Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers is part of Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers
Plus Two Chemistry Polymers One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Orion is a polymer of
(a) Styrene
(b) Tetrafluoroethylene
(c) Caprolactam
(d) Acrylonitrile
Answer:
(d) Acrylonitrile
Question 2.
Buna-S is a copolymer of styrene and ……………
Answer:
1,3-Butadiene
Question 3.
F2C = CF2 is a monomer of
(a) Glyptal
(b) Teflon
(c) Nylon 6
(d) PVC
Answer:
(b) Teflon
Question 4.
Say TRUE or FALSE :
Chloroprene is an addition polymer of Neoprene.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Bakelite is obtained from phenol by reacting with
(a) Vinyl chloride
(b) Ethylene glycol
(c) Ethanal
(d) Methanal
Answer:
(d) Methanal
Question 6.
Which one of the following is an example of a biode-gradable polyester
(a) PHBV
(b) PET
(c) Nylon
(d) Bakelite
Answer:
(a) PHBV
Question 7.
Novalac is ……………
Answer:
Phenol – formaldehyde resin
Question 8.
Ziegler-Natta catalyst is used in the preparation of …………….
Answer:
HDP
Question 9.
Nylon is a ………………….
Answer:
Polyamide
Question 10.
The polymer used in the manufacture of lacquers is ……………….
Answer:
Glyptal
Plus Two Chemistry Polymers Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
PVC is commonly used to make pipes.
- What is the monomer of PVC?
- What is the purpose of PVC covering of electrical connecting wire?
Answer:
- Vinyl chloride
- To provide electrical insulation.
Question 2.
Name the monomer units of natural rubber.
Answer:
2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene or Isoprene
Question 3.
Name two commercially important synthetic polymers. Also name their monomers.
Answer:
- Nylon 6,6 – Hexamethylene diamene and Adipic acid
- Bakelite – Phenol and Formaldehyde
Question 4.
What are polymers? Based on structure, how they are classified?
Answer:
Polymers are compounds of higher molecular mass formed by the combination of large number of small molecules.
Based on structure polymers are classified into 3 types:
- Linear polymers
- Branched polymer
- Cross linked or network polymers
Question 5.
How are the polymers classified on the basis of molecular forces?
Answer:
Based on molecular forces polymers are classified into four subgroups.
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastic polymers
- Thermosetting polymers
Question 6.
What are bio-degradable polymers?
Answer:
These are polymers which undergo degradation by the action of microorganisms, eg. Nylon 2-nylon 6
Question 7.
Name the monomers of Terylene and Buna-N?
Answer:
Ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid are the monomers of terylene. Buna-N is a copolymer of 1, 3-Butadiene and Vinyl cyanide.
Question 8.
Write the names of monomers of the following polymers.
- Glyptal
- Bakelite
Answer:
- Glyptal → Ethylene glycol and Phthalic acid
- Bakelite → Phenol and Formaldehyde
Question 9.
Explain the term copolymerisation and give two examples.
Answer:
Copolymerisation is a process in which a mixture of more than one monomeric species is allowed to polymerise. The copolymer contains multiple units of each monomer in the chain. The examples are copolymers of 1,3-butadiene and styrene (Buna-S) and 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile (Buna-N).
Question 10.
How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity?
Answer:
In this polymer the double bonds are located between C2 and C3 of isoprene units. This cis-configuration about double bonds do not allow the chains to come closer for effective attraction due to weak intermolecular attractions. Hence, the natural rubber has a coiled structure and shows elasticity.
Question 11.
Write the monomers of Teflon and Neoprene.
Answer:
- Teflon – Tetrafluoroethene
- Neoprene – 2-Chloro-1,3-butadiene
Question 12.
What is PHBV? What is its importance in polymer chemistry?
Answer:
PHBV is polyhydroxy butyrate – co – β – hydroxy valerate. PHBV is a biodegradable polymer.
Question 13.
What is meant by vulcanisation?
Answer:
The process of heating natural rubber with sulphur to improve its properties is called vulcanisation.
Plus Two Chemistry Polymers Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- What is bakelite?
- What is its use?
- Why bakelite is said to be an example for thermosetting polymer?
Answer:
- Bakelite is the condensation polymer of phenol and formaldehyde.
- It is used for the manufacture of electrical plugs and switches.
- Bakelite contains cross linked molecules which on heating undergo extensive cross linking in moulds and again become infusible. It cannot be reused. Hence, it is a thermosetting ploymer.
Question 2.
Classify the following compounds into natural and synthetic polymers.
(Starch, Nylon, Butadiene, Styrene rubber, Natural rubber, PVC, Cellulose)
Answer:
Natural polymers: Starch, Natural rubber, Cellulose Synthetic polymers: Nylon, Butadiene, Styrene rubber, PVC.
Question 3.
Write notes on
- Linear polymer
- Branched polymer
- Cross linked polymer
Answer:
- Here small monomer units are arranged one behind the other so as to form a chain.
