Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers is part of Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Question 1.
Phenols are more acidic than alcohols. (March – 2010)
i) Name the product obtained when phenol is treated with chloroform in the presence of NaOH.
ii) Name the above reaction.
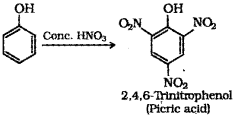
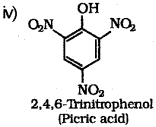
iii) What is the product obtained when phenol is treated with con. HNO3?
iv) Write the structure and IUPAC name of the above product.
v) Ethanol and propane have comparable molecular masses but their boiling points differ widely. Which of them has higher boiling point? Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
i) Salicylaldehyde or 2-Hydroxy benzaldehyde.
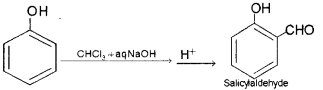
ii) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
iii) When phenol is treated with concentrated nitric acid, it is converted to 2,4,6 trinitrophenol, commonly known as picric acid.
v) Ethanol : Ethanol molecules can associate through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. But propane has no hydrogen bonding. Therefore, ethanol has high boiling point (351 K) than propane (231 K).
Question 2.
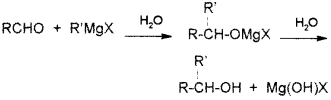
A compound A reacts with thionyl chloride to give compound B. B reacts with magnesium in ether medium to form a Grignard reagent which is treated with acetone and the product on hydrolysis gives. (Say – 2010)
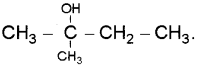
Identify (A) and (B). Write down the chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
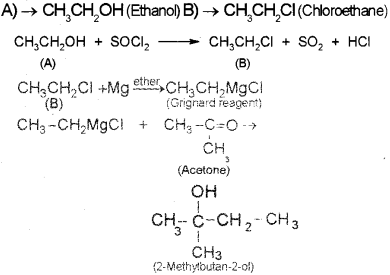
Question 3.
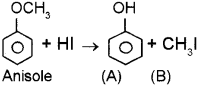
Ethers are generally non-reactive compounds. One of the important reactions of Ethers is the action of HI. (March – 2011)
![]()
ldentifyA& B. Explain the reaction.
Answer:
Alkyl aryl ethers on reaction with Hl are cleaved at the alkyl – oxygen bond. Cleavage does not occur at the aryl – oxygen bond. This is due to the fact that the aryl – oxygen bond has high stability caused by resonance. This reaction yields phenol and the corresponding alkyl iodide.
Question 4.
Mixture of conc. HCI and anhydrous ZnCl2 is an important reagent which helps to distinguish between 10, 20 and 3° alcohols. (Say – 2011)
a) Give the name of the above reagent.
b) Give one example each for 10, 20 & 30 alcohols.
c) Explain how the above reagent helps to distinguish above three types of alcohols.
Answer:
a) Lucas reagent
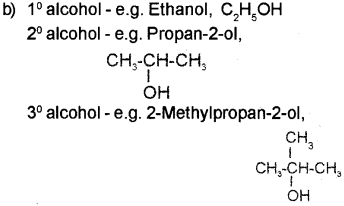
c) Lucas test 10, 20 and 3° alcohols can be distin guished by Lucas test. Alcohols are soluble in Lucas reagent while their halides are immiscible and produce turbidity in solution. The difference in reactivity of three classes of alcohols with HCI distinguishes from one another. The order of reactivity of alcohols with Lucas reagent is in the order 3> 20> 1°. Thus, in the case of 30 alcohols turbidity is produced immediately as they form the halides easily. In the case of 2° alcohols turbidity is produced within 5 minutes at room tem perature. In the case of 1° alcohols no turbidity is produced at room temperature since they are least reactive.
Question 5.
a) Write the name or structure of the compounds A and B in the following reactions: (March – 2012)
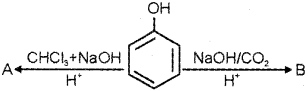
b) Vapours of an alcohol ‘C’ on passing over heated copper produce compound ‘D’. ‘D’ on reaction with CH3MgCI followed by hydrolysis produce 2-Methyl butan-2-ol. Write the name or structure of compounds ‘C’ and ‘D’.
