Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids is part of Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Question 1.
a) Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds containing carbonyl group. (March – 2010)
i) Write a chemical reaction to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
ii) Aldehydes and ketones can be subjected to Clemmensen reduction and Wolf-Kishner reduction. Name the reagents used in both cases.
b) How will you make the following conversions?
i) Ethanoic acid to ethanol.
ii) Propanoic acid to 2-chloropropanoic acid.
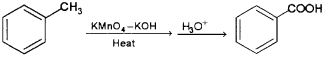
iii) Toluene to benzoicacid.
Answer:
a) i) Tollens’ Test: on warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared ammonical silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal.
RCHO+2[Ag(NH3)2]++3OH−→RCOO−+2Ag+2H2O+4NH3
Ketones, will not anwserTollens’ test.
ii) Clemensons reduction – Zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid
Woif-Kishner reduction – Hydrazine, KOHI Ethylene glycol
b) i) By reduction – When ethanoic acid is treated with lithium aluminium hydride it is reduced to ethanol.
CH3COOHLiAlH4⟶CH3CH2−OH
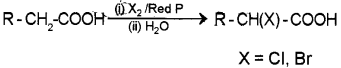
ii) By Hell-Volhartl-Zelinsky HVZ) reaction – When propanoic acid is treated with chlorine in presence of small amount of red phosphorus followed by hydrolysis 2-chloropropanoic acid is formed.
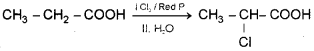
iii) When toluene is heated with alkaline solution of potassium permanganate the methyl side chain is oxidised to form benzoic acid.
Question 2.
Following are a group of compounds showing acidic behavior: (Say – 2010)
![]()
a) Give the IUPAC names of these compounds.
b) ![]() does not contain a carboxylic group, still it is acidic. Why?
does not contain a carboxylic group, still it is acidic. Why?
c) Phenols are less acidic than carboxylic acids Why?
d) Formic acid is stronger than acetic acid. Why?
Answer:
a) HCOOH → Methanoic acid
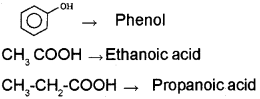
b) Thus, phenol always remains ionised in solution giving H+ ions and is acidic in nature.
Resonance in phenol:
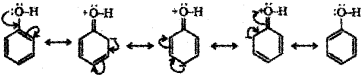
Resonance in phenoxide ion:
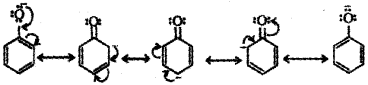
c) Carboxylic acids are more acidic than simple phenols because the carboxylate anion is more resonance stabilised by two equivalent resonance structures than phenoxide ion.
d) In acetic acid due to the I effect of the CH3 – group attached to the – COOH group, the resonance stabilisation of the corresponding carboxylate anion is decreased while there is not I effect for H in formic acid. Hence, formic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
Question 3.

a) What is its IUPAC name? (March – 2011)
b) Explain the conversion of the above acid to the following:
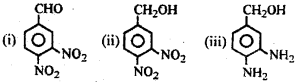
Answer:
a) 3,4 – Dinitrobenzoic acid.
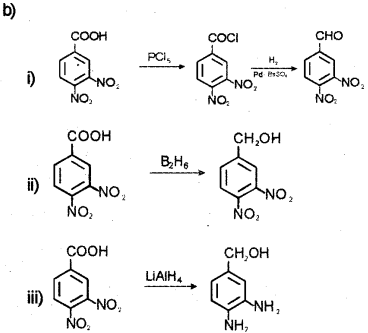
Question 4.
Aldehydes resemble ketones in many respects. (Say – 2011)
a) Give the reason fortheir resemblance.
b) Give a reaction in which aldehydes resemble ketones.
c) Write two tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
d) What is Cannizaro reaction?
