Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 The Solid State is part of Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Year Questions and Answers. Here we have given Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 15 Polymers.
Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 The Solid State
Plus Two Chemistry The Solid State 4 Marks Important Questions
Question 1
a) Schottky defects and Frenkel defects are two stoichiometric defects shown by crystals. (March – 2010)
i) Classify the following crystals into those showing Schottky defects and Frenkel defects:
NaCI, AgCI, CsCI, CdCI2
ii) Name a crystal showing both Schottky defect and Frenkel defect.
b) Schematic alignment of magnetic moments of ferromagnetic, antiferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic substances are given below. Identify each of them.
i) ????????
ii) ????????
iii) ????????
Answer:
a) i) Schottchydefect – NaCI, CsCI Frenkel defect – AgCI, CdCI2
ii) AgBr
b) i) Antifero magnetism
ii) Ferrimagnetism
iii) Ferromagnetism
Question 2.
Based on the nature of order present in the arrangement of the constituent particles, solids are classified into two, crystalline and amorphous. (Say – 2010)
a) List out any four points of difference between crystalline and amorphous solids.
b) A list of solids are given below:
Quartz, glass, iodine, ice.
From this, identify crystal (s)
i) having sharp melting point.
ii) which is/are isotropic
Answer:
| Crystalline | Amorphous |
| i) Long-range order ii) Sharp melting point iii) Newly formed surface is smooth iv) Anisotropic | i) Short-range order ii) Range of melting point iii) Newly formed surface is rough. iv) Isotropic |
b) i) Quartz, Iodine, Ice
ii) Glass
Question 3.
Cristal defects give rise to certain special properties in the solids. (March – 2011)
a) What is meant by Frenkel Defect?
b) Why does LiCI not exhibit Frenkel Defect?
c) Explain the pink colour of LiCI when heated in . the vapours of Li.
Answer:
a) The dislocation of a cation from its original site to an interstitial site. It creates a vacancy defect at its original site and an interstitial defect at its new location.
b) The size of the cation is bigger than the void.
c) Due to F – centre. It is an electron trapped anion vacancy.
Question 4.
A cubic unit cell is characterized by a = b = c and a = ß = ? = 90° (Say – 2011)
a) Name three important types of cubic unit cells and calculate the number of atoms in one unit cell in the above three cases.
b) A metal forms cubic crystals. The mass of one unit cell of it is M/NA gram, where M is the atomic mass of the metal and NA is Avogardo Number. What is the type of cubic unit cell possessed by the metal?
Answer:
a) Simple cubic unit cell or Primitive unit cell, Body – centred cubic unit cell (bcc) and Face – centred cubic unit cell (fee).
b) Primitive cubic unit cell: This unit cell has atoms only at its comers. There are 8 corners for a cube.
Contribution by atom at the corner = 1/8
Total number of atoms in one unit cell \(=8 \times \frac{1}{8}=1\) atom
Body – centred cubic unit cell:
This unit cell has an atom at each of its corners and also one atom at its body centre.
8 corners \(\times \frac{1}{8}\) per corner atom \(=8 \times \frac{1}{8}=1\) atom
1 body centre atom = 1 x 1 = 1 atom
? Total number of atoms per unit cell = 2 atoms
Face – centred cubic unit cell:
This unit cell contains atoms at all the corners and at the centre of all the faces of the cube.
8 corners \(\times \frac{1}{8}\) per corner atom \(=8 \times \frac{1}{8}=1\) atom Contribution by an atom at the face centre = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
6 face – centred atoms x \(\frac{1}{2}\) atom per unit cell \(=6 \times \frac{1}{2}=3\) atoms
? Total number of atoms per unit cell = 4 atoms
c) Mass of one unit cell = \(\frac{\mathrm{M}}{\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{A}}} \mathrm{g}\)
Mass of 1 mole of unit cells \(\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{A}} \times \frac{\mathrm{M}}{\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{A}}}\) = M gram = Gram atomic mass It means that 1 unit cell contains one atom of the metal. Hence, the type of unit cell is primitive cubic or simple cubic.
