Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids is part of Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Plus Two Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The reaction ![]() is called
is called
(a) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(b) Rosenmund’s reduction
(c) HVZ reaction
(d) Cannizaro’s reaction
Answer:
(b) Rosenmund’s reduction
Question 2.
Say TRUE or FALSE:
Aldol condensation is given by all aldehydes and ketones.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
A 40% solution of _________ is called formation
Answer:
formaldehyde (HCHO)
Question 4.
Benzamide on heating with bromine and caustic alkali gives
(a) benzene
(b) methylamine and benzene
(c) aniline
(d) m-Bromobenzaldehyde
Answer:
(c) aniline
Question 5.
In the reaction ![]() the product ‘B’ is
the product ‘B’ is
(a) acetanilide
(b) glycine
(c) ammonium acetate
(d) methane
Answer:
(b) glycine
Question 6.
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of acidity.
ClCH2COOH, Cl3CCOOH, CH3COOH, Cl2HCOOH
Answer:
Cl3CCOOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH
Question 7.
Reaction of butanone with methyl magnesium bromiode followed by hydrolysis gives_________
Answer:
2 methyl -2- butanol
Question 8.
The major product of the addition of water molecule to propyne in the presence of mercuric sulphate and dil sulphuric acid is ________
Answer:
Propanone
Question 9.
One mole of propanone and one mole of formalde¬hyde are the products of ozonolysis of one mole of an alkene. The alkene is ________
Answer:
2 methyl propene
Question 10.
Which of the following is a better reducing agent for the following reduction.
RCOOH → RCH2OH
(a) SnCI2/HCI
(b) NaBH4/ether
(c) H2/pd
(d) N2H4/C2H5ONa
(e) B2H6/H3O+
Answer:
(e) B2H6/H3O+
Question 11.
The total number of acyclic structural isomers possible for compound with molecular formula C4H10O is ________
Answer:
7
Plus Two Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Reactivity of ketone is less than that of aldehyde. Why?
Answer:
Due to steric hindrance and inductive effect of alkyl group.
Question 2.
Carboxylic acid decompose into carboxylate ion and H+ ion.
- Explain this on the basis of resonating structure of carboxylic acid.
- Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidity. HCOOH, CH3COOH
- Substantiate.
Answer:
- Carboxylic acid decomposes to give proton and carboxylate ion and is stabilized by resonance. This explains the acidic character of carboxylic acid.
- CH3COOH < HCOOH
- In acetic acid the electron donating effect (+l – effect) of -CH3 group destabilises the carboxylate anion and decreases the acid strength. Whereas in formic acid the H atom has not electron withdrawing or electron donating effect.
Question 3.
What is Etard’s reaction?
Answer:
Etard’s reaction:
When toluene is oxidized using chromyl chloride, benzaldehyde is obtained.
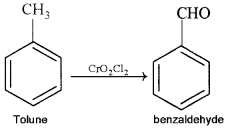
Question 4.
What is HVZ reaction? Explain.
Answer:
HVZ reaction – When a carboxylic acid is treated with red P and halogen, the α-H atoms are successively replaced by halogen.
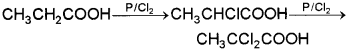
This reaction has great synthetic importance as the halogen atom can be replaced by a number of other groups giving useful products.
Question 5.
Predict the product and name the reaction:
- HCHO + NaOH → B + C
- CH3COOH + CH3OH → E
Answer:
- CH3OH + HCOONa – Cannizzaro reaction
- CH3COOCH3 – Esterification
Question 6.
Write the name of any two tests to distinguish between acetaldehyde and acetone.
Answer:
Benedict’s test, Fehling’s test – Both tests are answered by acetaldehyde and not by aceotne.
Question 7.
An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer:
From the given data it is clear that as the compound forms2, 4-DNP derivative it has /CO group. Since it reduces Tollens’ reagent therefore -CHO group is present. As it can also undergo Cannizzaro reaction therefore α -hydrogen is absent
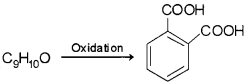
The oxidation product suggests that the compound has a benzene ring. One of the – COOH groups have been obtained by the oxidation of – CHO group and the other from alkyl group. Hence on these basis, the structure of C9H10O is
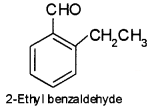
Question 8.
