Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers is part of Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers.
| Board | SCERT, Kerala |
| Text Book | NCERT Based |
| Class | Plus Two |
| Subject | Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions |
| Chapter | Chapter 11 |
| Chapter Name | Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers |
| Category | Kerala Plus Two |
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Plus Two Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is most acidic?
(a) H20
(b) CH3OH
(c) C2H5OH
(d) CH3CH2CH2OH
Answer:
(a) H2O
Question 2.
Propan-1 -ol on reaction with conc.H2SO4 at 413 K gives _____________
Answer:
1 -Propoxy propane
Question 3.
Which of the following alcohols can be obtained from HCHO?
(a) CH3OH
(b) C2H5OH
(c) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 4.
Phenol can be distinguished from ethyl alcohol by all reagents except
(a) NaOH
(b) Na
(c) Br2/H2O
(d) FeCl3
Answer:
(b) Na
Question 5.
Anisole on reaction with HI forms
(a) phenol and methyl iodide
(b) iodobenzene and methanol
(c) benzene and methyl iodide
(d) phenol and methanal
Answer:
(a) phenol and methyl iodide
Question 6.
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of acidity: Phenol, Alcohol, and Water.
Answer:
Alcohol < Water < Phenol
Question 7.
Phenol is distinguished from ethanol by the following reagents except.
(a) Iron
(b) Sodium
(c) Bromin
(d) NaOH
Answer:
(b) Sodium
Question 8.
Phenol can be converted to o-hydroxy benzaldehyde by
Answer:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Question 9.
4-methoxy acetophenone can be prepared from anisol by ______________
Answer:
Friedel crafts reaction.
Question 10.
Which of the following does not answer iodoform test?
(a) 1-propanol
(b) Ethanol
(c) 2 propanol
(d) Ethanal
Answer:
(a) 1- propanol
Question 11.
Chlorination of toluene in presence of light and heat followed by treatment with aqeous KOH gives ________
Answer:
Benzyl alcohol.
Plus Two Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Reaction of alcohol with metallic sodium is used as a test for alcohol. Substantiate this statement with the help of an equation.
Answer:
Alcohol reacts with metallic Na to form sodium alkoxide with the liberation of H2.
ROH + Na → RONa + 1/2 H2
Question 2.
Ethyl alcohol gives iodoform test. Methyl alcohol does not give iodoform test.
- Do you agree with this?
- If yes or no, substantiate your view.
- How can you distinguish between 1 -butanol and 2-butanol?
Answer:
1. Yes.
2. Compounds containing CH3CO- group and CH3CH(OH)- group on reaction with iodine and alkali give yellow colour of iodoform. Ethanol contains CH3CH (OH) – group.
3. 2-Butanol gives iodoform test as it contains CH3CH(OH)-group, whereas 1-Butanol does not answer iodoform test.
Question 3.
When an organic compound is treated with neutral ferric chloride a violet colour is obtained. What will be the compound? Explain.
Answer:
Phenol. Phenol forms a violet-coloured water soluble complex with ferric chloride.
Question 4.
– O – is the functional group of ether. Classify the following into two groups with an appropriate heading.
CH3-O-CH3, CH3-O-C2H5, C2H5-O-C2H5, C6H5– O – CH3.
Answer:
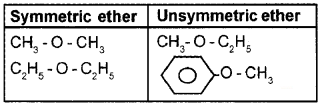
Question 5.
Explain how does the -OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution reaction?
Answer:
In phenol, the -OH group is directly attached to a carbon of benzene ring. The lone pair of oxygen participates in resonance with the benzene ring. As a result, electron density on benzene ring increases making it easier to attack by an electrophile.
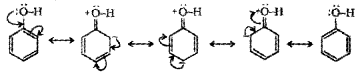
Question 6.
Write down the equations for the following conversions using Grignard reagent?
Methanal → Ethanol
Ethanal → 2-Propanol
Answer:
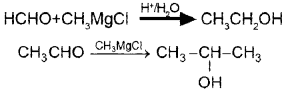
Question 7.
Explain why propanol has higher boiling point than that of hydrocarbon, butane?
Answer:
Propanol has higher boiling point than butane because it has stronger interparticle forces. In propanol intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present whereas in butane intermolecular forces are weak van der Waals’ forces. A lot of heat is required to break intermolecular hydrogen bonding among propanol molecules.
