Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Previous Year Question Paper March 2017 with Answers
| Board | SCERT |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Category | Plus Two Previous Year Question Papers |
Time: 2½ Hours
Cool off time : 15 Minutes
General Instructions to Candidates
- There is a ‘cool off time’ of 15 minutes in addition to the writing time of 2½ hrs.
- You are not allowed to write your answers nor to discuss anything with others during the ‘cool off time’.
- Use the ‘cool off time’ to get familiar with the questions and to plan your answers.
- Read questions carefully before you answering.
- All questions are compulsory and the only internal choice is allowed.
- When you select a question, all the sub-questions must be answered from the same question itself.
- Calculations, figures, and graphs should be shown in the answer sheet itself.
- Malayalam version of the questions is also provided.
- Give equations wherever necessary.
- Electronic devices except non-programmable calculators are not allowed in the Examination Hall.
Question 1.
a. Identify the nonstoichiometric defect
i. Schottky defect
ii. Frenkel defect
iii. interstitial defect
iv. Metal deficiency defect
b. What type of substance could make better permanent magnets ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic? Justify your answer.
c. In terms of Band theory write the differences between conductors and insulators.
Question 2.
a. Henry’slaw is related to the solubility of a gas in a liquid.
i. State Henry’s law
ii. Write any two applications of Henry’s law.
b. 1000 cm3 of an aqueous solution of a protein contains 1.26 gm of the protein. The osmotic pressure of such a solution at 300 K is found to be 2.57 × 10-3 bar. Calculate the molar mass of the protein. (R = 0.083 L bar mol1K1)
Question 3.
a. Represent the galvanic cell based on the cell reaction given below:
![]()
b. Write the half-cell reactions of the above cell.
c. \(\wedge _{ m }^{ 0 }\) for NaCl, HCl and NaAc are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol-1 respectively. Calculate \(\wedge _{ m }^{ 0 }\) for HAc.
Question 4.
a. Plot a graph showing variation in the concentration of reactants against time for a zero-order reaction.
b. What do you mean by the zero-order reaction?
c. The initial concentration of the first-order reaction, N2O5(g) → 2NO2(g) + 1/2O2(g) was 1.24 × 10-2 mol L-1 at 300 K. The concentration of N2O5 after ‘ 1 ’ hour was 0.20 × 10-10 mol L-1. Calculate the rate constant of the reaction of 300 k.
Question 5.
There are mainly two types of adsorption. They are physisorption and chemisorption.
a. Differentiate between physisorption and chemisorption.
b. Write any two applications of adsorption.
Question 6.
Leaching is a process of concentration of ores. Explain the leaching of alumina from bauxite.
Question 7.
Nitrogen forms a number of oxides and oxoacids.
a. Which of the following is a neutral oxide of nitrogen?
i. N2O
ii. N2O5
iii. NO2
iv.N2O4
b. Prepare a short write-up on Nitric acid highlighting its laboratory preparation, chemical properties and uses.
OR
Phosphorous forms a number of compounds, a. The gas liberated when calcium phosphide is treated with dil.HC/ is
i. Cl2
ii.H2
iii. PH3
iv. All of the above
b. Prepare a short write up on PCl3 and PCl5 highlighting the preparation and chemical properties of PCl3 and structure of PCl5
Question 8.
a. Transition elements are d block elements.
i. Write any four characteristic properties of transition elements.
ii Cr2+ and Mn3+ have d4 configuration. But Cr2+ is reducing and Mn3 is oxidizing. Why?
b. Which of the following is not a lanthanoid element?
i. Cerium
ii. Europium
iii Lutetium
iv. Thorium
Question 9.
[CO(NH3)5S04]Cl and [Co(NH3)5 Cl]SO4 are coordination compounds.
a. Identify the isomerism shown by the above compounds.
b. Write the IUPAC names of the above compounds.
c. Identify the ligands in each of the above compounds.
Question 10.
a. An ambident nucleophile is
i. Ammonia
ii Ammonium ion
iii Chloride ion
iv. Nitrite ion
b.Haloalkanes and Haloarenes are organohalogen compounds.
i. Suggest a method for the preparation of alkyl chloride.
ii. Aryl halides are less reactive towards Nucleophilic substitution reactions. Give reasons.
Question 11.
a. Arrange the following compounds in the order of increasing boiling points: Ethanol, Propan1 o 1, Butan1 o 1, Butan2ol
b. In the lab, students were asked to carry out the reaction between phenol and cone. HN03. But one student, ‘A’ carried out the reaction between phenol and dil. HNO3 Do you think that the student ‘A’ got the same result as others. Substantiate with suitable explanations. [Also write the chemical equations wherever necessary]
Question 12.
a. The product obtained when benzene is treated with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is
i. Chlorobenzene
ii. Phenol
iii. Benzaldehyde
iv. Benzoic acid
b. How will you carry out the following conversions?
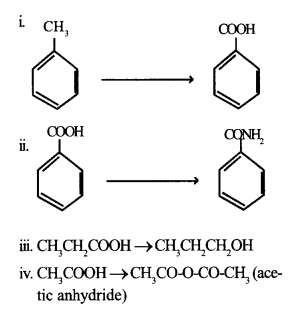
OR
b. Explain the following:
i. Esterification
ii. Tollen’s test
iii. HVZ reaction
iv. Dicarboxylic acid
Question 13.
a. Classify the following amines as primary, secondary and tertiary
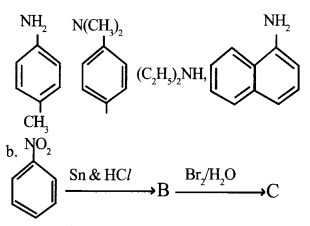
Identify products B and C and write their formulae.
Question 14.
a. Which of the following is a polysaccharide?
i. Maltose
ii. Sucrose
iii. Fructose
iv. Cellulose
b. Explain the amphoteric behavior of amino acids.
Question 15.
a. Which of the following is not applicable to Nylon 6, 6?
i. Synthetic polymer
ii. Fiber
iii. Addition polymer
iv. Condensation polymer.
b. Differentiate between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Write one example for each.
Question 16.
‘Antibiotics, antiseptics, and disinfectants are antimicrobial drugs.
Explain any one of the above-mentioned drugs with examples.