Write a notes on
- Reimer – Tiemann reaction
- Rosenmund Reduction
Answer:
1. Reimer – Tiemman reaction: When phenol is heated with CHCI3 at 340 K, o-hydroxy benzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde is obtained.
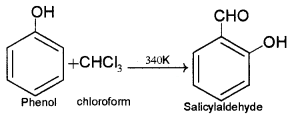
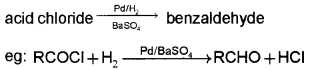
2. Rosenmund reduction: When an acid chloride is reduced by using hydrogen gas in presence of Pd and BaSO4, an aldehyde is obtained.
OR
Question 9.
Distinguish the following compounds using any one test.
H3C – CO – CH3 and CH3CH2CHO
Answer:
CH3COCH3 give Iodoform test which CH3CHO does not answer this test.
Question 10.
Aspirin is commonly used in medicine. How it is prepared? Give the equation.
Answer:
Aspirin is acetyl salicyclic acid. When salicyclic acid is treated with acetyl chloride, aspirin is obtained.
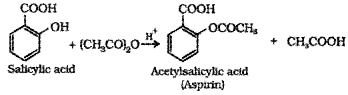
Salicylic acid + acetyl chloride → Aspirin
Question 11.
How will you prepare CH3-CO-NH2 and CH3COOCH3 from CH3COOH?
Answer:
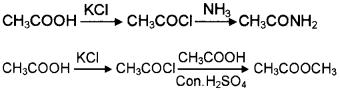
Question 12.
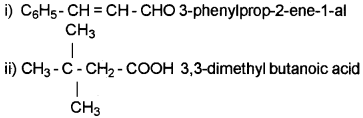
Give the IUPAC name of the following compounds.
i) C6H5CH = CHCHO
ii) (CH3)3CCH2COOH
Answer:
Question 13.
Give a test to distinguish between acetaldehyde and acetone.
Answer:
CH3 – CO – CH3 contains CH3CO – group and hence it gives iodoform test.
CH3 – CH2 – CHO does not give iodoform test.
Question 14.
Predict the major product in the following reactions:
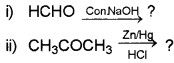
Answer:
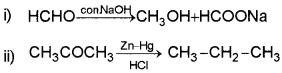
Question 15.
Distinguish between formaldehyde & acetaldehyde.
Answer:
| HCHO | CH3CHO |
| 1. It gives Cannizzaro reaction. | 1. It doesn’t give Cannizzaro reaction. |
| 2. It doesn’t give aldol condensation. | 2. It gives aldol condensation. |
| 3. It gives condensation products with NH3. | 3. It gives addition products with NH3. |
Question 16.
Which is more acidic, 2-chloropropanoic acid or 3- chloropropanoicacid? Why?
Answer:
2-chloropropanoic acid. Becasue the electron with drawing -Cl group is more closer to -COOH group in this compound.
Plus Two Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
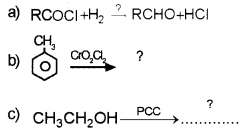
Answer:
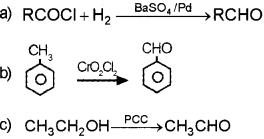
Question 2.
A student is given Tollens’ reagent for oxidation of aldehyde.
- What is Tollens’ reagent?
- Can you help him to do the experiment?
- What is the result of the experiment?
Answer:
- Tollens’ reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate solution
- Yes. To a little of the solution add Tollens’ reagent
- A black precipitate of silver or silver mirror is obtained
Question 3.
![]()
- What is the role of LiAIH4?
- Give one example of an oxidising agent?
- What is the action of a carboxylic acid with alcohol?
Answer:
- LiAIH4 is a strong reducing agent. It reduces RCOOH to 1° alcohol (RCH2OH)
- Acidified KMnO4.
- When carboxylic acid is treated with an alcohol in the presence of dehydrating agent like conc.H2SO4, an ester is formed. This is called esterification reaction.
![]()
Question 4.
What happens when primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are passed over red hot copper? Give equations.
Answer:
1° alcohol hot copper Aldehyde
2° alcohol over hot copper – Ketone
3° alcohol over hot copper- alkene
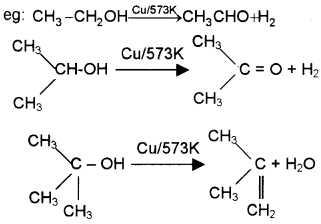
Question 5
Fill in the blanks.