Answer:
a) Both aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl functional group ![]() . The general formulae of aldehydes and ketones are given below:
. The general formulae of aldehydes and ketones are given below:
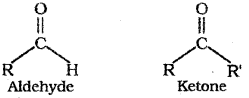
(R and R’ ar same or different alkyl or aryl groups)
b) Both aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. For example, both aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) to yield cyanohydrins.
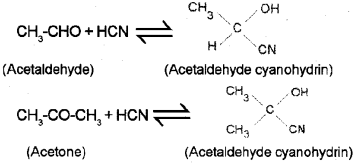
c) 1) Tollens’ Test – On warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared ammonical silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal. Here the aldehydes reduce Ag+ to metallic silver and are oxidised to the corre sponding carboxylate anion.
![]()
2) Fehlina’s Test – On heating an aldehyde with Fehling’s reagent (FehlingssolutionA- aqueous copper sulphate and Fehling’s solution B – alkaline sodium potassium tartarate), a red dish brown precipitate is obtained. Here the aldehydes reduce Cu2 to Cu2O and are oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion.
![]()
Ketones, being less reactive than aldehydes will not anwserTollens’ test and Fehling’s test.
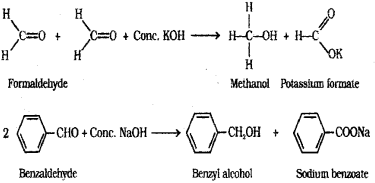
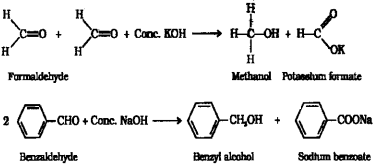
d) Cannizzaro reaction – Aldehydes which do not have α-hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. This reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction. In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to corresponding alcohol while another molecule is oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acid salt.
Question 5.
Aniline is an aromatic pnmary amine. Starting from aniline a number of organic compounds can be prepared.
a) How is aniline converted to benzene diazonium chlonde?
b) How are the following obtained from benzene diazonium chloride?
i) Ch loro benzene
ii) Phenol
Answer:
a) Aniline is treated with nitrous acid. Nitrous acid is produced in the reaction mixture by the reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid.
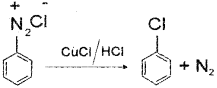
b) i) Benzenediazonium chloride when treated with cuprous chloride and HCI, the diazonium group is replaced by Cl ion to form chioroben zene.
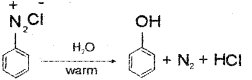
ii) When the aqueous solution of benzene-dia zonium chloride is warmed upto 283 K it is hydrolysed to phenol.
Question 6.
a) Which named reaction is used to reduce CH3COCI to CH3CHO? (March – 2012)
b) Aldehydes and Ketones undergo reactions due to the presence of α – hydrogen atom.
i) Write the name of the reaction of aldehyde which takes place only because of the presence of α – hydrogen atom.
ii) How will you bring about the above reaction?
c) i) CH2CICOOH is a stronger acid than CH3COOH Why?
ii) How will you convert CH3COOH to CH2CICOOH
Answer:
a) Rosenmund Reduction.
![]()
b) i) Aldol condensation.
ii) Aldehyde or ketone containing at least one x-hydrogen undergo self-condensation reaction with dil. alkali (e.g. dii. NaOH) as catalyst to form β – hydroxy aldehydes (atdol) or β – hydroxy ketones (ketol) respec travel.
c) i) Electron with drawing group or-leffect group ‘Cl’ stabilises the conjugate acid of the carboxylate anion through delocalisation of negative charge and strengthens the carboxylic acid.
CH2CI COOH > CH3 COOH
ii) When a carboxylic acid that contains α – hydrogen is treated with Cl2 or Br2 in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus the α – hydrogen atoms are replaced by chlonne or bromine atoms to give α – halo carboxylic acids. This reaction is known as the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) Reaction.