Question 8.
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by stream distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
Answer:
Ortho-Nitrophenol is steam volatile because in it there is intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
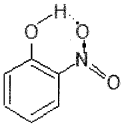
Due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding, the intermolecular forces in ortho-nitrophenol are weaker than that in para-nitrophenol (which has intermolecular hydrogen bonding) and hence it undergoes less association.
Question 9.
Give reason for higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxy methane.
Answer:
In ethanol the intermolecular forces are hydrogen bonds whereas in methoxymethane the intermolecular forces are dipole-diple forces. Since the intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than those in methoxymethane it has higher boiling point than methoxymethane.
Question 10.
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitro phenols by steam distillation, name the isomer, which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
Answer:
Ortho-Nitro phenol exhibit intramolecular hydrogen bonding and para-Nitro phenol exhibit intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The ortho isomer is steam volatile because there is not intermolecular association.
Plus Two Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a notes on:
- Rectified Spirit
- Power Alcohol
- Denatured Spirit
Answer:
1. 95.6% ethyl alcohol is known as a rectified spirit.
2. A mixture of ethyl alcohol and gasoline can be used as a fuel in the internal combustion engine. It is known as power alcohol.
3. Commercial alcohol is made unfit for drinking by adding certain substances like pyridine, methanol etc. Spirit thus obtained is called denatured spirit.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
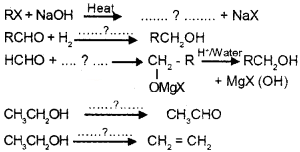
Answer:
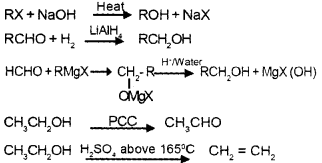
Question 3.
Ethyl alcohol can be prepared by fermentation of molasses.
- What do you mean by fermentation?
- Explain the process.
- What do you mean by ‘wash’?
Answer:
1. Fermentation is the process of breaking up of large molecules into small molecule in the presence of biological catalyst called enzymes.
2. Molasses is the mother liquor left behind after the crystallisation of cane sugar from sugar cane juice. It is 40% sucrose solution. First it is diluted to 10% solution. Then yeast is added. Temperature of the system is kept at 305 K. The following reactions will take place.
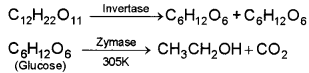
3. 8-10% ethyl alcohol is known as ‘wash’.
Question 4.
Raju prepared soap in the chemistry lab. A liquid remained after the preparation. He argued that it was useless.
- Do you agree with him? Why?
- How can you prepare glycerol from spentlye?
Answer:
- No. It can be used to prepare glycerol.
- Spentlye contains unreacted alkali, glycerol, water, NaCI, and soluble soap. It is first treated with acid to remove alkali, then with aluminium sulphate to remove soluble soap. It is then evaporated under reduced pressure to remove NaCI.
The resulting solution is then decolorised using animal charcoal, Then the solution is distilled under reduced pressure to remove water. In this way we get glycerol.
Question 5.
When an old sample of ether was heated, it exploded.
- What is the reason for this phenomenon?
- How can you detect peroxide content in ether?
- How can we remove peroxide from old sample of ether?
Answer:
- Due to the formation of peroxide.
- Presence of peroxide can be tested by adding ferrous salt solution followed by addition of KCNS solution. Formation of blood red colour indicates the presence of peroxide.
- The peroxide can be removed by washing with ferrous salt solution.
Question 6.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Because of the presence of O-H group in them, alcohols are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules whereas hydrocarbons cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. As a result, alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Question 7.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
Answer:
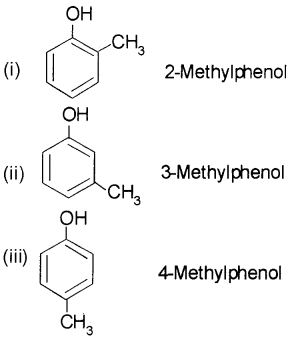
Question 8.
Explain why ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol?
Answer:
ortho-Nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho- methoxyphenol because nitro group by its electron withdrawing resonance effect stabilises the phenoxide ion whereas methoxy group by its electron releasing effect destabilises the phenoxide ion. Greater the stability of the phenoxide ion, greater is the dissociation of phenol and greater is its acid strength.