Question 5.
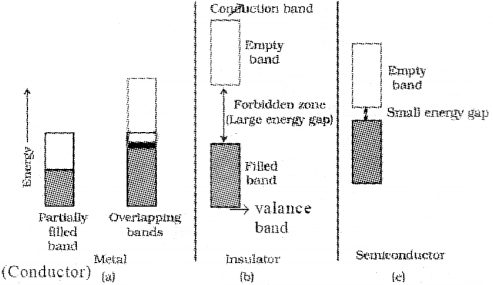
Solids can be classified into three types on the basis of their electrical conductivities. (March – 2012)
i) Name three types of solids classified on the basis of electrical conductivities.
ii) How will you explain such classification based on Band theory?
Answer:
i) Conductors, insulators & semiconductors
ii) In conductors, the valance band overlaps with Ir e conduction band or no energy gap exists between the valance band and conduction band.
? The electrons can easily go into the conduction band and hence metals are good conductors. In insulators, the energy gap between valance band and conduction band is very large. Hence electrons from valance band cannot move into the conduction band.
Semi conductors have energy gap between conductors and insulators. At room temperature, these are not good conductors. But with an in crease in temperature electrons acquire sufficient energy to move from valance band into conduction band resulting in an increase in conductivity.
Question 6.
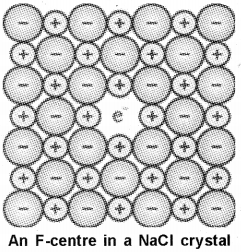
Schottky and Erenkel defects are stoichiometric defects. (Say – 2012)
i) Write any two differences between Schottky defect and Frenkel defect.
ii) When pure NaCI (Sodium Chloride) crystal is heated in an atmosphere of sodium vapours, it turns yellow. Give reason.
Answer:
i)
| Schottky defect | Frenkel defect |
| 1. Vacancy defect which arises due to the messing of equal number of cations and anions from the lattice sites. | Interstitial defector dislocation defect which arises when the smaller ion, usually cation is dislocated from its normal site to an interstitial site. |
| 3. Cation and anion in are of almost similar sizes | there is a large difference size of ions |
| 4. The density of the crystal is lowered | It does not affect the density of the crystal |
ii) It is caused by metal excess defect due to anion vacancies. When crystals of NaCI are heated in a atmosphere of sodium vapour, the sodium atoms are deposited on the surface of the crystal. The Cl- ions diffuse to the surface of the crystal and combine with Na atoms to give NaCI. The electrons released from Na atoms diffuse into the crystal and occupy anionic sites to form Fcentres, which impart yellow colourto the crystal. The colour results by excitation of these electrons when they absorb energy from the visible light falling on the crystals.
Question 7.
a) NaCI has fcc structure. Calculate the number of NaCI units in a unit cell of NaCI. (March – 2013)
b) Calculate the density of NaCl, if edge length
of NaCI unit cells is 564pm. [Molar mass of
NaCI =58.5g/mol].
Answer:
a) Number of Na ions = 12 (at edge centres) x \(\frac{1}{4}\) +
= 1(at body centre) x 1
= 3 + 1 = 4
Number of Cl- ions = 8 (at the corners) x \(\frac{1}{8}\) +
= 6 (at face centres) x \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 1 + 3 = 4
? Number of NaCI units per unit cell (z) = 4

Question 8.
Unit cells can be broadly classified into 2 categories primitive and centred unit cells. (Say – 2013)
a) What is a unit cell?
b) Name the three types of centred unit cells.
c) The unit cell dimension of a particular crystal system is a = b = c, a = ß = ? = 90°. ldentify the crystal system.
d) Give one example for the above crystal system.