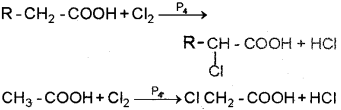
Question 7.
a) Complete the following. Write down the structure of A, B and C. (Say – 2012)
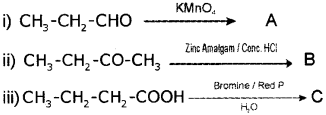
b) Write down the IUPAC names of A, B and C.
c) Explain the following reactions.
i) Cannizzaro reaction
ii) Esterification
Answer:
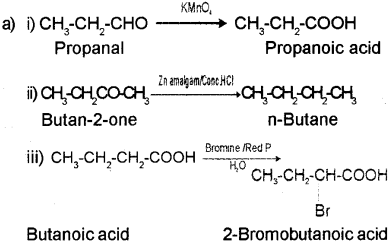
b) A – Propanoic acid
B – n-Butance
C – 2-Bromobutanoic acid
c) i) Canizzaro reaction -Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohot while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt. e.g.
ii) Carboxylic acids react with alcohols or phenols in the presence of mineral acids such as concentrated H2SO4 or HCI gas as catalysts to form esters. This reaction is known as esterification.
![]()
Question 8.
a) Suggest a method of preparation of benzaldehyde from toluene. (March – 2013)
b) Aldehydes and ketones differ in their chemical reactions. How do they react with the following?
i) Tollen’s reagent
ii) Alcohol.
c) How will you convert propanoic acid into the following compounds?
i) Ethane
ii) Butane.
Answer:
a) Toluene on treating with chromyl chloride give benzaldehyde.This reaction is called Etard reaction.
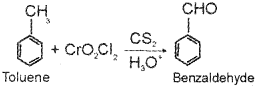
b) i) Tollens’ Test: on warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared ammonical silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal.
RCHO+2[Ag(NH3)2]++3OH−→RCOO−+2Ag+2H2O+4NH3
Ketones, will not anwserTollens’ test.
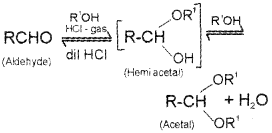
ii) Aldehydes react with one equivalent of monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry hydrogen chloirde to yield alkoxy alcohol known as hemiacetalswhich further react with one more molecule of alcohol to give a gem-dialkoxy compound known as acetal.
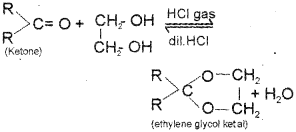
Ketones react with ethylene glycol in presence of dry hydrogen chloride to form cyclic products known as ethylene glycol ketals.
c) Propanoic acid → Ethane
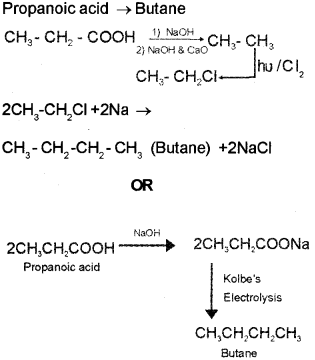
Question 9.
a) Among formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, benzalde hyde and formic acid, which compounds undergo Cannizzaro reaction? Give reason. (Say – 2013)
b) What is esterification?
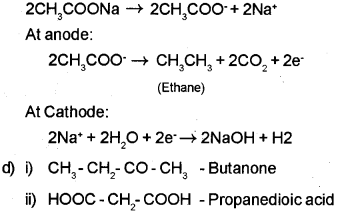
c) Write the chemical reaction to effect the transformation of sodium acetate to ethane.
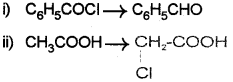
d) Write the IUPAC names of the compounds given below,
i) CH3-CH2-CO-CH3
ii) HOOC-CH2-COOH
Answer:
a) i) Canizzaro reaction -Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohot while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt. e.g.

ii) Carboxylic acids react with alcohols or phenols in the presence of mineral acids such as concentrated H2SO4 or HCI gas as catalysts to form esters. This reaction is known as esterification.
![]()
b) Formation of ester is known as esterification. Carboxylic acid react with alcohols or phenols in presence of acids like HCI to give ester.
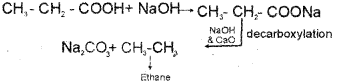
c) By Kolbe’s electrolytic method – An aqueous solution of sodium acetate on electrolysis gives ethane at the anode.