- Small monomer units combine together in such a way that branched arrangement is possible in the polymer.
- A rigid arrangement is possible when different monomer units are connected by cross linking.
Question 4.
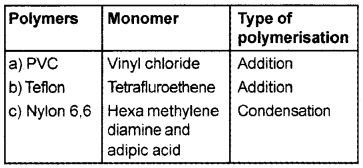
Some polymers are given below:
- PVC
- Teflon
- Nylon 6,6.
Make a table using the above representing name of polymer, name of monomer and type of polymerisation.
Answer:
Question 5.
Distinguish between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Answer:
S Buna N: It is a synthetic rubber and it is a copolymer of 1,3-Butadiene and Vinyl cyanide.
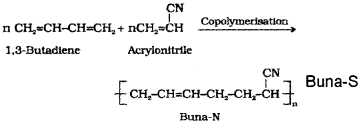
is a synthetic polymer formed by the copolymerisation of 1,3-butadiene and styrene.
Question 6.
In a science exhibition, one student mixed two transparent liquids in a beaker and got a sticky material from the interface of two liquids and he claims that the material formed is nylon 6,6.
- Name the two liquids he mixed.
- Name the monomer of nylon 6.
- Suggest two uses of nylon 6, 6.
Answer:
1. Hexamethylene diammine & adipic acid.
2. Caprolactum
3. Uses of nylon 6, 6:
- For making sheets, bristles for brushes.
- In textile industry.
Question 7.
Rubber is a polymer.
- Name the monomer of natural rubber.
- Discuss the importance of the vulcanisation of rubber.
- How is Neoprene prepared?
Answer:
1. 2-Methyl-1, 3-butadiene (or Isoprene) is the monomer.
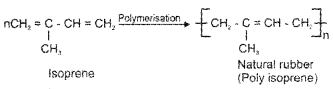
2. Vulcanised rubber has high elasticity, low water absorption, good resistance to oxidation and organic solvents.
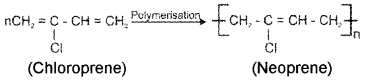
3. Neoprene is formed by the free radical polymerisation of chloroprene.
Plus Two Chemistry Polymers Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In rubber industry, natural rubber is processed using sulphur.
- What is the need of processing rubber in this way?
- Name this process.
- What is the monomer unit of natural rubber?
Answer:
- Natural rubber is a gummy substance which has poor elasticity when it is heated with sulphur, it becomes non sticky and more elastic.
- Vulcanisation
- 2-Methyl-1, 3-butadiene or Isoprene
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
Table
| Polymers | Monomer |
| a) PVC | i) ………………… |
| b) Terylene | i) ………………… |
| c) Buna-N | iii) ………………. |
| d) ……………….. | iv) 2-Chloro-1,3-butadiene |
Answer:
- Vinyl chloride
- Glyptal
- 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile
- Neoprene
Question 3.
- Give the monomeric repeating units of nylon 6 and nylon 6, 6.
- Differentiate between addition polymerisation and condensation polymerization.
Answer:
1. monomeric repeating units:
- Nylon – 6 – Caprolactam
- Nylon – 66 – Adipic acid, Hexamethylene diamine
2. Difference between addition polymerisation and condensation polymerization:
- Addition polymer: Simple monomer units combine together to form polymer.
Example: polythene. - Condensation polymer: Simple monomer units combine together to form polymer followed by the removal of small molecules like H2O, NH3 etc.
Example: Nylon-6,6
Question 4.
- What is polymerisation?
- What is a homo-polymer?
Answer:
- Polymerisation is the process of formation of polymers from respective monomers,
- Homopolymers are polymers formed by the addition polymerisation of a single monomeric species.
Plus Two Chemistry Polymers NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are natural and synthetic polymers? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
Natural polymers are high molecular mass macromolecules and are found in plants and animals, e.g. proteins, nucleic acids.
Synthetic polymers are man-made high molecular mass macromolecules. These include synthetic- plastics, fibres and rubbers, e.g. polythene, dacron.
Question 2.
In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecular forces?
Answer:
On the basis of molecular forces present between the chains of various polymers, the classification of polymers is give as follows:
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastics and
- Thermosetting plastics
Question 3.
How do you explain the functionality of a monomer?
Answer:
Functionality of a monomer is the number of bonding sites in a monomer.
Question 4.
Is (NH-CHR-CO)n, a homopolymer or copolymer?
Answer:
Since the unit (NH-CHR-CO)n is obtained from a single monomer unit, it is a homopolymer.
Question 5.
How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity?
Answer:
From the structural point of view, the natural rubber is a linear cis-1, 4-polyisoprene. In this polymer, the double bonds are located between C2 and C3 of isoprene units. This cis-configuration about double bonds do not allow the chains to come closer for effective attraction due to weak intermolecular attractions. Hence, the natural rubber has a coiled structure and shows elasticity.
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
