Kerala Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 2 Principles of Management
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the job of ‘speed boss’ under Functional Foremanship?
Answer:
He supervises matter relating to the speed of work.
Question 2.
Who is the father of Modem Management?
Answer:
Henry Fayol
Question 3.
Which principle of management suggest that employees should be treated with justice and kindness?
Answer:
Equity.
Question 4.
Fayol pointed out the danger and costs of unnecessary labour turnover in one of his principles. Name the principle.
Answer:
Stability of personnel.
Question 5.
Obedience, respect for authority and observation of established rules is known as
(a) Order
(b) Discipline
(c) Equity
(d) Initiative
Answer:
(b) Discipline
Question 6.
Systematic concentration of authority at top level is known as
Answer:
Centralisation
Question 7.
Identify the management principle which states that ‘Union is Strength’.
Answer:
Esprit De Corps
Question 8.
“Have a place for everything and everything should be in its place”. Which management principle is referred here?
Answer:
Order
Question 9.
Identify the management principle which is based on an idea of “one head and one plan”.
Answer:
Unity of direction
Question 10.
Lack of this principle may lead to conflict among subordinates. Briefly explain this principle of management.
Answer:
Unity of command
Question 11.
A factory has three departments – Production, Marketing and Finance. These departments take decisions without mutual understanding and consultation. So conflicts, confusion and duplication are quite common. State which function of management is violated here?
Answer:
Unity of direction.
Question 12.
A subordinate receives orders from three senior officers in an organization. Which principle of management is violated here.
Answer:
Unity of command
Question 13.
Study the diagram and mention the shortcut used for direct communication between ‘D’ and ‘P’.
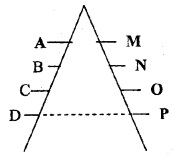
Answer:
Gangplank
Question 14.
Identify the management principle which promotes specialization.
Answer:
Division of work
Question 15.
This principle is against the policy of divide and rule. Which principle of Henry Fayol is referred to in this context?
Answer:
Esprit de corps
Question 16.
It is a chain of command from the highest level to the lowest level. It’is called
Answer:
Scalar Chain.
Question 17.
“Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for development. “Identify the principle of management formulated by Fayol.
Answer:
Initiative.
Question 18.
The father of scientific management is
Answer:
F.W. Tayor.
Question 19.
‘She/he keeps machines, materials, tools, etc., ready for operations by concerned workers’. Whose work is described by this sentence under functional foremanship?
(a) Instruction Card Clerk
(b) Repair Boss
(c) Gang Boss
(d) Route Clerk
Answer:
(c) Gang Boss
Question 20.
Management should find ‘One best way’ to perform a task. Which technique of scientific management is defined in this sentence?
(a) Time Study
(b) Motion Study
(c) Fatigue Study
(d) Method Study
Answer:
(d) Method Study
Question 21.
Find the odd one.
(a) Order
(b) Equity
(c) Fatigue study
(d) Unity of direction
Answer:
(c) Fatigue study
Question 22.
The scientific technique of task setting is known as
(a) Method study
(b) Motion study
(c) Work-study
(d) Time study
Answer:
(c) Work-study
Question 23.
Which technique of scientific management gives high compensation to better performer?
Answer:
Differential piece rate system
Question 24.
Name the technique of scientific management which focuses on separation of planning and execution function.
Answer:
Functional foremanship.
Question 25.
It involves the study of movement of operations of a worker. It is
Answer:
Motion study
Question 26.
The change in attitudes of employers and employees towards each other referred to as
Answer:
Mental revolution
Question 27.
Which principle of Taylor advocates scientific enquiry as opposed to hit and trail?
Answer:
Science; not rule of thumb
Question 28.
Taylor advocated that specialization must be introduced in an organization. He developed a technique for this purpose, which consists of 8 specialist foremen. Identify technique of scientific management referred here.
Answer:
Functional foremanship
Question 29.
