Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules is part of Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Plus Two Chemistry Biomolecules One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is an example of globular protein?
(a) Myosin
(b) Collagen
(c) Insulin
(d) Keratin
Answer:
(c) Insulin
Question 2.
The vitamin essential for blood clotting is
Answer:
Vitamin K
Question 3.
Which base is present in RNA but not in DNA?
(a) Uracil
(b) Thymine
(c) Guanine
(d) ytosine
Answer:
(a) Uracil
Question 4.
Say TRUE or FALSE:
The coagulation of egg white on boiling is an example of protein denaturation.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
The linkage that holds monosaccharide units together in a polysaccharide is called …………………….
Answer:
Glycosidic linkage
Question 6.
Proteins are essential for growth in animals. They are build up of amino acid molecules. How are different amino acid molecules linked in a proteins?
Answer:
By peptide linkage.
Question 7.
What are the different types of RNA found in the cell?
Answer:
m-RNA, t-RNA, r-RNA
Question 8.
Lactose is made of ………………….
Answer:
β -D galactose and β -D glucose
Question 9.
Glucose does not react with ………………..
a) Br2/H2O
b) NH2OH
c) HI
d) NaHSO3
e) CH3-CO-O-CO-CH3
Answer:
(d) NaHSO3
Question 10.
Anaemia is caused by the deficiency of vitamin ………………………
Answer:
B12
Question 11.
The number of chiral C atoms on glucose and fructose are
Answer:
4 in glucose and 3 in fructose
Question 12.
Glucose on oxidation with bromine water give …………………………
Answer:
Gluconic acid
Question 13.
Name the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood.
Answer:
Vitamin K.
Plus Two Chemistry Biomolecules Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the denaturation of protein.
Answer:
When a protein is treated with acid, alkali or heated or subjected to change in pH, the secondary and primary structure of protein gets ruptured. Denaturation does not change the primary structure of proteins.
Question 2.
Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
Answer:
Vitamin ‘C’ is a water soluble vitamin and they are readily excreted in urine and cannot be stored in our body.
Question 3.
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose.
Answer:
- Monosaccharides – Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, galactose and fructose.
- Disaccharides – Maltose and lactose.
Question 4.
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Answer:
The two monosaccharide units are linked together by an oxide or either linkage formed by the loss of water molecules. Such a linkage called glycosidic linkage.
Question 5.
Distinguish between essential and non-essential amino acids. Give examples.
Answer:
- The amino acids which can be synthesized in our body are known as non-essential amino acids, eg. Glycine, Alanine.
- Those amino acids which can not be synthesized in our body and must be obtained through diet are known as essential amino acids. eg. valine, Lysine.
Question 6.
What is ‘peptide linkage’ as related to proteins?
Answer:
The linkage, – CO – NH – which unites various amino acid units in a peptide molecule is called peptide linkage.
Question 7.
Amino acids show amphoteric behavior. Why?
Answer:
Amino acids contain both NH2 & -COOH group and hence they exhibit amphoteric character.
NH3+ – CH2 – COO–
Question 8.
What are reducing sugars? Give one example.
Answer:
Sugar units which are having free – CHO groups are reducing sugars, eg. Maltose.
Question 9.
What is primary structure of proteins?
Answer:
The primary structure gives an idea regarding the sequence in which amino acids are arranged.
Question 10.
Differentiate between fibrous & globular proteins.
Answer:
Fibrous proteins have threads lying side by side to form a fiber-like structure, e.g. Keratin. Globular proteins have molecules which are folded into compact units that often approach spherical shape.
Plus Two Chemistry Biomolecules Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
D-glucose is obtained in two different forms, α- D- glucose, and β-D-glucose.
- In which name the α and β forms of glucose are known?
- Explain the difference in their configuration with diagram.
Answer:
1. They are known as anomers.
2. Anomers are a pair of stereo isomeric ring forms of a sugar which differ in configuration only around first carbon atom.
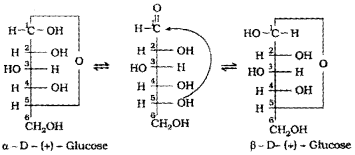
Question 2.
Complete the following table:
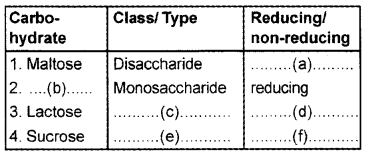
Answer:
- Reducing
- Fructose
- Disaccharide
- Reducing
- Disaccharide
- Non-reducing
Question 3.
There are two types of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA.
- Identify the sugar that is present in DNA and RNA.
- Give the differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
1. Sugar that is present in DNA and RNA:
- DNA – β-D-2-deoxyribose
- RNA – β-D-ribose
2.
| DNA | RNA |
| 1) Double helix structure | 1) Single helix |
| 2) Sugar-deoxyribose | 2) Sugar-Ribose |
| 3) Bases – A, G, C, T | 3) Bases A, G, C, U |
| 4) Transmits Traits | 4) Responsible for protein synthesis |
Question 4.
Classify the given vitamins as fat soluble and water soluble.
- Vitamin A, D, B, E, K, C
- Name a deficiency disease caused by the deficiency of Vitamin A.
- The deficiency of which vitamin is responsible for the disease Rickets?
Answer:
- Fat soluble – Vitamins A, D, E and K. Water soluble – Vitamins B and C
- Night blindness
- Vitamin D
Question 5.
Write the products obtained when glucose is treated with the following reagents?
- HF
- Bromine water
- HNO3
Answer:
- When glucose is heated with HI, n-Hexane is formed.