Question 9.
With the help of a mixture of con. HCI and ZnCI2 how can you distinguish between 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols.
Answer:
- 1° alcohol + Lucas reagent → no reaction
- 2° alcohol + Lucas reagent → turbidity within five minutes
- 3° alcohol + Lucas reagent → turbidity occurs immediately
Lucas reagent anhydrous ZnCI2/HCI
Plus Two Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Match the following:
| A | B |
| Oxidising Agent | Lucas Test. |
| Dehydrogenation | LiAIH4. |
| Anhydrous ZnCI2, HCI | Copper at 573K. |
| Reducing Agent | Acidified KMnO4. |
Answer:
| A | B |
| Oxidising Agent | Acidified KMnO4. |
| Dehydrogenation | Copper at 573K. |
| Anhydrous ZnCI2, HCI | Lucas Test. |
| Reducing Agent | LiAIH4. |
Question 2.
a) Alcohols are having high boiling points than corresponding alkyl halides and ethers. Why?
b) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. Give the reason.
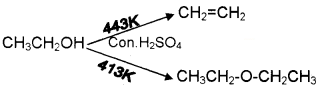
c) Predict the products :
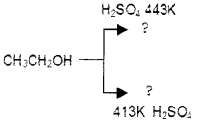
Answer:
a) Due to the presence of polar hydroxyl group alcohols can associate through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
b) Phenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance while alkoxide ion has no resonance stabilisation.
c)
Question 3
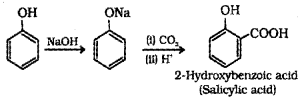
- Phenol is acidic even though it has no carboxylic group, why?
- Convert phenol to salicylic acid and name the reaction.
Answer:
1. By the removal of a proton from phenol a phenoxide ion is obtained. It is stabilised by resonance. Hence phenol acts as an acid.
2.
Question 4.
1. Compare the solubility of diethyl ether and n-butane in water.
2. Give the product(s) from the reaction of one mole of diethyl ether with
- one mole of conc. HI and
- excess of HI.
Answer:
1. Diethyl ether being weakly polar is capable of forming intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water. Hence, diethyl ether is soluble in water while n-butane is not.
2. The product(s) from the reaction of one mole of diethyl ether.
- C2H5OH and C2H5I
- 2C2H5I
Question 5.
Identify X and Y.
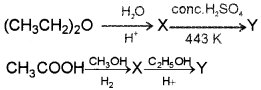
Answer:
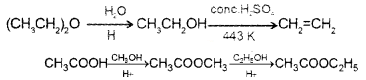
Question 6.
1. Boiling point depends on the inter molecular hydrogen bonding.
- Ethanol and propane have comparable molecular masses but their boiling points differ widely. Why?
2. Williamson synthesis is an important method of ether synthesis. Which of the following reactions is better for ether synthesis? Justify.
Answer:
1. Ethanol molecules are associated by intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Ethanol molecules are associated by intermolecular hydrogen bonding. This is absent in propane. So Ethanol has higher boiling point.
2. (CH3)3C-ONa + CH3-Br is better. The tertiary alkyl halide undergoes elimination in presence of base to form alkene.
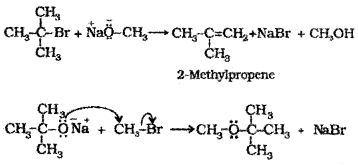
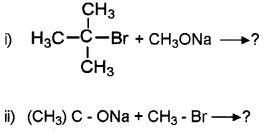
Question 7.
Chloro methane reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form methanol.
- What happens when chlorobenzene reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide? Justify.
- Write the reaction by which chlorobenzene can be converted to phenol.
Answer:
- No reaction. This is due to sp2 state of carbon to which CI is attached, less polarity of C-X bond and resonance stabilisation.
- Dow’s process.
When chlorobenzene is heated with sodium hydroxide solution at 623 K under a pressure of 200 atm in the presence of copper catalyst, sodium phenoxide is obtained. This on hydrolysis gives phenol.
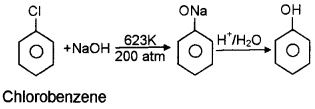
Question 8.
Phenol exhibit acidic character.
- Why phenol exhibit acidic character?
- Explain it with the help of resonating structure of phenoxide ion.
