Kerala Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 10 Financial Markets
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
It is a market for medium and long-term instruments having a period of maturity of more than one year is?
(a) Money market
(b) Capital market
(c) Commercial bill market
(d) Call market
Answer:
(b) Capital market
Question 2.
Identify the related term from the following.
- Share : Capital Market
- Commercial Paper : ………………………
Answer:
2. Money Market
Question 3.
Identify the odd one.
(a) Bill of Exchange
(b) Treasury bills
(c) Certificate of deposits
(d) Equity shares
Answer:
(d) Equity shares
Question 4.
Find the odd one out.
(a) Call money market
(b) Commercial bill market
(c) Treasury bill market
(d) New issue market
Answer:
(d) New issue market.
Question 5.
Which among the following is not related with Money Market?
(a) Call money market
(b) Equity shares
(c) Commercial Paper
(d) Certificate of Deposit
Answer:
(b) Equity shares
Question 6.
Offering the shares to existing shareholders whenever fresh issue is made. Identify the method of primary issue.
Answer:
Right issue
Question 7.
These shares are issued as fully paid shares to the existing shareholders in the ratio of shares held by them. Identify the share.
Answer:
Bonus shares
Question 8.
Birla White Ltd., a leading cement manufacturing company, proposes to give 1 Equity share to every 10 shares held by the existing Equity shareholders as dividend due to poor liquidity position. Identify the type of dividend the company proposes to declare.
(a) Cash dividend
(b) Property dividend
(c) Script dividend
(d) Stock dividend
Answer:
(d) Stock dividend
Question 9.
Treasury Bills are basically ……………….
(a) An instrument to borrow short term funds
(b) An instrument to borrow long term funds
(c) An instrument of capital market
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) An instrument to borrow short term funds
Question 10.
………………….. securities are not required to be listed in the
stock exchange.
Answer:
Government securities
Question 11.
A Method of floating new issues does not deal directly to public but operates issuing houses and brokers. Name the Method.
Answer:
Offer for sale
Question 12.
Identify the watchdog of the capital market.
Answer:
SEBI (Securities Exchange Board of India)
Question 13.
Complete the series.
Money market: RBI
Capital market: ………….
Answer:
SEBI
Question 14.
National Stock Exchange of India was recognized as stock exchange in the year.
(a) 1992
(b) 1993
(c) 1994
(d) 1995
Answer:
(b) 1993
Question 15.
NSE commenced futures trading in the year.
(a) 1999
(b) 2000
(c) 2001
(d) 2002
Answer:
(c) 2001
Question 16.
To be listed on OTCEI, the minimum capital requirement for a company is …………….
(a) Rs. 5 crore
(b) Rs. 30 lakh
(c) Rs. 6 crore
(d) Rs. 1 crore
Answer:
(b) Rs. 30 lakh
Question 17.
Admission of a company for trading its securities in the stock exchanged is called ………….
Answer:
Listing
Question 18.
Certificate of Deposit is issued by
(a) Bank
(b) Mutual Fund
(c) Government
Answer:
(a) Bank
Question 19.
The process by which physical share certificate are converted into an equivalent number of securities to be held in electronic form is termed as …………………..
Answer:
Dematerialization
Question 20.
The issuing company will give a price band at which securities will be offered and gives the investors an opportunity to bid. Can you suggest the name for this method?
Answer:
Book building
Question 21.
At present trading in stock exchanges is taking place through ………………..
Answer:
Online trading
Question 22.
Smt. Faseela is a shareholder of ABC Co. Ltd, She gets an allotment of 50 shares free of cost from the company. ABC Ltd.
- Find out the method of share allotment referred here.
- Will it affect ownership?
Answer:
- Bonus shares
- Will not affect the ownership
Question 23.
Certain instruments of money market is short term, self – liquidating and used to finance credit sales. Name the instruments.
Answer:
Commercial bill
Question 24.
It is a long term financial market. It is divided as ………….. and ………………..
Answer:
Capital market, Primary market, Secondary market
Question 25.
Issue of shares through online trading system of stock exchange is called …………………
Answer:
Electronic – Initial Public Offer (e-IPO)
Question 26.
Which is the organised market where second hand securities are traded?
Answer:
Stock Exchange
Question 27.
………………. is the mirror which reflects the economic policies of a nation?
Answer:
Stock exchange
Question 28.
Exchange of paper certificate of securities into electronic form is called …………….
Answer:
De-mat (De Materialisation)
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
“Financial market perform an allocative function”. How?
Answer:
Financial markets channelise savings of investors and makes them available for needs of industry and hence they are set to perform the allocated function.
Question 2.