Question 10.
a) Aldol condensation reaction is a special reaction of aldehydes. (March – 2014)
i) What is a Idol condensation reaction?
ii) Write the structural formula of aldol formed from ethana I.
b) Write simple chemical tests and observations used to distinguish between the following compounds:
i) Propanal and propanone
ii) Phenol and benzoic acid
c) Write the names of the reagents used to bring about the following transformations:
Answer:
a) i) Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a condensation reaction in the presence of dilute alkali to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol) respectively. This reaction is known as Akiol condensation.
b) i) Propanal and propanone – They can be distin guished by Tollens’ Test – When propanal is warmed with freshly prepared ammonical silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal. Here propanal is oxidised to propanoate anion while it reduces Ag+ to metallic silver. Since ketones are less reactive, propanone will not answer this test.
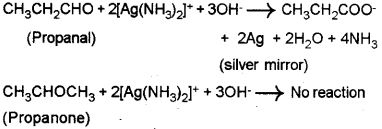
[Other tests: (1) Fehling’s test – Propanal gives a red precipitate on heating with Fehling’s reagent while propanone does not answer this test. (2) iodoform test – Propanone being a methyl ketone, when heated with NaOH and 12 sOlUtiOn an yellow precipitate of lodoform is formed. But propanal does not answer the jodo-form test.]
ii) Phenol and benzoic acid – When benzoic acid is treated with NaHCO3 solution there is bnsk effervescence of CO2. But phenol being less acidic than benzoic acid will not react with NaH CO3 solution.
c)
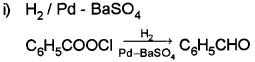
This reaction is caNed Rosenmund reduction.
![]()
This reaction is called Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction.
Question 11.
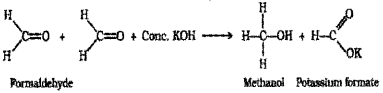
a) Methanal (HCHO) is an aldehyde having no α – hydrogen atom. What are the products formed when methanal is treated with strong KOH solution? (Say – 2014)
b) How are the following conversions achieved?
i) Benzoyl chloride (C6H5COCI) to benzalde hyde (C6H5 – CHO)
ii) Acetic acid (CH2COOH) to chioro acetic acid (CH2CI – COOH)
iii) Ethanal (CH3 – CHO) to Ethane (CH3 – CH3)
Answer:
a) Aldehydes which do not have α -hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (dispropor tionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. This reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction. ie, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to corresponding alcohol while another molecule is oxidised to the carboxylic acid salt. eg when methanal is treated with strong KQH solution it under goes self oxidation and reduction to give a mixture of potassium formate and methanol.
b) i) Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated over catalyst, palladium on barium sulphate to get benzaldehyde (Rosenmund reduction).
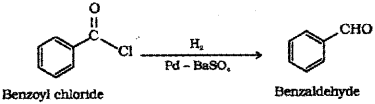
ii) Acetic acid on treatment with chlorine in presence of small amount of red phosphorus is chlorinated at the a position to get α-chioroacetic acid (HeIl-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction).

iii) When ethanal is treated with zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid the carbonyl group is reduced to -CH2 group to get ethane.
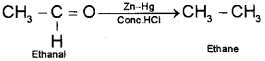
Question 12.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Acids contain ![]() . (March – 2016)
. (March – 2016)
a) Name the product obtained by the reaction between Acetic acid and Ethanol.
b) a) Give any Iwo tests to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
ii) Two chemical reactions are given below:
1) Identify the products of each reaction.
2) Give the name of each reaction.
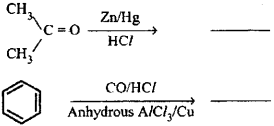
Answer:
a) Acetic acid reacts with ethanol in presence of mineral acids such as concentrated H2SO4 as catalyst to form the ester ethyl acetate or ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H. This reaion is known as esterification.
