Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes is part of Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes
Plus Two Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Alcoholic KOH is a specific reagent for
(a) dehydration
(b) dehalogenation
(c) dehydrohalogenation
(d) dehydrogenation
Answer:
(c) dehydrohalogenation
Question 2.
Chloroform is slowly oxidised by air in the presence of light to an extremely poisonous gas called ………………
Answer:
carbonyl chloride/phosgene
Question 3.
Which of the following represents a gem di halide?
(a) ethylene dichloride
(b) 2,2-dichloropropane
(c) 1,3-dichloropropane
(d) 1,2-dichloropropane
Answer:
(b) 2,2-dichloropropane
Quesiton 4.
![]() Here ‘A’ is
Here ‘A’ is
(a) phenol
(b) sodium phenoxide
(c) benzene
(d) cyclohexyl chloride
Answer:
(b) sodium phenoxide
Question 5.
There are _________ structural isomers of C4H9Br.
Answer:
Four
Question 6.
Name the insecticide prepared from chloral and chloro benzene.
Answer:
DDT
Question 7.
The reaction between arylhalide and alkylhalide in the presence of sodium and dry ether.
Answer:
Wurtz-Fittig reaction
Question 8.
Name the substance which is used as anaesthetic.
Answer:
Chloroform
Question 9.
Name an alkyl magnesium halide.
Answer:
Methyl magnesium chloride (CH3MgCI) – Grignard reagent
Question 10.
Compounds in which the halogen atom is directly attached to an aromatic ring carbon.
Answer:
Aryl halides
Question 11.
Even though alkylhalides are polar in nature, they are insoluble in water. Comment on it.
Answer:
This is because alkylhalides can neither make or break hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Question 12.
From the following select those compounds which are used for the preparation of alkyl halide?
| NH3, SOCI2, Na, aq.KOH, HCI, alc.KOH, CH3-CH2-CI, anhyd.ZnCI2. |
Answer:
SOCI2, HCI, and ZnCI2
Question 13.
When (-) 2methyl butan-1-ol is heated with con. HCI +1-chloro-2 methyl butane is obtained. This reaction is an example of
(a) retension
(b) invission
(c) racemisation
(d) resolution
Answer:
(a) retension
Question 14.
If alkaline hydrolysis of a tertiary alkyl halide by aqeous alkali, if concentration of alkali is doubled then the reaction rate at constant temperature will be ___________
Answer:
will be tripled.
Question 15.
The organic compound used as feedstock in the synthesise of chlorofluorocarbon is ___________
Answer:
CCI4
Question 16.
DDT is prepared from _____________
Answer:
Chlorobenzene and B.H.C
Question 17.
Chlorination of benzene in the presence of halogen is an example of ____________
Answer:
aromatic electrophilic substitution
Plus Two Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the preparation of extra pure alkyl halide from ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
When ethyl alcohol is heated with thionyl chloride, chloroethane is obtained. Here the byproducts are in gaseous state and hence this method is used for the preparation of extra pure alkyl halide.
CH3-CH2-OH + SOCI2 → CH3CH2CI + HCI + SO2
Question 2.
A student was treating iodoform with silver nitrate and he got yellow precipitation. Then he used chloroform instead of Iodoform.
- Will he get the earlier result?
- Why?
Answer:
- No
- C-I bond in iodoform is weaker than C-CI bond of chloroform. So C-I bond of iodoform is easily broken to form yellow precipitate of AgI when heated with AgNO3 solution.
Question 3.
| Choral, Sodium carbonate, Bleaching power, Iodine, Ethyl alcohol. |
From the box, write the raw materials of chloroform and Iodoform.
Answer:
Chloroform – ethyl alcohol and bleaching powder Iodoform – Sodium carbonate, ethyl alcohol and iodine
Question 4.
During a class room discussion a student 1 argued: “When chlorobenzene is allowed to react with metallic sodium in the presence of dry ether medium, diphenyl is obtained”. Then student 2 countered: “This reaction will take place in the presence of ale. KOH”.
