result T1 ∪ T2 is 13, then what is the cardinality of T1 ∩ T2? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Cardinality of table T1 is 10 means it has 10 rows Cardinalty of table T2 is 8 means it has 8 rows Normally T1 ∪ T2 is 10 + 8 = 18 But Here T1 ∪ T2 is 13 means after eliminating duplication of 5 rows this happened. This means 5 rows are common That is T1 ∩ T2 is 5.
Question 23.
Cardinality of a table T1 is 10 and of table, T2 is 8 and the two relations are union compatible.
- What will be the maximum possible cardinality of T1 ∪ T2?
- What will be the minimum possible cardinality of T1 ∩ T2?
Answer:
1. Degree(CD) – The number of Columns is the Degree
Cardinality (RC) – the number of Rows is the Cardinality
T1 ∪ T2 = Sum of cardinalities of Table1 and Table2.
i. e.T1 ∪ T2 = 10 + 8 = 18
2. T1 ∩ T2 is the common rows(tuples) in T1 and T2 If there is no common tuples then T1 ∩ T2is o hence the cardinality is 0.
Plus Two Computer Science Database Management System Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
For catering to the needs of users, a database is implemented through three general levels. Name the three levels and discuss them.
Answer:
1. Physical Level is the lowest level. it describes how the data is actually stored in the storage medium. At physical level complex, low-level data structures are described in detail.
2. Logical level describes what data are stored in the database and what relationships exist among data. Here database is described in terms of simple structures. Records are defined in this level. Programmers work at this level.
3. View level is the highest level of data abstraction. It is concerned with the way in which the users view the database. It describes only part of the database.
Question 2.
Consider the following table arid write relational algebra operations for the following DEPOSIT.
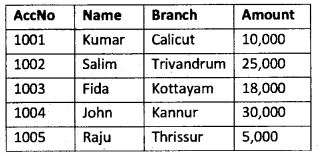
- To display those tuples from DEPOSIT relation where amount is greater than 25,000.
- To display only AccNo and Amount of all depositors.
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
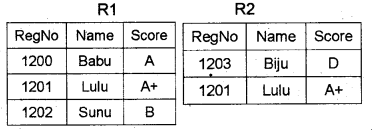
Show the output of the following relational operations.
a) R1 – R2
b) R1 ∩ R2
c) R1 ∪ R2
Answer:
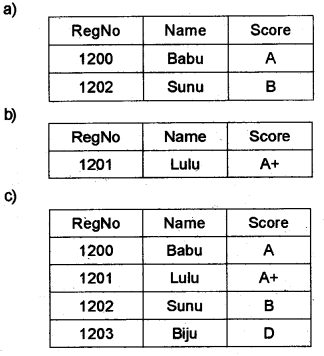
Question 4.
Developers hide the complexity of Database system three several levels of abstraction. What are they?
Answer:
Physical – logical – view level.
(how data) (what data) (view data)
Physical Level is the lowest level. It describes how the data is actually stored in the storage medium. At physical level complex, low-level data structures are described in detail.
Logical level describes what data are stored in the database and what relationships exist among data. Here database is described in terms of simple structure. Records are defined in this level. Programmers work at this level.
View level is the highest level of data abstraction. It is concerned with the way in which the users view the database. It describes only part of the database.
Question 5.
How data are organized in a database.
Answer:
- Field: Smallest unit of data. Eg: RolINo, Name
- Record: Collection of related fields. Eg: The information of a particular student.
- File: Collection of related records. Eg: The information of 10 students.
Question 6.
Salih checks his account details using an ATM machine.
- Identify the levels of abstraction associated with this?
- Specify other levels.
Answer:
- View level
- Logical level Physical level
Question 7.
Match the following.
A | B |
| 1. Database Administrator | a. Not concerned with or even aware of details of the DBMS |
| 2. Application Programmer | b. Person who has central control over definition and DBMS |
| 3. Users | c. Computer professionals who interact with the DBMS through Application programs |
Answer:
1 – b
2 – c
3 – a.
Question 8.
Match the following.
| A | B |
| Domain | Table |
| Tuple | No. of rows in a relation |
| Attribute | No. of columns in a relation |
| Cardinality | Rows in a relation |
| Degree | A pool of values |
| Relation | Column in a Table |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Domain | A pool of values |
| Tuple | Rows in a relation |
| Attribute | Column in a Table |
| Cardinality | No. of rows in a relation |
| Degree | No. of columns in a relation |
| Relation | Table |
Question 9.