![]()
b) i) 1) Tollens test (Silver mirror test) – on warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared am moniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent) a bright silver mirror is produced due to the formation of silver metal. Here the aldehydes are oxidised to the corresponding carboxylate anion while they reduœ Ag to metallic silver.
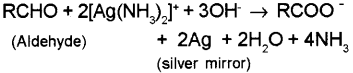
2) Fehling’s Test – on heating an aldehyde with Fehlings reagent (mbdure of aqueous copper sulphate and alkaline sodium potassium tartarate), a reddish brown precipi tate is obtained. Here aldehydes are oxidised to the corresponding carboxylate anion while they reduce Cu2+ to Cu2O.
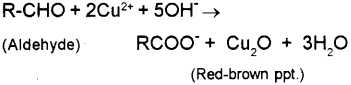
Since ketones are less reactive than aldehydes they will not answer these two tests.
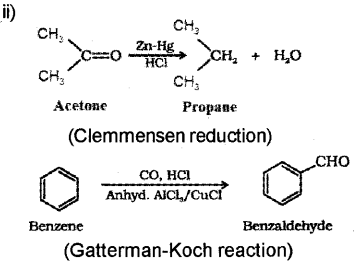
Question 13.
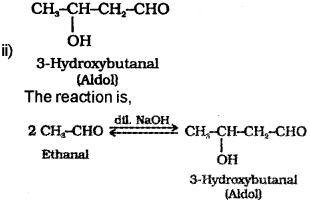
a) Explain aldol condensation taking CH2-CHO example. (Say – 2015)
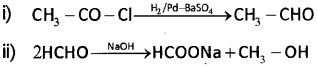
b) Write the named reactions involved in the following conversions:
c) How are the following conversions achieved?
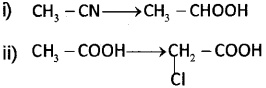
Answer:
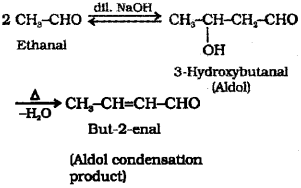
a) Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy aIde hydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively. This is known asAldol reaction. The aldol and ketol readily lose water to give α, β unsaturated carbonyl compounds which are al-dol condensation products and the reaction is called Aldol condensation.
e.g. CH3-CHO undergo Aldol reaction in presence of dil NaOH to form 3-Hydroxybutanal which on heating lose water to form the Aldol condensation product But-2-enal.
b) i) Rosenmund reduction
ii) Cannizzaro reaction
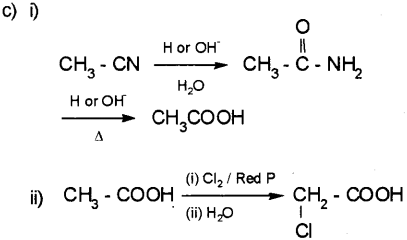
Question 14.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids are Car bonyl compounds. (March – 2016)
a) Aldehydes differ from Ketones in their oxidation reactions. Illustrate with one example.
b) How will you prepare benzaldehyde by Gatterman Koch reaction?
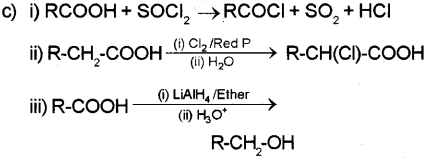
c) Write the reactions of carboxylic acid with the following reagents. (Write the chemical equations)
i) Thinoyl chloride (SOCl2)
ii) Chlorine in presence of small amount of red phosphorous.
iii) Lithium Aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) I ether.
a) Write a test to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
b) How will you prepare benzaldehyde by Etard’s rea dio n?
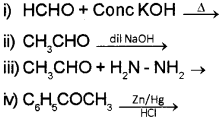
c) Howwillyou bring about the followng conversions? (Write the chemical equations)
i) Ethanol → Ethanoic acid
ii) Benzamide → benzoic acid
iii) Benzaldehyde → meta nitro benzaldehyde
Answer:
a) Aldehydes are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids containing same number of carbon atoms on treatment with mild or strong oxidising agents. Ketones are oxidised under vigorous conditions Le., with strong oxidising agents and at elevated temperatures to give carboxylic acids containing lesser number of carbon atoms.