Answer:
- HVZ reaction
- CH3CH3
- Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
- HCOONa + CH3OH
- Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- C6H5Cl
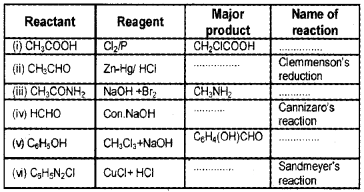
Question 6.
Draw the structure of the following derivatives.
(i) The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
(ii) Cyclopropanone oxime
(iii) Acetaldehydedimethylacetal
(iv) The semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
(v) The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
(vi) The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde
Answer:
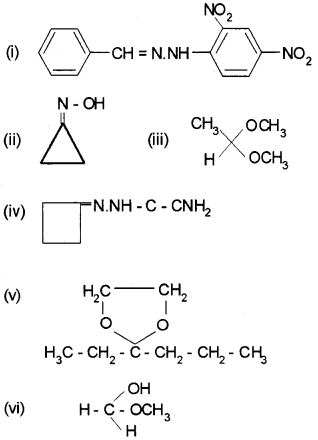
Question 7.
i) 2HCHO + NaOH → CH3OH + HCOONa
ii) 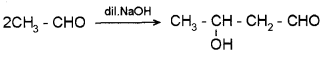
(a) Identify Cannizzaro and Aldol condensation.
(b) What is the difference between the above two reactions?
Answer:
(a) Cannizzaro reaction:
2HCHO + NaOH CH3OH + HCOONa
Aldol condensation:
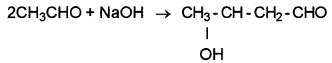
(b) Cannizzaro reaction is given by aldehydes having no α-H atom whereas aldol condensation is given by aldehydes containing α-H atom.
Question 8.
a) In a practical class a group of students heated ethanal with NaOH. Another group heated methanal with conc.NaOH.
i) Identify the products in each reaction with equation.
ii) Name the reactions.
b) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones. Comment on the statement.
Answer:
a)
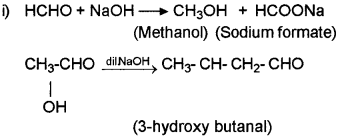
ii) The first reaction is Cannizarro reaction and the second reaction is aldol condensation.
b) Due to the ‘+l’ effect and steric hindrance of surrounding alkyl group ketones are less reactive than aldehydes.
Plus Two Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
i) Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidic strength and justify your answer.
CH3COOH, CHCI2COOH, CH2CICOOH, CCI3COOH
ii) Suggest a method to convert acetic acid to chloroacetic acid. Name the reaction and write the chemical equation.
Answer:
i) CH3COOH < CH2CI-COOH < CHCI2COOH < CCI3COOH This is due to the electron withdrawing character of chlorine.
ii) HVZ reaction – When a carboxylic acid is treated with red P and halogen, the a-H atoms are successively replaced by halogen.
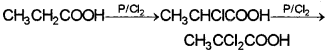
This reaction has great synthetic importance as the halogen atom can be replaced by a number of other groups giving useful products.
Question 2.
a) Which of the following carbonyl compounds answer aldol condensation reaction and give equation.
HCHO, CH3CHO, CCI3CHO, C6H6-CHO
b) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of acidity:
CH3COOH, CH2CICOOH, CH3-CH2-COOH, C6H5-COOH
Answer:
a) Among these compounds only CH3CHO answer aldol condensation reaction. Others will not answer this reaction because they have no α – hydrogen atom.
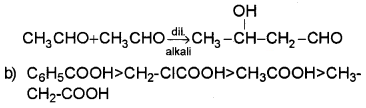
Question 3.
- Aldehydes and ketones are carbonyl compounds Give a test for identification of aldehydes.
- Acidic strength is related to the stability of carboxylate anion. Which acid of each pair is stronger?
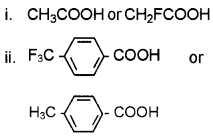
Answer:
1. Benedict test. Benedict reagent is a mixture of sodium carbonate and sodium citrate. This on reaction with aldehyde gives red precipitate of Cu2S.
2. Acidic strength is related to the stability of carboxylate anion. Acid of each pair is stronger:
i) CH2FCOOH. This is due to the high electron with drawing effect of F.