Explain the major components of DBMS.
Answer:
Components of DBMS
- Databases – It is the main component.
- Data Definition Language (DDL) – It is used to define the structure of a table.
- Data Manipulation Language (DML) – It is used to add, retrieve, modify and delete records in a database.
- Users- With the help of programs users interact with the DBMS.
Question 10.
Categorise the users of DBMS and write their functions.
Answer:
Users of Database
- Database Administrator – It is a person who has central control over the DBMS.
- Application Programmer – These are computer professionals who interact with the DBMS through programs.
- Naive users – He is an end user. He does not know the details of DBMS.
Question 11.
A table with three columns is given below. For each relational operation given in the 1st column find the best matches from 2nd and 3rd columns.
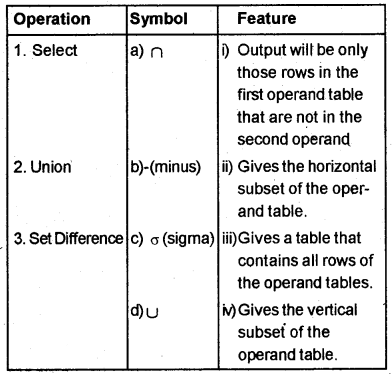
Answer:
1. Select → c) o → (ii)
2. Union → d) ∪ → (iv)
3. Set difference → b) – → (i)
Question 12.
Observe the given table BOOK and write down the outputs of the following relational expressions:
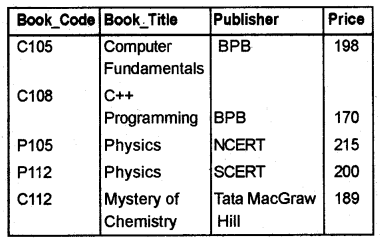
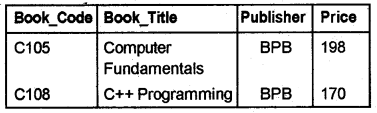
Answer:
a. This query returns all the tuples(rows) that contain BPB in column Publisher.
b. This query returns the column Book_Title with price < 200.
Book Title
Computer Fundamentals C++ Programming Mystery of Chemistry.
Plus Two Computer Science Database Management System Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Cardinality of table A is 10 and of table, B is 8 and the two relations are union compatible.
What will be the maximum possible cardinality of (A ∪ B) and (A ∩ B)?
What will be the minimum possible cardinality of (A ∪ B) and (A ∩ B)?
Give justifications for your answers.
Answer:
1. Both relations contain different tuples (rows).
2. The 8 tuples (rows) of table B are same as that of table A.
Case 1.
If both relations contain different tuples then the maximum possible cardinality of A ∪ B is 10 + 8 = 18
Case 2.
If 8 tuples of table B are same as that of table A then the maximum possible cardinality of A C B is 8.
Case 3
If 8 tuples of table B are same as that of table A then the minimum possible cardinality of A ∪ B is 10.
Case 4.
If both relations contain different tuples then the mini-mum possible cardinality of A ∩ B is 0.
Question 2.
There are different data models of which one is currently used in all business transactions. Specify it and discuss in detail.
Answer:
Relational data model is currently used in all business transactions. It is based on the concept introduced by E F Codd. It is composed of one or more tables. Tables are made up of rows and columns. Here tables are called relations, rows are called tuples and the columns are called attributes. The advantages of this model is neither data redundancy nor complexity.
Eg:
| Customer | Address |
| Gita | Add1 |
| Lata | Add2 |
| Ram | Add 3 |
Question 3.
You have to present a seminar on the topic “Keys in RDBMS”. Prepare the seminar report.
Answer:
- Candidate Key: It is a set of attributes that uniquely identifies a row. There may be more than candidate key and maybe a combination of more than one attribute.
- Primary Key: A primary key is one of the Candidate Keys. It is a set of one or more attributes that can uniquely identify tuples in a relation.
- Alternate Key: The Candidate key that is not the. primary key is called the alternate key.
- Super Key: A combination of a primary key with any other attribute or group of attributes is called a super key.
- Foreign Key: A single attribute or a set of attributes, which is a candidate key in another table, is called foreign key.
Question 4.
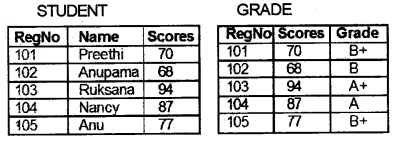
Consider the relations STUDENT and GRADE given above and predict the output of the following relational operations in table format.