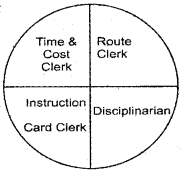
Complete the following circle.
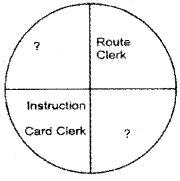
Answer:
Question 30.
Name the personnel who work under the production in charge?
Answer:
Speed Boss, Gang Boss, Repair Boss, and Inspector.
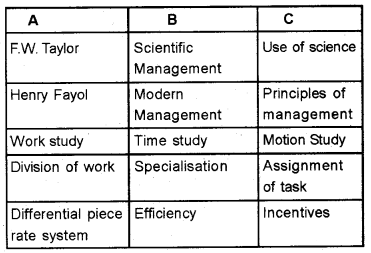
Question 31.
Link column A with B and C.
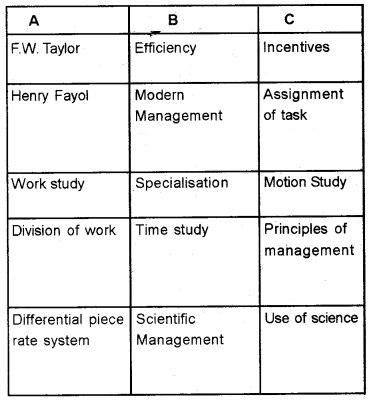
Answer:
Question 32.
Mr. Syam, the Production Manager of a firm, instructs Mr. Kiran to produce 50 units of a product per day. Mr. Arun, the Assistant Production Manager, instructs Mr. Kiran to produce 75 units. Which management principle is violated here?
Answer:
Unity of command.
Question 33.
Find out the odd one and state the reason.
(a) Stability of tenure of personnel.
(b) Scientific selection and training of workers.
(c) Maximum output.
(d) Replacement of old rule of thumb method.
Answer:
(a) Stability of tenure of personnel.
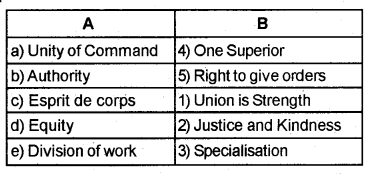
Question 34.
Match the following.
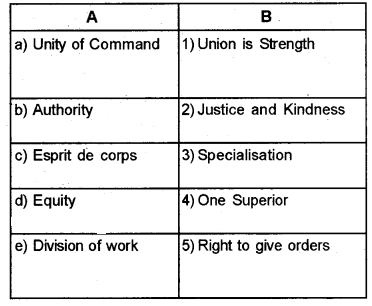
Answer:
Question 35.
Avoiding unnecessary efforts, expenses and tools in the factory is called in scientific management.
Answer:
Simplification of works.
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- Which technique of scientific management suggests that each worker should be supervised by specialists?
- Give the names of two designations of any two types of specialist.
Answer:
- Functional foremanship
- Gang boss, Speed boss
Question 2.
What do you mean by managerial principles?
Answer:
Management principles are statement of fundamental truth which provide guidelines for management decision making and action.
Question 3.
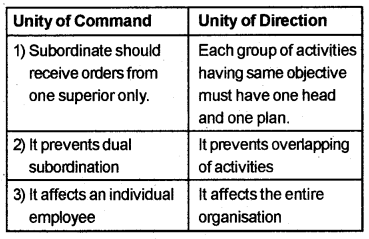
Distinguish between unity of command and unity of direction.
Answer:
1. Unity of Command:
The principle of unity of command state that each employee should receive orders from one superior only. It helps to avoid confusion and conflict in the employees
2. Unity of Direction:
Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and co-ordination.
Question 4.
What is ‘fatigue study’?
Answer:
Fatigue study:
Fatigue study seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task.
Question 5.
How does ‘mental revolution’ helpful ineffective management?
Answer:
Mental revolution:
It involves a change in the mental attitude of workers and management towards each other. Both parties should realise each other’s importance and work towards the profit of the firm.