- When glucose is treated with bromine water, it is oxidised to gluconic acid.
- Glucose is oxidised by HNO3 to saccharic acid.
Question 6.
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer:
Starch has 2 components namely amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long unbranched chain made of α-D-(+)-glucose units held by C1 – C4 glycosidic linkage.
Amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1 – C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by C1 – C6 glycosidic linkage. Cellulose is a straight chain polysaccharide composed of only β-D-glucose units joined by C1 – C4 glycosidic linkage.
Plus Two Chemistry Biomolecules Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Amino substituted carboxylic acids are called amino acids.
- Analyse the statement and explain what are essential amino acids?
- How many essential amino acids are there?
- Give two examples of essential amino acids.
Answer:
- The amino acids which can be synthesized in our body are known as non-essential amino acids, eg. Glycine, Alanine
Those amino acids which can not be synthesized in our body and must be obtained through diet are known as essential amino acids. eg. valine, Lysine - Ten
- Valine and Lysine
Question 2.
Starch on enzymatic hydrolysis by diastase gives a reducing disaccharide ‘A’ which undergoes hydrolysis by enzyme maltase to form ‘B’ which is also a reducing sugar.
- Identify the compound ‘A’ and ‘B’ with suitable chemical equations.
- Explain the term reducing sugar.
Answer:
1. Compound A-Maltose
Compound B – Glucose
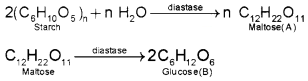
b) All those carbohydrates which contain free aldehydic or ketonic group to reduce Tollens reagent and Fehling’s solution and are called reducing sugars, e.g. Glucose, Fructose.
Question 3.
In the following table, the names of Vitamins, their sources, and deficiency diseases are tabulated in the wrong order. Match them in the correct order.
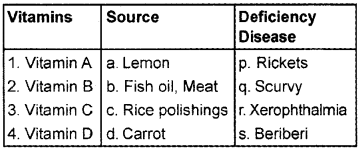
Answer:
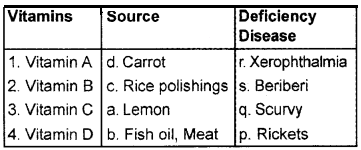
Question 4.
- Draw the pyranose structures of the α and β forms of glucose.
- Draw the furanose structures of the α and β
Answer:
1.
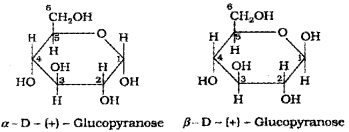
2.
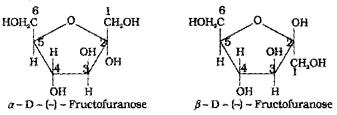
Question 5.
When egg is boiled its physical structure changes.
- Is there any change in its chemical nature?
- Mention the peculiar type of bond present in proteins.
- When egg is boiled it become hard. Why? Explain.
Answer:
- No
- Peptide bond
- This is due to denaturation of protein. On boiling egg, the soluble form of globular proteins undergo coagulation to give fibrous proteins which are insoluble in water.
Question 6.
- What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α – helix structure of proteins?
- What is nucleotide?
Answer:
1. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding between -NH group of each amino acid and carbonyl group of an adjacent turn of the helix.
2. The repeating structural units of nucleic acids are called nucleotides.
- Pentose sugar + Base → nucleoside
- Nucleoside + Phosphoric acid → nucleotide
Question 7.
- What do you mean by isoelectric point of amino acids?
- What are Zwitter ions? Give one example.
Answer:
1. The pH at which the Zwitter ions do not migrate neither towards cathode nor towards anode is known as isoelectric point of the amino acids.
2. Amino acids possess both acidic and basic group, they generally exist as dipolar ions called Zwitter ions.
e.g. glycine H3N(+) – CH2 – COO(-)
Plus Two Chemistry Biomolecules NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose.
Answer:
- Monosaccharides – Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, galactose and fructose.
- Disaccharides – Maltose and lactose.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Answer:
In oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, the two monosaccharide units are linked together by an oxide or ether linkage formed by the loss of water molecules. Such a linkage between two monosaccharide units through oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage.
Question 3.
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer:
Both starch and cellulose contain a large number of α -D(+)-glucose units. Starch consists of two components:
- Amylose which is a linear polymer and
- Amylopectin which is a branched polymer but in both the D-glucose units are linked through α -glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose with C4 of next glucose unit. In amylopectin branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.
Cellulose is only a linear polymer of D-glucose units joined through β -glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose with C4 of next glucose unit.
Question 4.
Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot obe explained by its open chain structure.
Answer:
- Glucose does not give 2,4-DNP test, Schiff’s test and it does not form the hydrogen sulphite addition product with NaHSO3.
- The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
- Glucose exists in two different crystalline forms such as α – form and β -form.
Question 5.
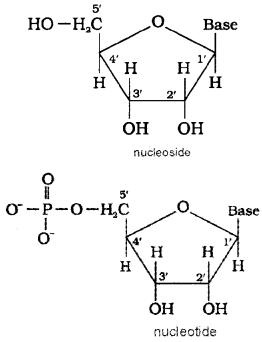
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Answer:
Nucleoside is formd by condensation of a purine or pyrimidine base with pentose sugar at position 1. When nucloeside is linked to phosphoric acid at 5 position of sugar moeity, we get a nucleotide. So a nucleoside has two units: pentose sugar and a base while a nucleotide has three units: phosphate group, pentose sugar and a base.
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 14 Biomolecules, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