Answer:
- Phenol can donate proton and phenoxide ion thus formed is stabilized by resonance.
- The resonating structure of phenoxide ion is given below.
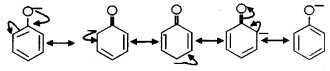
Question 9.
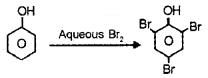
What is the action of phenol with
- Aqueous Br2?
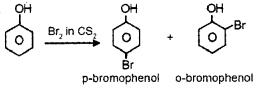
- Br2 in CS2?
- Nitrating mixture?
- dil. HNO3?
Answer:
1. Phenol on action with aqueous Br2 gives 2, 4, 6,- tribromophenol.
2. Phenol on action with Br2 in CS2 gives o- bromophenol and p-bromophenol.
3.
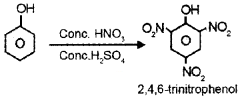
4.
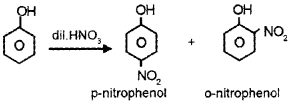
Question 10.
Write notes on
a) Kolbe’s reaction
b) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Answer:
a) Kolbe’s reaction: When Sodium phenoxide is heated with CO2 at 400 K and under a pressure 6-7 atm, sodium salicylate is obtained. This on hydrolysis gives ortho-hydroxy benzoic acid or salicylic acid.
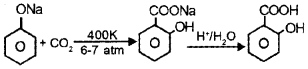
Reimer – Tiemman reaction: When phenol is heated with CHCI3 at 340 K, o-hydroxy benzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde is obtained.
Question 11.
- Fill in the blanks:
CH3CH2OH + SOCI2 → CH3CH2CI+ …?… +….?…. - This method is used to prepare extra pure alkyl halide. Do you agree? Why?
Answer:
- CH3CH2OH + SOCI2 -> CH3CH2CI + SO2 + HCI
- Yes. The by products are escapable gases. Hence, the reaction gives pure alkyl halides.
Question 12.
1. Arrange the compounds in the increasing order of their strength.
- 4-Nitro phenol
- Phenol
- Propan-1-ol
- 4-Methyl phenol.
2. You are given benzene, conc.H2SO4, and NaOH. Prepare phenol using these compounds.
Answer:
1. 4-Nitrophenol > Phenol > 4-Methylphenol > 1- Propanol. Presence of electron with darwing groups at ortho and para positions increases the acidic strength of substituted phenols.
2. By the action of benzene with conc.H2SO4 & NaOH, sodium benzene sulphonate is formed. This on acidification gives phenol.
Plus Two Chemistry Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain why propanol has higher boiling point than that of hydrocarbon, butane?
Answer:
Propanol has higher boiling point than butane because it has stronger interparticle forces. In propanol intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present whereas in butane intermolecular forces are weak van der Waals’ forces. A lot of heat is required to break intermolecular hydrogen bonding among propanol molecules.
Question 2.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Because of the presence of O-H group in them, alcohols are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules whereas hydrocarbons cannot form hydrogen bonds with water. As a result, alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Question 3.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
Answer:
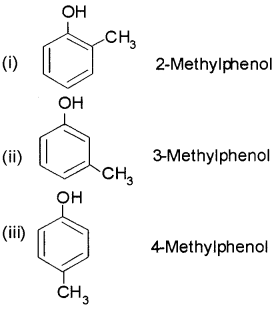
Question 4.
Explain why ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxy phenol?
Answer:
ortho-Nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho methoxy phenol because nitro group by its electron withdrawing resonance effect stabilises the phenoxide ion whereas methoxy group by its electron releasing effect destabilises the phenoxide ion. Greater the stability of the phenoxide ion, greater is the dissociation of phenol and greater is its acid strength.
Question 5.
Give IUPAC names of the following ethers:
i) C2H5OCH2-CH(CH3)CH3
ii) CH3OCH2CH2CI
iii) O2N-C6H4-OCH3(p)
iv) CH3CH2CH2OCH3
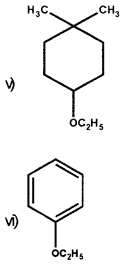
Answer:
i) 1-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
ii) 2-Chloro-1-methoxyethane
iii) 4-Nitroanisole
iv) 1-Methoxypropane
v) 1-Ethoxy-4, 4-dimethyl cyclohexane
vi) Ethoxybenzene
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