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“Management principles are dynamic”. Comment
Answer:
Management principles are dynamic – Management principles are flexible and can be utilized under different conditions of the organizations. They are influenced by the need of the given situation.
Question 2.
Which principle of management is violated in the following situations?
- When a worker receives order from more than one boss.
- When the employee is given responsibility to achieve target production of 1000 units with no authority to access to raw materials.
- Where a worker is wasting time in search of tools in the organization.
Answer:
- Unity of command
- Authority and responsibility
- Order
Question 3.
Mr. Dileep, a newly recruited clerk for accounts department was initially posted in the cash section. After one month he was transferred to supplies section. Again a week later, he was transferred to EDP section.
- Which principle is violated here?
- What is the consequence of such frequent change?
Answer:
1. Stability of tenure of personnel.
2. If employees are frequently changed from one job to another, the entire production process will be disturbed. Also, both quantity and quality of work get reduced. Frequent change in job will create job dissatisfaction in employees.
Question 4.
Fayol points out the danger and cost of unnecessary labour turnover in one of these ‘Principles’. Name & explain the principle.
Answer:
a. Principle of stability of personnel
b. Stability of Personnel:
According to Fayol, workers should not be moved from one job to another frequently. It helps to minimize labour turnover in the organization.
Question 5.
Hina and Harish are typists in a company. They have the same educational qualifications. Hina is getting Rs. 3000 per month and Harish Rs. 4000 per month as salary for the same working hours. Which principle of management is violated in this case? Name and explain the principle.
Answer:
Principle of equity:
This principle requires the managers to be kind and just to workers. Superiors should be impartial while dealing with their subordinates.
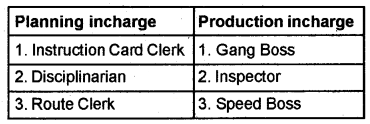
Question 6.
Group the following persons coming under Planning incharge and production incharge based on F.W. Taylor’s functional foremanship.
Gang Boss, Instruction Card Clerk, Inspector, Disciplinarian, Speed Boss, Route Clerk.
Answer:
Question 7.
Distinguish between unity of command and unity of direction.
Answer:
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Briefly explain the nature or features of managerial principles.
Answer:
Nature of Principles of Management:
Principles of management are statements of fundamental truth which provides guidelines for management decision making and action. The nature of management principles are:
1. Universal applicability: Management principles ha/e universal application in all types of organizations.
2. General guidelines: The principles are guidelines to action.
3. Formed by practice and experimentation: The principles of management are formed by experience and experimentation of managers.
4. Flexible: The principles of management are not rigid. They are flexible and can be modified according to the situation.
5. Influencing human behaviour: Management principles aim at influencing behaviour of human beings.
6. Cause and effect relationship: The principles of management establish the relation between the cause and effect.
Question 2.
State any 4 points highlighting the importance of principles of management.
Answer:
1. Increase efficiency:
The understanding of the management principles provides guidelines to the managers for handling effectively the complex problems.
2. Optimum utilization of resources:
The principles of management helps in the optimum utilization of resources through division of work, delegation of authority, etc.
3. Scientific decision:
Management principles help in thoughtful decision-making. Such decisions are free from bias and prejudices.
4. Meeting the changing environmental requirements:
Management principles are flexible and can be modified to meet changing requirements of environment.
5. Fulfilling social responsibility:
Management principles help the managers to fulfill the social responsibilities towards society.
Question 3.
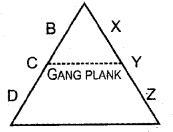
If we follow the principle of scalar chain strictly, there is a possibility of unnecessary delay in communication.
- What is the alternative proposed by Fayol to overcome this issue?
- Explain this principle.
Answer:
Gang Plank:
According to the concept of gangplank persons of the same rank can communicate with each other especially in emergency situations. It helps to save a lot of time in communication and possibility of distortion of messages can be reduced.
Question 4.