Answer:
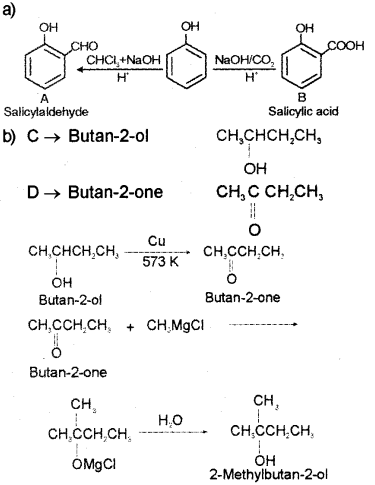
Question 6.
Methanol and ethanol are two commercially important alcohols. (Say – 2012)
i) Write one method of preparation of methanol and ethanol.
ii) Name the products obtained when ethanol is treated with CrO3 in an anhydrous medium.
iii) The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxy methane. Give reason.
Answer:
i) Methanol is produced by catalytic hydrogenation of carbon monoxide at high pressure (200 atm – 300 atm) and temperature (573 K -673 K) and in presence of ZnO – Cr2O3 catalyst.

Ethanol is obtained commercially by fermentation of molasses. The enzyme invertase present in yeasf converts sugar (sucrose) glucose and fructose invertase converts sugar to glucose and fructose Zymase converts glucose and fructose to ethanol and CO2.
ii) When ethanol is treated with CrO3 in anhhdrous medium it is oxidised to ernanal (acetaldehyde).
\(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{OH} \stackrel{\mathrm{CrO}_{3}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CHO}\)
iii) In ethanol there is a presence of hydrogen bond but in methoxy methane no hydrogen bond. Therefore boiling point of ethanol is higher than methoxy methane.
Question 7.
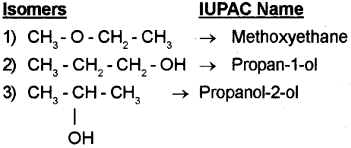
a) Write the IUPAC names of all the possible isomers with molecular formula C3H8O. (March – 2013)
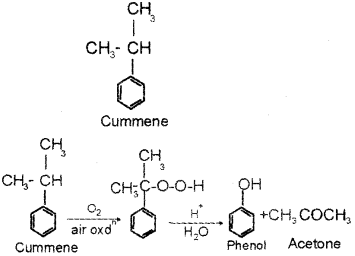
b) Phenol is usually manufactured from cumene. Write the structure of cumene.
c) Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols can be distinguished by Lucas test.
i) What is Lucas reagent?
ii) Write the observation for primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols in Lucas test.
Answer:
a) C3H8O
b) Cumene is isopropyl benzene. Its structure is
c) i) Mixture of concentrated HCI and ZnCl2
ii) Refer SAY 2011, Question 1.c
Question 8.
How are the following conversions carried out? Represent the chemical reactions. (Say – 2013)
a) Ethanol to Ethanal
b) Phenol to Picric acid
c) Phenol to Benzene
d) Phenol to Tribromophenol
Answer:
a) Ethanol to Ethanal – When the vapors of ethanol are passed over heated copper at 573 K, dehydrogenation takes place to form ethanal.
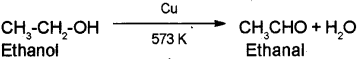
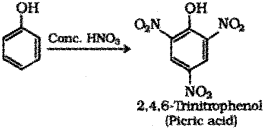
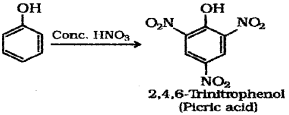
b) Phenol to Picric acid – When phenol is treated with concentrated nitric acid it is converted to 2,4,6-Tnnitrophenol commonly known as picric acid.
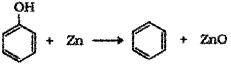
c) Phenol to benzene – When phenol is heated with zinc dust it is converted to benzene.
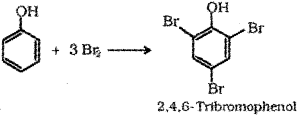
d) Phenol to Tnbromophenol – When phenol is treated with bromine water 2,46-Tribromophenol is formed.