Answer:
a) The smallest repeating unit of a crystal.
b) Body centred unit cell, Face centred unit cell and End centred unit cell.
c) Cubic crystal system.
d) NaCI (Rock salt struãture)
Question 9.
a) Every substance has some magnetic properties associated with it. How will you account for the following magnetic properties? (March – 2014)
i) Paramagnetic property
ii) Ferromagnetic property
b) A compound is formed by two elements P and Q. Atoms of Q (as anions) make hep lattice and those of the element P (as cations) occupy all the tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound?
Answer:
a) i) Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by a magnetic field. They are magnetised in a magnetic field in the same direction. They lose their magnetism in the absence of magnetic field. Paramagnetism is due to presence of one or more unpaired . electrons, e g., O2, Cu2+
ii) Ferromagnetic substances are strongly attracted by a magnetic field. They are permanantly magnetised. When a ferromagnetic substance is placed in a magnetic field all the magnetic domains get oriented in the direction of the magnetic field and a strong magnetic effect is produced, e.g,, Fe, Co
![]()
For hep lattice, No. of particles per unit cell = 6
? Number of anions of Q in the unit cell = 6
Number of tetrahedral voids = 2 x N = 2 x 6 = 12
? Number of cations of P in the unit cell = 12
Hence, formula of the compound = P12Q2 = P2Q
Question 10.
a) Crystalline solids are ‘anisotropic’. What is ‘anisotropy’? (Say – 2014)
b) Copper crystals have fee unit cells.
i) Compute the number of atoms per unit cell of copper crystals.
ii) Calculate the mass of a unit cell of copper crystals. (Atomic mass of copper = 63.54 u)
Answer:
a) Anisotropy means physical properties shows different values along different directions, eg. refrative index electrical resistance,
b) i) Face centred cubic unit cell (fee) – It contains atoms at all the corners and at the centre of all the faces of the cube.
8 corners x \(\frac{1}{8}\) per corner atom

Question 11.
Unit cells can be divided into two categories, primitive and centred unit cells. (March – 2015)
a) Differentiate between Unit Cell and Crystal Lattice.
b) Calculate the number of atoms per unit cell in the following:
i) Body centred cubic unit cell (bcc)
ii) Face centred cubic unit cell (fee)
Answer:
a) Unit Cell – It is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice which, when repeated in different directions, generates the entire lattice.
Crystal Lattice – It is the regularthree dimensional arrangement of points in space.
b) i) Body centred cubic unit cell (bcc) – It has atoms at each of its corners and one atom at its body centre.
8 corners x \(\frac{1}{8}\) per corner atom = 8 x \(\frac{1}{8}\) = 1 atom
1 body centre atom = 1 x 1 = 1 atom
? Total number of atoms per unit cell = 2 atoms
ii) Face centred cubic unit cell (fee) – It contains atoms at all the corners and at the centre of all the faces of the cube.
8 corners x \(\frac{1}{8}\) per corner atom
\(=8 \times \frac{1}{8}=1\) atom
6 face – centred atoms x \(\frac{1}{2}\) atom per unit cell \(=6 \times \frac{1}{2}=3\) atoms
? Total number of atoms per unit cell = 4 atoms
Question 12.
a) Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid? (Say – 2015)
i) Definite heat of fusion
ii) Isotropic nature
iii) A regular ordered arrangement of constituent particles
iv) A true solid
b) Frenkel defect and Shottky defects are two stoichiometric defects found in crystalline solids.
i) What are stoichiometric defects?
ii) Write any two differences between Frenkel defect and Schottky defect.
Answer:
a) ii) Isotropic nature
b) i) Stoichiometric defects are those point defects which do not disturb the stoichiometry of the solid.
ii)
| Schottky defect | Frenkel defect |
| 1. Cation and anion in are of almost similar sizes | there is a large difference size of ions |
| 2. The density of the crystal is lowered | It does not affect the density of the crystal |
Question 13.
a) Which of the following is a molecular solid? (March – 2016)
a) Diamond
b) Graphite
c) Ice
d) Quartz
b) Unit cells can be classified into primitive and centered unit cells. Differentiate between primitive and centered unit cells.
c) Presence of excess Sodium makes NaCI crystal coloured. Explain on the basis of crystal defects.