What contradiction do you find in the principle of unity of command and the technique of functional foremanship?
Answer:
In case of unity of command, every employee receives instructions from one boss only and he is responsible and accountable to him alone. In case of functional foremanship, every worker receives instructions from eight losses, four from planning department and four from production department. In this way, unity of command stresses on centralisation and functional foremanship on decentralization.
Question 5.
“Proper understanding of management principles makes the managers more realistic in their profession.” Explain the concept.
Answer:
Significance of the Principles of Management
1. Increase efficiency:
The understanding of the management principles provides guidelines to the managers for handling effectively the complex problems.
2. Optimum utilization of resources:
The principles of management helps in the optimum utilization of resources through division of work, delegation of authority, etc.
3. Scientific decision:
Management principles help in thoughtful decision-making. Such decisions are free from bias and prejudices.
4. Meeting the changing environmental requirements:
Management principles are flexible and can be modified to meet changing requirements of environment.
5. Fulfilling social responsibility:
Management principles help the managers to fulfill the social responsibilities towards society.
Question 6.
Henry Fayol is of the opinion that ‘workers should not be shifted from their job position frequently’.
- Identify the functional principle referred to here.
- State any 3 characteristics of management principles.
Answer:
1. Stability of personnel
2. Nature of Principles of Management:
Principles of management are statements of fundamental truth which provides guidelines for management decision making and action. The nature of management principles are:
1. Universal applicability: Management principles ha/e universal application in all types of organizations.
2. General guidelines: The principles are guidelines to action.
3. Formed by practice and experimentation: The principles of management are formed by experience and experimentation of managers.
4. Flexible: The principles of management are not rigid. They are flexible and can be modified according to the situation.
5. Influencing human behavior: Management principles aim at influencing behavior of human beings.
6. Cause and effect relationship: The principles of management establish the relation between the cause and effect.
Question 7.
Complete the diagram.
Answer:
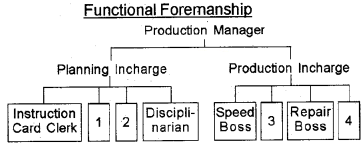
- Route Clerk
- Time & Cost Clerk
- Gang Boss
- Inspector
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mr. Arioop, a supervisor has been instructed to produce 100 units Jer day in a factory while the marketing manager instructs to produce 120 units per day in order to meet the demand.
- Which principle of management is violated here?
- Name any 5 adverse effects that may take place due to this violation.
Answer:
1. Unity of command
2. The violation of this principle will have the following consequences:
- It will be very difficult to maintain discipline.
- Duplication of work.
- Escaping responsibility.
- Disobeying the orders of superiors.
- Overlapping of orders and instructions
Question 2.
Explain the characteristics of Management Principles.
Answer:
Nature of Principles of Management:
Principles of management are statements of fundamental truth which provides guidelines for management decision making and action.
The nature of management principles are:
1. Universal applicability: Management principles ha/e universal application in all types of organizations.
2. General guidelines: The principles are guidelines to action.
3. Formed by practice and experimentation: The principles of management are formed by experience and experimentation of managers.
4. Flexible: The principles of management are not rigid. They are flexible and can be modified according to the situation.
5. Influencing human behavior: Management principles aim at influencing behaviour of human beings.
6. Cause and effect relationship: The principles of management establish the relation between the cause and effect.
Question 3.
Give a short note on importance of management principles.
Answer:
Significance of the Principles of Management
1. Increase efficiency:
The understanding of the management principles provides guidelines to the managers for handling effectively the complex problems.
2. Optimum utilization of resources:
The principles of management helps in the optimum utilization of resources through division of work, delegation of authority, etc.
3. Scientific decision:
Management principles help in thoughtful decision-making. Such decisions are free from bias and prejudices.
4. Meeting the changing environmental requirements:
Management principles are flexible and can be modified to meet changing requirements of environment.