Question 9.
a) How will you prepare the following compounds using Grignard reagent? (March – 2014)
i) Primary alcohol
ii) Secondary alcohol
b) How will you distinguish primary and secondary alcohols using the Lucas test?
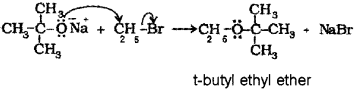
c) Write the correct pair of reactants for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether by Williamson synthesis.
Answer:
a) i) When a suitable Grignard reagent is treated with formaldehyde gives which on hydrolysis primary alcohol.
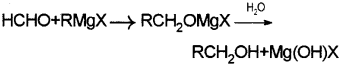
ii) When a suitable Grignard reagent is treated with any suitable aldehyde other than formaldehyde an adduct is formed which on hydrolysis yields secondary alcohol.
b) Refer SAY 2011, Question f.c
c) When sodium tert-butoxide is treated with ethyl bromide, t-butyl ethyl ether is formed.
Question 10.
a) Write the name or formula of the following: (Say – 2014)
i) A simple ether
ii) A mixed ether
iii) A dihydnc alcohol
iv) A trihydric alcohol.
b) Phenol on treatment with Br2 in CS2 at low temperature gives two isomenc monobromo phenols ‘X’ and ‘Y’. But phenol on treatment with bromine water gives a white precipitate ‘Z’. Identify the products ‘X’, ‘Y’. and ‘Z’.
Answer:
a) I) Dimethyl ether(Methoxymethane) – CH3 – O – CH3
ii) Ethylmethyl ether (Methoxyethane) – CH3– O – C2H5
iii) Ethylene glycol (Ethane-1 ,2-diol) – HO – CH2– CH2 – OH
iv) Glycerol (Propane-1, 2, 3-trio I) – HO – CH2 – CH(OH) – CH2 – OH
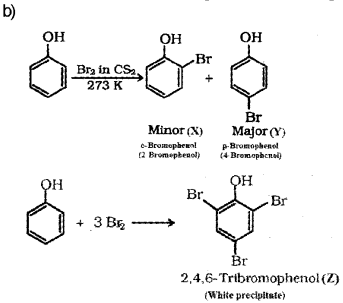
Question 11.
Alcohols are compounds with general formula R-OH. (March – 2015)
a) Alcohols are soluble in water. What is the reason?
b) i) Explain a method formanufadure of Ethanol.
ii) How will you convert phenol to benzene?
Answer:
a) Solubility of alcohols in water is due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
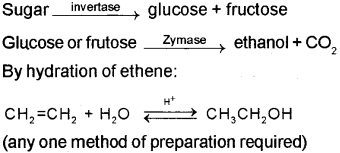
b) i) Ethanol (C2H5OH) is obtained commercially by fermentation. The sugar in molasses, sugarcane or fruits such as grapes is converted to glucose and fructose in the presence of an enzyme invertase. Glucose and fructose un dergo fermentation in the presence of an other enzyme zymase, which is found in yeast.
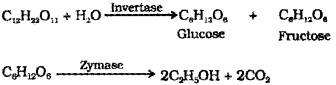
OR
By hydration of ethene – Ethene reacts with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form ethanol.
OR
By hydration of ethene – Ethene reacts with water in the presence of acid as catalyst to form ethanol.
CH2 = CH2 + H2O CH3CH2OH
ii) Phenol is converted to benzene by heating with zinc dust.
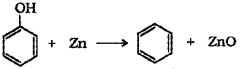
Question 12.
a) Write suitable reagent or reagents used for the following conversions: (Say – 2015)
b) Wnte a test to distinguish between phenol and alcohol.
Answer:
a) i) aq.NaOHoraq,KOH
ii) Conc. H2SO4 at 413 K
iii) CHCI3 + aq. NaOH
b)
| Alcohols | Phenols | ||
| 1 | Do not show any effect on litmus solution. | 1 | Turn blue litmus red. |
| 2 | Do not give any characteristic colour with FeCI3 solution. | 2 | Give characteristic colours such as violet, red, etc. with FeCI3 solution. |
| 3 | Do not react with NaOH solution. | 3 | React with NaOH solution and form corresponding sodium salt |
Question 13.