![]()
This is due to the high electron with drawing effect of the -CF3 group.
Question 4.
Substituents on carboxylic acids have much effect on their acidity. Substantiate the statement with the following examples.
a) HCOOH, CH3COOH, CH2CICOOH
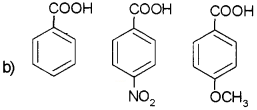
Answer:
CH2CICOOH > HCOOH > CH3COOH
The methyl group will intensify the negative charge on the carboxylate ion and destabilise it as compared to formate ion. So HCOOH is stronger than CH3COOH. The electron withdrawing effect of a Cl makes chloroacetic acid stronger than HCOOH and CH3COOH.
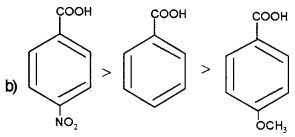
In the case of aromatic carboxylic acids, presence of electron withdrawing groups at ortho and para position increases their acidity while presence of electron donating groups decreases their acidity.
In 4-nitro benzonic acid acid strength is greater than that of benzoic acid due to the electron withdrawing nature of -NO2 group while in 4-methoxy benzoic acid acid strength decreases due to the electron donating nature of the methoxy group.
Question 5.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between each of
the following pair of organic compounds.
- Propanal and Propanol
- Propanone and Propanal
Answer:
1. Propanal is an aldehyde and it gives a silver mirror with Tollens’ reagent while propanol is an alcohol and will not answer Tollens’test.
2. Propanone gives yellow precipitate of iodoform on reaction with I2 and NaOH while propanal does not give iodoform test. OR Propanal gives silver mirror with Tollens’ reagent while propanone does not give silver mirror test.
Question 6.
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
- Cyanohydrin
- Acetal
- Semicarbazone
- Aldol
- Hemiacetal
- Oxime
- Ketal
- Imine
- 2,4-DNP-derivative
- Schiff’s base
Answer:
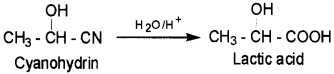
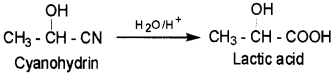
1. Cyanohydrin – It is a compound which contain both OH and CN groups. For example, Lactic acid can be obtained by hydrolysis of cyanohydrin.
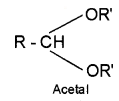
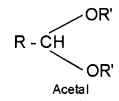
2. Acetal – compounds formed by the reaction of aldehydes with monohydric alcohols in presence of dry HCI gas.
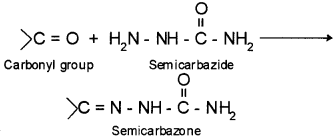
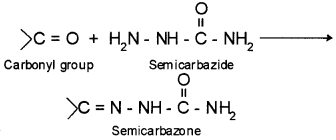
3. Semicarbazone – the product of carbonyl compounds with semicarbazide is known as semicarbazone.
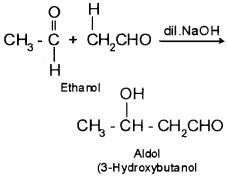
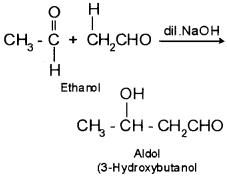
4. Aldol – It is a condensation product of aldehydes or ketones having atleast one α – hydrogen atom with dilute alkali as catalyst.
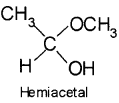
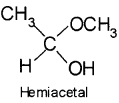
5. Hemiacetal – It is a compound which contains an ether as well as alcohol functional group. For example, methoxyethanol is a hemiacetal.
6. Oxime – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine.
![]()
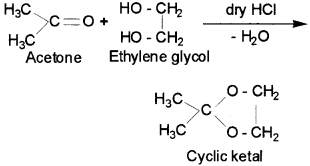
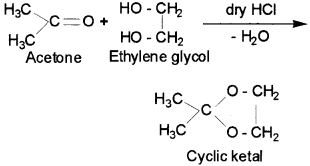
7. Ketal – It is a cyclic compound obtained by reaction of aceone with ethylene glycol.
8. Imine – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with ammonia.
![]()
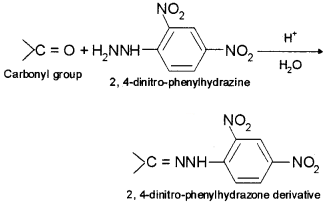
9. 2, 4-DNP derivative – 2, 4-phenylhydrazone (DNP) is the addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.