5. Fulfilling social responsibility:
Management principles help the managers to fulfill the social responsibilities towards society.
Question 4.
Discuss the techniques and methods developed by Taylor.
Answer:
Techniques of Scientific Management
1. Functional foremanship:
Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are separated. He classified 8 specialist foremen into two departments viz. Planning and Production department. Both departments have four foremen each. Functional foremanship is based on the principle of division of work.
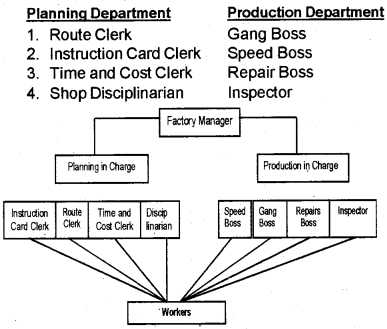
- Route clerk: To lay down the sequence of operations through which the raw materials have to pass in the production process.
- Time & cost clerk: To lay down the standard time for completion of the work.
- Instruction card clerk: He is expected to deal the instructions to be followed by workers in handling the job.
- Disciplinarian: He maintains proper discipline in the factory.
- Gang boss: He arranges material, machine, tool, etc. for operation.
- Speed boss: He supervises matters relating to the speed of work.
- Repair boss: He ensures repairs and maintenance of the tools and machines.
- Inspector: He checksthe quality of work done.
2. Standardisation and simplification of work:
Standardisation refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity. It includes use of standard tools and equipment, methods, working conditions, etc. for the maximisation of output. Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary diversity of products. -It results in savings of cost of labour, machines, and tools.
3. Method study:
The objective of method study is to find out one best way of doing the job. The main objective is to minimize the cost of production and maximize the.quality of the work.
4. Motion study:
Motion study involves close observation of the movements of the workers and machines to perform a particular job. It helps to eliminate unnecessary movements of men, materials, and machine.
5. Time study:
It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes and determine labour costs.
6. Fatigue study:
Fatigue study seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task.
7. Differential piece wage system:
Under this system of wage payment, two kinds of rates are laid down.
- Higher rates are offered to those workers who produce more than standard output.
- Lower rates for those who produce below standard output.
8. Mental revolution:
It involves a change in the mental attitude of workers and management towards each other. Both the parties should realise each other’s importance and work towards the profit of the firm.
Plus Two Business Studies Principles of Management Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Prepare a seminar report showing all the principles of management suggested by Henry Fayol.
Answer:
Fayol’s Principles of Management:
Henry Fayol (1841-1925) is known as the ‘Father of General Management’. The 14 principles of management given by him are:
1. Division of Work:
This principle states that a complex work should be divided into small tasks, and each task should be assigned a particular employee. Division of work leads to specialization.
2. Authority and Responsibility:
Authority is the right to give orders to the subordinates and responsibility is the obligation to perform the work in the mannerdirected by authority. There should be a balance between authority and responsibility.
3. Discipline:
it is the obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement which are necessary for working of the organization.
4. Unity of Command:
The principle of unity of command statej that each employee should receive orders ffom one superior only. It helps to avoid confusion and conflict in the employees.
5. Unity of Direction:
Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. This ensures unity of action and co-ordination.
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest:
The Interest of an organization should take priority over the interests of any one individual employee.
7. Remuneration of Employees:
Remuneration should be just, equitable and fair to both employees and the organization.
8. Centralization and Decentralization:
Centralisation means concentration of authority at the top management. Decentralisation means dispersal of authority to the lower levels in the organisation. There should be a balance between Centralisation and decentralization.
9. Scalar Chain:
The formal lines of authority from highest to lowest ranks are known as scalar chain. According to this principle, communication should passthrough the established chain of command. It ensures unity of command and effective communication.
Gang Plank:
According to the concept of gang plank persons of the same rank can cprnmunicate with each other especially in emergency situations. It helps to save a lot of time in communication and possibility of distortion of messages can be reduced.