- Whom you will support?
- Name the reaction? Explain it.
Answer:
- Student 1
- Fittig reaction
When aryl halide is allowed to heat with sodium in dry ether medium, diaryl is obtained, or
![]()
Question 5.
Analyse the following statements:
Statement 1: Alkyl halides are polar compounds.
Statement 2: Alkyl halides are insoluble in water because alkyl halides are non-polar compounds. What is your opinion? Explain it.
Answer:
Even though alkylhalides are polar compounds, they are insoluble in water. Because they can neither form hydrogen bonds with water nor break the hydrogen bonds existing between water molecules.
Question 6.
Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
- CH2CI2
- CHCI3
- CCI4
Answer:
Dipole moment of CH2CI2 (1.60 D) is the highest. The dipole moment of CCI4 is zero while that of CHCI3 is 1.03 D. The dipolement of CHCI3 is less than that of CH2CI2 because the bond dipole of third C-CI bond opposes the resultant of bond dipoles of the other two C-CI bonds.
Question 7.
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9CI in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Answer:
Since the hydrocarbon gives only one monochloro compound, it indicates that all the hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon are equivalent. Thus, the compound is cyclopentane.
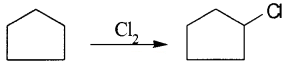
Question 8.
Which of the following has the highest dipole moment? CH2CI2, CHCI3, CCI4. Justify.
Answer:
The dipole moment of CH2CI2 (1.6 D) is the highest. The dipole moment of CCI4 is zero while that of CHCI3 is 1.03 D. The dipole moment of CHCI3 is less than that of CH2CI2 because the bond dipole of third C-CI bond opposes the resultant of bond dipoles of the other two C-CI bonds.
Question 9.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by SN2 reaction mechanism? Justify your answer. CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-Br or CH3-CH2-CH(Br)-CH3
Answer:
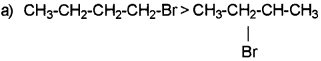
Presence of bulky groups around carbon atoms induce an inhibitory effect. Bulky group hinders the approaching nucleophiles in SN2 mechanisam.
Question 10.
Explain the stereochemical aspects of SN1 and SN2 reactions selecting suitable example.
Answer:
SN1 reaction:
In the case of optically active alkyl halides, SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemisation. This is because the attack of the nucleophile may be accomplished from either side resulting in a mixture of products, one having the same configuration and the other having opposite configuration.
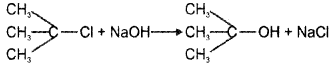
SN2 reaction:
In the case of optically active alkyl halides, there is inversion of configuration. This is because the nucleophile attaches itself on the side opposite to the one where the halogen atom is present
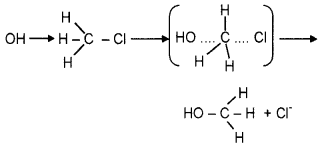
Question 11.
Arrange the following compounds in the order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement. 2-Bromo-2-methyl butane, 1-Bromopentane 2-Bromopentane
Answer:
1-Bromopentane > 2-Bromo-pentane > 2-Bromo-2- methyl butane
Question 12.
What happens when methyl bromide is treated with sodium in presence of dry ether? Write the chemical equation and name the reaction.
Answer:
Ethane is formed.
![]()
called Wurtz reaction.
Question 13.
Chloroform is stored in black coloured bottles. Why?
Answer:
In presence of sunlight chloroform undergoes oxidation to form carbonyl chloride (phosgene).
Plus Two Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Raju heated the test tube containing ale. KOH and primary amine with one compound. A foul smell is obtained.
- What is the compound?
- Name the foul smelling product obtained.
- Name the reaction.
Answer:
- Chloroform
- Isocyanide/Carbyl amine
- Carbyl amine reaction/lsocyanide test
Question 2.
Nitration is one of the ring substitution reactions.