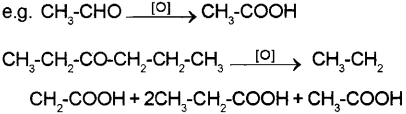
OR
On warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver mirror is produced due to formation of silver metal. The aldehydes are oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion.
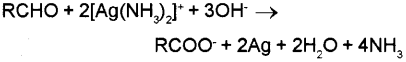
Ketones will not give this reaction because Tollens’ reagent being a mild oxidising agent cannot oxidise ketones.
[Or, any other suitable example – Reaction with Fehling’s reagent, Reaction with Benedict’s reagent etc.]
b) When benzene is treated with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride or cuprous chloride, it gives benzaldehyde.
Or, the chemical equation:
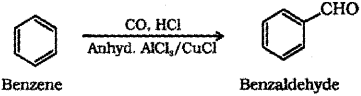
a) Fehling’s Test – on heating an aliphatic aldehyde with Fehling’s reagent (aqueous copper sulphate + alkaline sodium-potassium tolerate), a reddish-brown precipitate is obtained. Aldehydes are oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion.
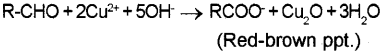
Aromatic aldehydes and ketones do not answer this test. This is because Fehling’s reagent being a mild oxidising agent cannot oxidise them.
[Or, any other suitable example – Fehling’s test, Benedict’s test etc.]
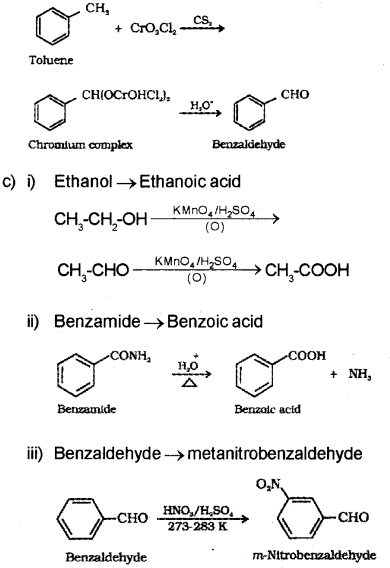
b) Toluene on treating with chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) in CS2 forms a chromium complex WNCII on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
Or, the chemical equation:
Question 15.
Aldehydes and ketones are the compounds having >C = O group (Say – 2016)
a) Choose the IUPAC name of the compound CH3 – CH = CH – CHO
i) propen-1 -al
ii) But-2-en-1 -al
iii) Butanal
iv) But-2-en-2-al
b) Complete the following reaction:
OR
Aldehydes, Ketones and acids contain > C= O group.
a) Choose the IUPAC name of the compound (CH3)2CHCOOH
i) Butanoic acid
ii) Ethanoic acid
iii) 2-methyl propanoic acid
iv) Propanoic acid
b) Complete the following reaction:
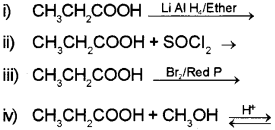
Answer:
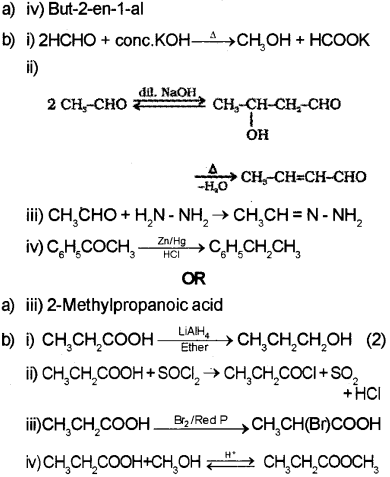
Question 16.
a) The product obtained when benzene is treated with carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in presence of anhydrous AICI3 is (March – 2017)
i) Chlorobenzene
ii) Phenol
iii) Benzaldehyde
iv) Benzoic acid
b) How will you carry out the following conversions?