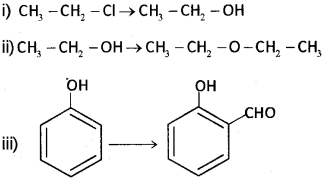
a) Complete the following: (March – 2016)
b) Explain the following:
i) Estenfication
ii) Williamson Synthesis
Answer:
b) i) Esterification – Alcohols and phenols react with carboxylic acids, and acid anhydrides in presence of small amount of concentrated sulphuric acid and with acid chlorides in presence of pyridine to form esters. This reaction is known as estenfi cation.
Or, any of the following chemical equations:
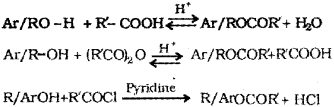
ii) Wihiamson synthesis – When and alkyl halide is treated with sodium alkoxide ether is formed. It is an important laboratory method for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
Or, the chemical equation:
R-X + R’ – ONa → R-O-R’ + NaX
Or, any other specific example.
Question 14.
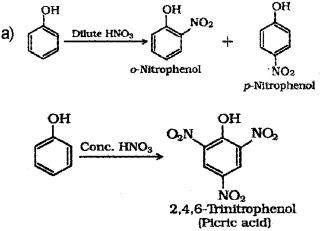
a) Phenol when treated with Con. HNO3 gives, (Say – 2016)
i) o-Nitrophenol
ii) p-Nitropbenol
iii) 2,4,6 -Thnitro phenol
iv) a mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol.
b) Methanol and ethanol are two commercially important alcohols. Write one method each for the preparation of methanol and ethanol.
Answer:
a) iii) 2,4,6-Tnnitrophenol
b) Methods of preparatIon of methanol :
1. Destructive distillation of wood.
2. Catalytic hydrogenation of carbon monoxide at high pressure and temperature in the presence of ZnO – Cr2O3 catalyst.
![]()
Methods of preparation of ethanol:
Fermentation: The sugar in sugarcane or grapes is converted to glucose and fructose in the presence of an enzyme invertase. Glucose and fructose are converted to ethanol and CO2 by the enzyme zymase, which is found in yeast.
OR
Question 15.
a) Arrange the following compounds in the order of increasing boiling points: (March – 2017)
Ethanol, Propan-1-ol, Butan-1 -01, Butan-2-ol
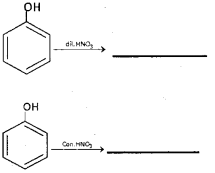
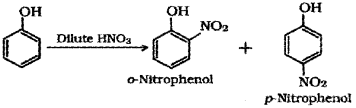
b) In the lab students were asked to carry out the reaction between phenol arid conc. HNO3. But one student, ‘A’ carried out the reaction between phenol and dil. HNO3. Do you think that the student ‘A’ got the same result as others. Substantiate with suitable explanations. (Also write the chemical equations wherever necessary.)
Answer:
a) Ethanol < Propan-1-ol < Butan-2-ol < Butan-1-ol
b) Student ‘A’ will get a mixture of o-Nitropehnol and p-Nitrophenol.
Other students will get 2,4,6-tnnirophenol (picncacid) as the product.
Question 16.
a) Identify the product (Say – 2017)
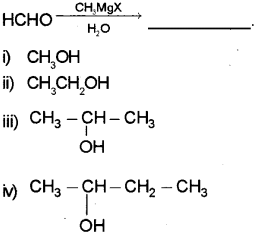
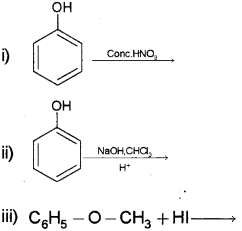
b) Complete the following:
Answer:
a) ii) CH3CH2OH
b) i) Picric acid or 2, 4, 6, Trinitro phenol
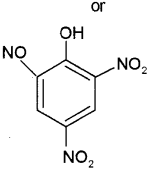
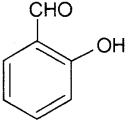
ii) Salicyl aldehyde or2-hydroxy benzaldehyde or
iii) C6H5OH + CH3l
phenol + iodomethane
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