- How it will be carried out?
- What are the products obtained when chloro-benzene is heated with the nitrating mixture?
- What is the difference if the same compound is heated with fuming H2SO4?
Answer:
1. By heating with nitrating mixture (mixture of conc.HN03 and conc.H2O4)
2. A mixture of 1-Chloro-2-nitrobenzene (minor product) and 1-Chloro-4-nitrobenzene (major product) is obtained.
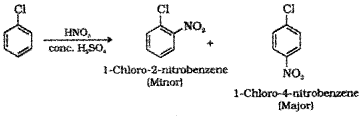
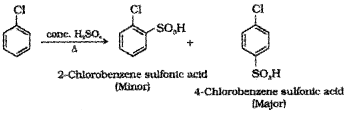
3. If chloro benzene is heated with fuming H2So4 sulphonation will take place resulting in the formation of a mixture of 2-Chlorobenzene sulphonic acid (minor product) and 4- Chlorobenzene sulphonic acid (major product).
Question 3.
Consider the reaction: RX + Mg → RMgX
- Identify the compound ‘RMgX’.
- Explain the reaction.
Answer:
- Grignard Reagent
- When alkyl halides are treated with magnesium in the presence of dry ether, alkyl magnesium halide is obtained.
![]()
Question 4.
Chloroform kept in brown coloured bottles filled up to the neck.
- What is the reason for this?
- Few drops of 1% ethyl alcohol is added to chloroform to be kept for long. Give reason.
Answer:
1. In the presence of sunlight chloroform undergoes oxidation to form carbony chloride or phosgene, a highly poisonous gas.
![]()
This reaction can be avoided by storing it in dark bottles, completely filled upto brim. The use of brown bottles cuts off active light radiations and filling upto brim keeps out air. So chloroform is kept in brown bottles.
2. Addition of a little ethanol fixes the toxic COCI2 as non-poisonous diethyl carbonate.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks:
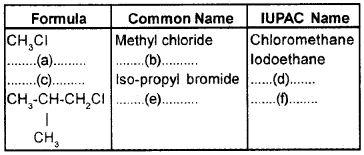
Answer:
- CH3CH2I
- Ethyl Iodide
- CH3-CHBr-CH3
- 2-Bromopropane
- Iso-butyl chloride
- 1-Chloro-2-methylpropane
Question 6.
In a Chemistry class, teacher explained that when benzene diazonium chloride is allowed to react with cuprous chloride and HCI, Chloro benzene is obtained. Then teacher asked
- If we use copper powder instead of cuprous chloride. What will be the product?
- Write the name of the reaction.
- Write the equation which shows the reaction between benzene diazonium chloride with copper powder and HCI.
Answer:
1. Chlorobenzene is obtained.
2. Gattermann reaction.
3.
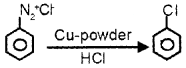
Question 7.
In a Lab, one student took a compound in test tube and he added iodine and alkali. He notices a yellow precipitate.
- Write the name of the test.
- Which type of compounds give this test?
- According to the above answer, ethyl alcohol or methyl alcohol, which one gives this test?
Answer:
- Iodoform test
- Iodoform test is given by those compounds which are having CH3CO – group or CH3CHOH group.
- Ethyl alcohol gives Iodoform test becuase it has CH3CHOH group.
Question 8.
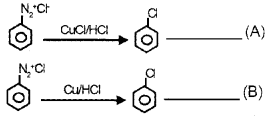
For the preparation of chlorobenzene, Nikhil wrote the equation ‘A’ and Nishanth wrote the equation ‘B’.
- Which of the above equation is correct? Why?
- Write the name of the reactions ‘A’ and ‘B’
- Explain any one reaction.
Answer:
- Both the reactions (A) and (B) are correct.
- (A) -Sandmeyer reaction (B) – Gattermann reaction
- Sandmeyer reaction – When benzene diazonium chloride is allowed to react with cuprous chloride and HCI, chlorobenzene is obtained, benzene diazonium chloride + cuprous chloride
Question 9.
a. In the following pairs of compounds which would undergo SN2 reaction faster?