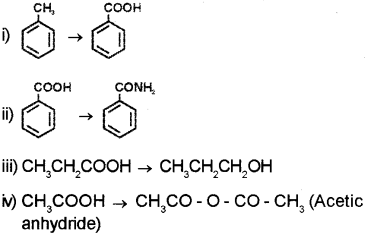
OR
Explain the following:
i) Esterification
ii) Tollen’s test
iii) HVZ reaction
iv) Decarboxylation of Carboxylic acid.
Answer:
a) iii) Benzaldehyde
b) i) Toluene on heating with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acid hydrolysis give benzoic acid.
![]()
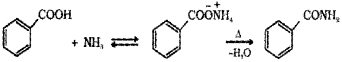
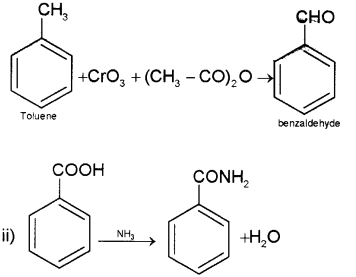
ii) Benzoic acid reacts with ammonia to give ammonium benzoate which on further heating at high temperature gives benzamide.
iii) Propanoic acid on reduction using LiAIH4 gives Propan-1 -al.
![]()
iv) Ethanoic acid on heating with mineral acids such as H2SO4 or with P2O5 gives ethanoic anhydride.
![]()
i) Estenfication: Carboxylic acids are estenfied with alcohols or phenols in the presence of a mineral acid such as concentrated H2SO4 or HCI gas as a catalyst.
![]()
ii) Tollens’s Test: On warming an aldehyde with freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution (Tollens’ reagent), a bright silver minor is produced due to formation of silver metal. The aldehydes are oxidised to corresponding carboxylate anion.
![]()
Ketones will not give this reaction because Tollens’ reagent being a mild oxidising agent cannot oxidise ketones.
iii) HVZ reaction: Carboxylic acids having an α – hydrogen are halogenated at the α – position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to give halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell-Volharti-Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction.
iv) Decarboxylation: Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with sodalime (NaOH and CaÇ. in the ratio of 3: 1). The reaction is kriownas decar carboxylation.
![]()
Question 17.
a) Which among the following reduces Tollen’s reagent? (Say – 2017)
i) Methanal
ii) Propanone
iii) Benzophenone
iv) Acetophenone
b) Since both aldehydes and ketones possess carbonyl functional group, they undergo similar chemical reactions.
i) Explain the structure of carbonyl group.
ii) Explain Aldol condensation with an example.
OR
a) Which among the following does not give red precipitate with Fehling’s solution?
i) Ethanal
ii) Propanal
iii) Butanal
iv) Benzaldehyde
b) How will you bring about the following conversions?
i) Toluene into Benzaldehyde
ii) Benzoic Acid to Benzamide
c) Explain Cannizaro reaction with an example.
Answer:
a) i)Methanal
b) i) The carbonyl C atom is sp2 hybridized. Carbon forms 3 α bonds and one π bond. ![]()
The C = O bond is polarised due to higher electronegativity of oxygen relative to carbon.
ii) Aldehyde or ketone containing at least one x-hydrogen undergo self-condensation reaction with dil. alkali (e.g. dil. NaOH) as catalyst to form β – hydroxy aldehydes (atdol) or β – hydroxy ketones (ketol) respec travel.
OR
a) iv) Benzaldehyde
b) i) Etard’s reaction
Toluene on treatment with CrO3 and acetic unhydride gives benzaldehyde
c) i) Canizzaro reaction -Aldehydes which do not have an α-hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali. In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohot while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt. e.g.

ii) Carboxylic acids react with alcohols or phenols in the presence of mineral acids such as concentrated H2SO4 or HCI gas as catalysts to form esters. This reaction is known as esterification.
![]()
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