Answer:
a) Ice
b) In primitive unit cell constituent particles are present only at the corner positions. Unit cells in which one constituent particles are present at the centres of a faces in addition to those at corners.
c) Such anionic sites occupied by unpaired electrons are called F – centres (colour centres). They impart yellow colourto the crystals of NaCI. The colour results by excitation of these electrons when they absorb energy from the visible light falling on the crystals.
Question 14.
A unit cell is a term related to crystal structure. (Say – 2016)
a) What do you mean by unit cell?
b) Name any two types of cubic unit cells.
c) Calculate the number of atoms in each of the above – mentioned cubic unit cells.
d) Identify the substance which shows Frenkel defect:
i) NaCI
ii) KCI
iii) ZnS
iv) AgBr
Answer:
a) Unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice which, when repeated in different directions, generates the entire lattice.
b) Simple cubic unit cell, body centred cubic (bcc) unit cell, face centred cubic (fee) unit cell (any two)
c) Number of atoms per unit cell
i) Simple cubic unit cell:
Total number of atoms in one unit cell \(=8 \times \frac{1}{8}=1\) atom
ii) Body centred cubic (bcc) unit cell: Total number of atoms in one unit cell
\(=\left(8 \times \frac{1}{8}\right)+(1 \times 1)=1+1=2\) atoms
iii) Face centred cubic (fee) unit cell: Total number of atoms in one unit cell \(=\left(8 \times \frac{1}{8}\right)+\left(6 \times \frac{1}{2}\right)=1+3=4\)
(any two required)
d) ZnS or AgBr
(AgBr shows both Schottky and Frenkel defects)
Question 15.
a) Identify the non – stoichiometric defect (March – 2017)
i) Schottky defect
ii) Frenkel defect
iii) Interstitial defect
iv) Metal deficiency defect
b) What type of substance could make better permanent magnets – ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic? Justify your answer.
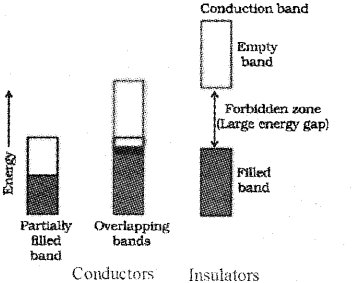
c) In terms of Band theory write the differences between conductor and insulator.
Answer:
a) iv) Metal deficiency defect
b) Ferromagnetic substances could make better permanent magnets because when these substances are placed in a magnetic field all the magnetic moments (domains) get oriented in the direction of the magnetic field and a strong magnetic effect is produced. This ordering of domains persist even when the magnetic field is removed and the ferromagentic substance becomes a permanent magnet.
The schematic alignment of magnetic moments in a ferromagnetic substance is as shown below:
![]()
c) In conductors the valence band is either partially filled or it is overlaped with a higher energy unoccupied conduction band so that the electrons can flow easily under an applied electric field. Whereas in insulators the energy gap between the filled valence band and the next higher unoccupied conduction band is large so that electrons cannot jump to it.
Question 16.
a) From the following choose the incorrect statement about crystalline solids. (Say – 2017)
i) Melt at sharp temperature.
ii) They have definite heat of fusion.
iii) They are isotropic
iv) They have long range order.
b) Cubic unit cells are divided into primitive, bcc and fee.
i) Calculate the number of atoms in a unit cell of each of the following:
* bcc
* fcc
ii) Write two examples for covalent solids.
a) iii) They are isotropic
b) i) \(\begin{array}{l}
\text { bcc }-2\left(8 \times \frac{1}{8}+1=2\right) \\
\text { fCc }-4\left(8 \times \frac{1}{8}+6 \times \frac{1}{2}=4\right)
\end{array}\)
ii) Graphite, Diamond
We hope the Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 The Solid State help you. If you have any query regarding Kerala Plus Two Chemistry Chapter Wise Previous Questions Chapter 1 The Solid State, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