(CH3)3C-Brand CH3-CH2-Br
b. i) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH + SOCI2 → ……..
![]()
Answer:
a. CH3CH2Br. SN2 reaction is faster in the case of primary alkyl halides since the transition state is more stable.
b. i) CH3CH2CH2CI
ii) CH3-CH2 -CH2 – CH2Br (Anti-Markownikoff’s addition)
Question 10.
- Nucleophilic substitution of haloalkane takes place through two different mechanisms, SN1 and SN2. Why do inversion of configuration take place in SN2?
- What is racemic mixture?
- Comment on the optical activity of recemic mixture.
Answer:
- is because the nucleophile attaches itself on the side opposite to the one where the halogen atom is present.
- Equimolar mixture of ‘d’ and T forms of an optically active compound is called racemic mixture.
- Racemic mixture is optically inactive due to external compensation. A mixture containing two enantiomers in equal proportions will have zero optical rotation, as the rotation due to one isomer will be cancelled by the rotation due to the other isomer.
Question 11.
Write equations for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from
i) 1 – butanol
ii) 1 – chlorobutane
iii) but -1- ene
Answer:
i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH+ HI → CH3CH2CH2CH2I + H2O
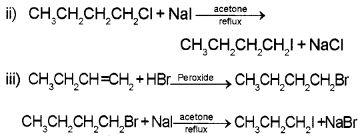
Question 12.
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with – OH?
- CH3Br or CH3I
- (CH3)3CCI or CH3CI
Answer:
- CH3I will react faster because C-I bond undergoes cleavage more easily as compared to C-Br bond.
- CH3CI will react faster because in it the carbon carrying halogen is sterically less hindered.
Question 13.
Identify the product X, Y, and Z in the following reaction.
![]()
Answer:
- X = CH3CH2CI
- Y = CH3CH2CN
- Z = CH3CH2CONH2
Question 14.
Identify the compounds X, Y, and Z in the following.
![]()
Answer:
- X = CH3 – CH2Br
- Y = CH3CH2OH
- Z = CHI3
Plus Two Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
CH3-CH = CH2 + HCI
- What are the possible products?
- Of these which one is the major product?
- Name the rule which helps you to answer the above question.
- Explain the rule.
Answer:
1.
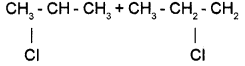
2. 2-Chloropropane is major.
3. Markownikoffs rule.
4. When a hydrogen halide is added to an unsymmetrical alkenethe halogen atom of alkyl halide will go to double-bonded carbon atom containing lesser number of hydrogen atom.
Question 2.
Two compounds are given ![]()
- What is the difference between these two compounds?
- Write the name of reaction they undergo and explain it.
Answer:
- 1st compound is cyanide. 2nd compound is isocyanide
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions.
The reactions in which a stronger nucleophile substitutes or displaces a weaker nucleophile are called nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Question 3.
![]()
- Name ‘A’.
- What is the role of ‘A’?
- Name the product obtained.
- What is this reaction called?
Answer:
- Dry ether
- Dry ether is used to prevent explosion
- Diphenyl
- Fittig reaction
Question 4.
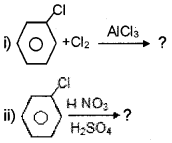
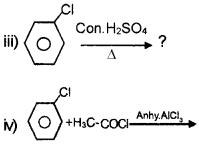
Answer:
Question 5.
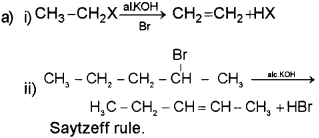
a) Haloalkanes give β-elimination.
i) Prepare CH2 = CH2 from CH3 – CH2X and alchoholic KOH.
ii) Give the major product of the β-elimination of
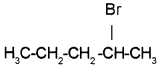
Name the related rule.
b) In the following pairs of halogen compounds which would undergo SN2 reaction faster? Justify.