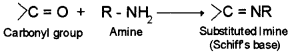
10. Schiff’s base – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with amine.
Question 7.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature.
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
- CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CI
- CH3CH=CHCHO
- CH3COCH2COCH3
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
- (CH3)2CCH2COOH
- OHCC6H5CHO-p
Answer:
- 4-Methylpentanal
- 6-Chloro-4-ethylhexan-3-one
- But-2-enal
- Pentane-2,4-dione
- 3, 3, 5-Trimethylhexane-3-one
- 3, 3-Dimethylbutanoicacid
- Benzene 1, 4-dicarbaldehyde
Question 8.
- What is the relation between an electron donating group and acidic character?
- How carboxylic acids maintain their acid character?
Answer:
- Electron donating group decreases the acid character.
- Carboxylic acid decomposes to give proton and carboxylate ion and is stabilized by resonance. This explains the acidic character of carboxylic acid.

Question 9.
Predict the product formed when cyclohexane carbaldehyde reacts with following reagents:
i) PhMgBr and then H3O+
ii) Tollens’reagent
iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
iv) Excess ethanol and acid
v) Zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid
Answer:
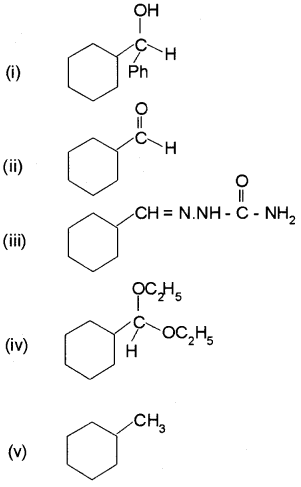
Plus Two Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case
- Cyanohydrin
- Acetal
- Semicarbazone
- Aldol
- Hemiacetal
- Oxime
- Ketal
- Imine
- 2,4-DNP-derivative
- Schiff’s base
Answer:
1. Cyanohydrin – It is a compound which contain both OH and CN groups. For example, Lactic acid can be obtained by hydrolysis of cyanohydrin.
2. Acetal – compounds formed by the reaction of aldehydes with monohydric alcohols in presence of dry HCI gas.
3. Semicarbazone – the product of carbonyl compounds with semicarbazide is known as semicarbazone.
4. Aldol – It is a condensation product of aldehydes or ketones having atleast one α – hydrogen atom with dilute alkali as catalyst.
5. Hemiacetal – It is a compound which contains an ether as well as alcohol functional group. For example, methoxyethanol is a hemiacetal.
6. Oxime – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine.
![]()
7. Ketal – It is a cyclic compound obtained by reaction of aceone with ethylene glycol.
8. Imine – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with ammonia.
![]()
9. 2, 4-DNP derivative – 2, 4-phenylhydrazone (DNP) is the addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.
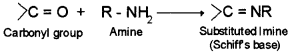
10. Schiff’s base – Addition compound formed by the reaction of aldehyde or ketone with amine.
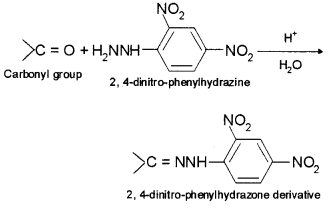
Question 2.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature.
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
- CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CI
- CH3CH = CHCHO
- CH3COCH2COCH3
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
- (CH3)3CCH2COOH
- OHCC6H5CHO-p
Answer:
- 4-Methylpentanal
- 6-Chloro-4-ethylhexan-3-one
- But-2-enal
- Pentane-2,4-dione
- 3, 3, 5-Trimethylhexane-3-one
- 3, 3-Dimethylbutanoicacid
- Benzene 1, 4-dicarbaldehyde
Question 3.