Answer:
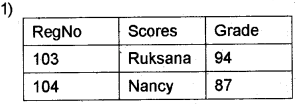
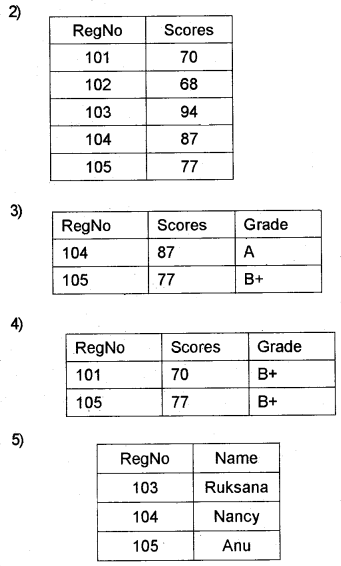
Question 5.
Explain any 4 Relational Algebra Operations.
Answer:
1. SELECT operation:
SELECT operation is used to select tuples in a relation that satisfies a selection condition. Greek letter a (sigma) is used to denote the operation. Syntax – σ condition(relation)
eg. σsalary < 10000 (EMPLOYEE) – selects tuple whose salary is less than 10000 from EMPLOYEE relation.
2. PROJECT operation:
PROJECT operation selects certain columns from the table and discards the other columns. Greek letter7i(pi) is used to denote PROJECT operation. Syntax – πcondition(relation)
eg. πname, salary (EMPLOYEE) displays only the name and salary of all employees
3. UNION operation:
This operation returns a relation consisting of all tuples appearing in either or both of the two specified relations. It is denoted by ∪. duplicate tuples are eliminated. Union operation can take place between compatible relations only, i.e., the number and type of attributes in both the relations should be the same and also their order.
e.g. SCIENCE ∪ COMMERCE gives all the tuples in both COMMERCE and SCIENCE.
4. INTERSECTION operation:
This operation returns a relation consisting of all the tuples appearing in both of the specified relations. It is denoted by ∩. It can takes place only on compatible relations.
e.g. FOOTBALL ∩ CRICKET returns the players who are in both football and cricket teams.
Question 6.
Why should you choose a database system instead of simply storing data in conventional files?
Answer:
Advantages of DBMS over conventional files:
1. Data Redundancy – It means duplication of data. DBMS eliminates redundancy. DBMS does not store more than one copy of the same data.
2. Inconsistency can be avoided – If redundancy occurs there is a chance to inconsistency. If redundancy is removed then inconsistency cannot occur.
3. Efficient data access – It stored huge amount of data efficiently and can be retrieved whenever a need arise.
4. Data can be shared – The data stored in the database can be shared by the users or programs.
5. Standards can be enforced – The data in the database follows some standards.
Eg: a field ‘Name’ should have 40 characters long. Some standards are ANSI, ISO, etc.
6. Security restrictions can be applied – The data is of great value so it must be kept secure and private. Data security means the protection of data against accidental or intentional disclosure or unauthorized destruction or modification by unauthorized person.
7. Integrity can be maintained – It ensures that the data is to be entered in the database is correct.
8. Crash recovery – Some times all or a portion of the data is lost when a system crashes A good DBMS helps to recover data after the system crashed.
Question 7.
We have admission register, attendance register, marks register, etc. in our school to keep various details of students. Briefly describe how DBMS can replace these registers by stating any five merits.
Answer:
Advantages of DBMS
1. Data Redundancy – It means duplication of data. DBMS eliminates redundancy. DBMS does not store more than one copy of the same data.
2. Inconsistency can be avoided – If redundancy occurs there is a chance to inconsistency. If redundancy is removed then inconsistency cannot occur.
3. Data can be shared – The data stored in the database can be shared by the users or programs.
4. Standards can be enforced – The data in the database follows some standards.
Eg: a field ‘Name’ should have 40 characters long. Some standards are ANSI, ISO, etc.
5. Security restrictions can be applied – The data is of great value so it must be kept secure and private. Data security means the protection of data against accidental or intentional disclosure or unauthorized destruction or modification by unauthorized persons.
6. Integrity can be maintained – It ensures that the data is to be entered in the database is correct.
7. Efficient data access – It stored huge amount of data efficiently and can be retrieved whenever a need arise.
8. Crash recovery – Sometimes all or a portion of the data is lost when a system crashes. A good DBMS helps to recover data after the system crashed.