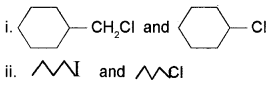
Answer:
It is primary halide and therefore undergoes SN2 reaction faster.
![]()
An iodide is a better leaving group because of its large size. It will be released at a faster rate in the presence of attacking nucleophile.
Question 6.
- Which among the following compounds undergo SN1 substitution easily – 3° or 1° alkyl halide? Give reason. Justify.
- Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Give reason.
Answer:
- 3°- alkyl halide. Because the 3° carbocation is more stable than a 1° carbocation.
- Grignard reagents react with water and get decomposed (hydrolysed). Hence they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Question 7.
a. In the following pair of halogen compounds which undergo SN2 reactions faster.
- C6H2 – CH2 – CI and C6 H3 -CI
- CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CI and CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – I
b.
![]()
Answer:
a. Undergo SN2 reactions faster
- C6H5CH2CI
- CH3 -CH2 -CH2 -I (R-I bond is weaker than R-CI bond)
b.
i) CH3 -CH2 -CH2 -CH2 Br
ii) CH3-CH2-CN
Question 8.
![]() Complete the reaction.
Complete the reaction.
b) R- CH2– CI, R2CHCI, R3CCI. Arrange these alkylhalide in the order of reactivity towards SN1 and SN2 mechanism.
Answer:
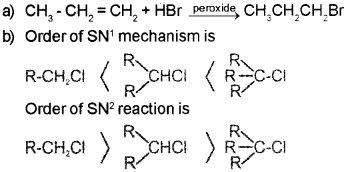
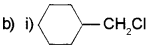
Question 9.
Write the isomers of compound having molecular formula C4H9Br.
Answer:
For the molecular formula C4H9Br four isomers are possible.
(i) CH3-CH2 – CH2 – CH3 (1-Bromobutane)
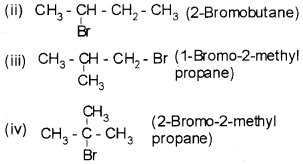
Plus Two Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H10CI in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Answer:
Since the hydrocarbon gives only one monochloro compound, it indicates that all the hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon are equivalent. Thus, the compound is cyclopentane.
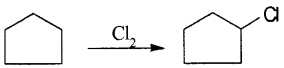
Question 2.
Write the isomers of compound having molecular formula C4H9Br.
Answer:
For the molecular formula C4H9Br four isomers are possible.
(i) CH3-CH2 – CH2 – CH3 (1-Bromobutane)
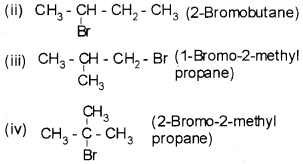
Question 3.
Write equations for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from
i) 1 – butanol
ii) 1 – chlorobutane
iii) but – 1 – ene
Answer:
i) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH+ HI → CH3CH2CH2CH2I + H2O
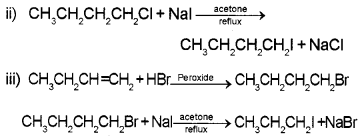
Question 4.
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH–?
Answer:
- CH3I will react faster because C-I bond undergoes cleavage more easily as compared to C-Br bond.
- CH3CI will react faster because in it the carbon carrying halogen is sterically less hindered.
Question 5.
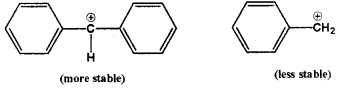
Out of C6H5CH2CI and C6H5CHCIC6H5which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH?
Answer:
C6H5CH2CIC6H5 is more easily hdrolysed because in this case the reaction proceeds through more stable intermediate carbocation.
The intermediate carbocation in this case is stabilised by resonance effect of two phenyl groups whereas in the other case it is stabilised by resonance effect of only one phenyl group.
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