Draw the structure of the following compounds
(i) 3-Methylbutanal
(ii) p-Nitropropiophenone
(iii) p-methylbenzaldehyde
(iv) 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one
(v) 3-bromo-4-phenylpentanoicacid
(vi) 4-Chloropentan-2-one
(vii) p, p-Dihydroxybenzophenone
(viii) Hex-2-en-4-ynoicacid
Answer:
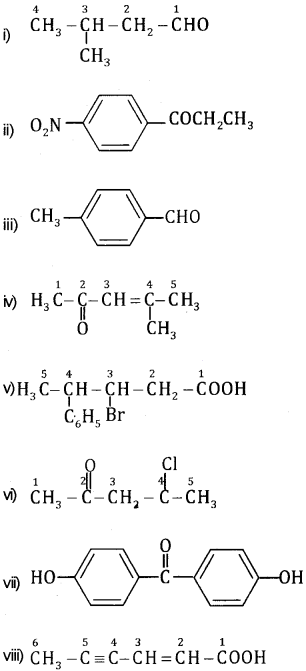
Question 4.
An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzene dicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer:
From the given data it is clear that as the compound forms 2, 4-DNP derivative it has >CO group. Since it reduces Tollens’ reagent -CHO group is present. As it can also undergo Cannizzaro reaction α- hydrogen is absent.
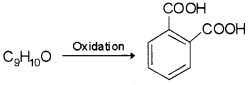
The oxidation product suggests that the compound has a benzene ring. One of the – COOH groups have been obtained by the oxidation of – CHO group and the other from alkyl group. Hence on these basis, the structure of C9H10O is
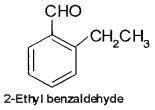
Question 5.
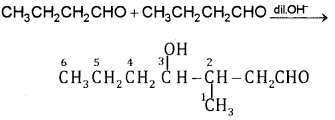
Write structural formulas and names of the four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde served as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
Answer:
i) Propanal as electrophile as well as nucleophile
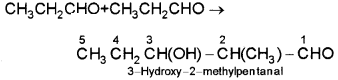
ii) Propanal as electrophile and butanal as nucleophile
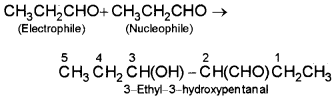
iii) Butanal as electrophile and propanal as nucleophile
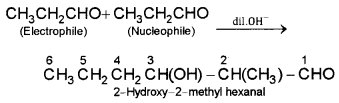
iv) Butanal as electrophile as well as nucleophile
Question 6.
Predict the product formed when cyclohexane carbaldehyde reacts with following reagents:
i) PhMgBr and then H3O+
ii) Tollens’reagent
iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
iv) Excess ethanol and acid
v) Zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid
Answer:
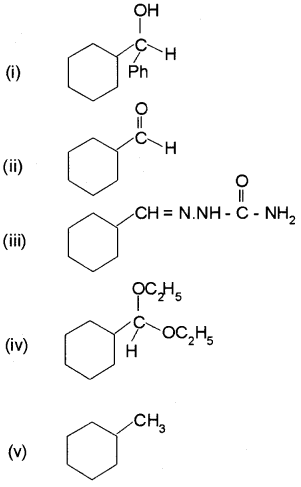
Question 7.
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between
- Propanal and propanone
- Acetophenone and Benzophenone
- Phenol and Benzoic acid
- Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
- Ethanal and propanal
Answer:
1. Propanal and propanone:
Propanal and propanone can be distinguished by iodoform test as it is given by propanone and not by propanal
Propanone reacts with hot NaOH/I2 to give yellow precipitate of iodoform.
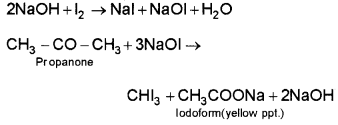
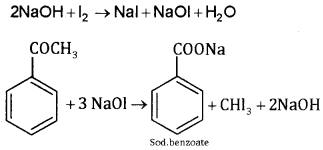
2. Acetophenone and benzophenone:
Acetophenone gives iodoform test but benzophenone does not respond.
3. Phenol and benzoic acid:
This can be distinguished by treating FeCI3 solution. Phenol gives violet colour with FeCI3 solution while benzoic acid gives buff colured precipitate.
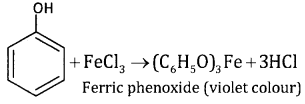
4. Benzaldehyde and acetophenone:
Acetophenone responds to iodoform test while benzaldehyde does not.
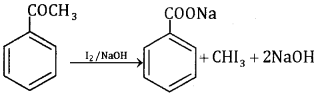
5. Ethanal and propanal:
Ethanal gives yellow ppt. of iodoform with an alkaline solution of iodine (iodoform test)
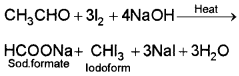
Propanal does not give yellow ppt.
![]()
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