10. Order:
According to Fayol, “People and materials must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency.”
11. Equity:
This principle requires the managers to be kind and just to workers. Superiors should be impartial while dealing with their subordinates.
12. Stability of Personnel:
According to Fayol, workers should not be moved from one job to another frequently. It helps to minimise labour tumoverin the organization.
13. Initiative:
Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements. Maximum kpuKishcrs
14. Espirit De Corps (Union is strength):
According to Fayol, Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees.
Question 2.
- Who formulated principles for managing an organisation scientifically.
- Explain the principles.
Answer:
1. Taylor’s Scientific Management:
Fredrick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915) is known as the Father of Scientific Management. His book ‘Principles of Scientific Management’was published in 1911.
In the words of Taylor, “Scientific management means knowing exactly what you want men to do and seeing that they do it in the best and cheapest way”.
2. Principles:
- Principles of Scientific Management
- Techniques of Scientific Management
1. Principles of Scientific Management
a. Science and not the rule of thumb :
The first principle of scientific management requires scientific study and analysis of each element of job in orderto replace old rule of thumb approach.
b. Harmony, not discord:
As per this principle, there should be complete harmony between the management and workers. Taylor called for complete mental revolution on the part of both management and workers. Both the parties should realize each other’s importance and work towards the profits of the firm.
c. Co-operation not individualism:
There should be complete co-operation between the labour and the management instead of individualism. According to Taylor, there should be an almost equal division of work and responsibility between workers and management.
d. Development of each and every person to his or her greatest efficiency and prosperity:
The growth and development of an organisation depends on the efficiency and prosperity of employees. The efficiency of employees can be developed by giving propertraining and development. This ensure the growth of an organisation.
2. Techniques of Scientific Management
a. Functional foremanship:
Functional foremanship is a technique in which planning and execution are separated. He classified 8 specialist foremen into two departments viz. Planning and Production department. Both departments have four foremen each. Functional foremanship is based on the principle of division of work.
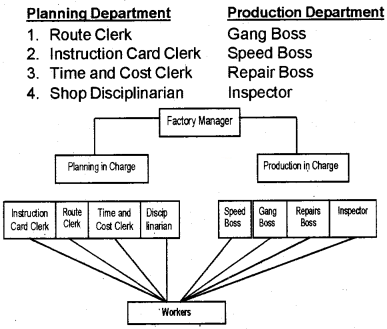
- Route clerk: To lay down the sequence of operations through which the raw materials have to pass in the production process.
- Time & cost clerk: To lay down the standard time for completion of the work.
- Instruction card clerk: He is expected to deal with the instructions to be followed by workers in handling the job.
- Disciplinarian: He maintains proper discipline in the factory.
- Gang boss: He arranges material, machine, tool, etc. for operation.
- Speed boss: He supervises matters relating to the speed of work.
- Repair boss: He ensures repairs and maintenance of the tools and machines.
- Inspector: He checks the quality of work done.
b. Standardisation and simplification of work:
Standardisation refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity. It includes use of standard tools and equipment, methods, working conditions, etc. for the maximisation of output. Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary diversity of products. -It results in savings of cost of labour, machines, and tools.
c. Method study:
The objective of method study is to find out one best way of doing the job. The main objective is to minimize the cost of production and maximize the.quality of the work.
d. Motion study:
Motion study involves close observation of the movements of the workers and machines to perform a particular job. It helps to eliminate unnecessary movements of men, materials, and machine.
e. Time study:
It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The objective of time study is to determine the number of workers to be employed, frame suitable incentive schemes and determine labour costs.
f. Fatigue study:
Fatigue study seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task.
g. Differential piece wage system:
Under this system of wage payment, two kinds of rates are laid down.
- Higher rates are offered to those workers who produce more than standard output.
- Lower rates for those who produce below standard output.
h. Mental revolution:
It involves a change in the mental attitude of workers and management towards each other. Both parties should realise each other’s importance and work towards the profit of the firm.