State the two categories into which financial markets are classified?
Answer:
Two categories into which financial markets are classified:
- Money Market
- Capital Market
Question 3.
Explain the features of Certificate of Deposit (CD).
Answer:
Money Market Instruments
1. Treasury Bill:
They are issued by the RBI on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short term requirement of funds. They are issued at a discount on the face value of the instruments and repayable at par.
They are issued in the form of promissory notes. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds as no interest is paid on such bills.They are highly liquid. The maturity period of these bills may be between 14 to 364 days.
2. Commercial Paper:
Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a maturity period of 15 days to one year. It is sold at a discount and redeemed at par.
3. Call Money:
Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions.
4. Certificate of Deposit:
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are short-term instruments issued by Commercial Banks and Special Financial Institutions (SFIs), which are freely transferable from one party to another. The maturity period of CDs ranges from 91 days to one year.
5. Commercial Bill:
A commercial bill is a Bill of Exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. When goods are sold in credit, the seller draws the bill and the buyer accepts it. The seller can discount the bill before its maturity with the bank. When a trade bill is accepted by a commercial bank it is known as commercial bills.
Question 4.
Define stock exchange.
Answer:
Stock Exchange:
According to Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act 1956, stock exchange means any body of individuals, whether incorporated or not, constituted for the purpose of assisting, regulating or controlling the business of buying and selling or dealing in securities.
Question 5.
Explain briefly how stock exchanges provide liquidity and marketability to existing securities?
Answer:
Stock exchange provides a continuous market where securities are brought and sold. It provides opportunities for investors to disinvest and reinvest in securities. It there by provides liquidity and easy marketability to securities.
Question 6.
Write the full form of
- OTCEI
- NSE
Answer:
- OTCEI is Over the Counter Exchange of India.
- NSE is the National Stock Exchange.
Question 7.
State the minimum capital requirement for a company to be listed with OTCEI
Answer:
For company to be listed with OTCEI minimum paid up capital Rs. 30 Lack or more.
Question 8.
In a classroom discussion, Asharaf argued that only listed securities are permitted to be in a stock exchange. While, Sundar argued that certain unlisted securities are also tilled in a stock exchange.
- Whose argument do you support?
- Justify your answer.
Answer:
- We support the argument of Sundar.
- Government securities do not require to be listed.
Question 9.
What is Primary Market?
Answer:
Primary Market:
The primary market is also known as the new issues market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time. A company can raise capital through the primary market in the form of equity shares, preference shares, debentures, loans and deposits.
Funds raised may be for setting up new projects, expansion, diversification, etc. of existing enterprises. The investors in this market are banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, mutual funds and individuals.
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
It is a market for short term financial assets having a maturity period of less than one year.
- Explain the concept referred above.
- How does it differ from capital market?
Answer:
1. Money market
2. Difference between capital market and money market
| Capital Market | Money Market |
| 1) Market deals only long term fund. | 1) Market deals only short term fund. |
| 2) It arranges large amount of fund. | 2) It arranges small amount of fund. |
| 3. Return is high. | 3) Return is law. |
| 4) The instruments used are equity shares, preference shares, debentures and bonds. | 4) The instruments used are call money, treasury bills, trade bills, commercial paper and certificate of deposit. |
| 5) SEBI is the market regulator. | 5) RBI is the market regulator. |
| 6) Capital market instruments are highly risky. | 6) Money market instruments are safe. |
Question 2.
Define primary market. State any two methods of issuing securities in primary market.
Answer:
Primary Market:
The primary market is also known as the new issues market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time. A company can raise capital through the primary market in the form of equity shares, preference shares, debentures, loans and deposits.
Funds raised may be for setting up new projects, expansion, diversification, etc. of existing enterprises. The investors in this market are banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, mutual funds and individuals.
Methods of flotation:
There are various methods of floating new issues in the primary market. They are:
a. Offer through Prospectus:
Prospectus is an invitation to the public for the subscription of shares and debentures of a company. The issues may be underwritten and also are required to be listed on at least one stock exchange.
b. Offer for Sale:
Under this method new securities are not offered directly to the public. Initially the entire lots of securities are sold to an intermediary at a fixed price. The intermediary sells these securities to the public at a higher price.
c. Private Placement:
Private placement is the allotment of securities by a company to institutional investors or some selected individuals. It is less expensive and saves time.
d. Rights Issue:
According to the Companies Act, if a public company wants to issue additional shares, it must first be offered to the existing shareholders, in proportion to the amount paid up on their shares. This right is known as ‘Pre-emptive right’ and such an issue is called right issue.
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following documents traded in a capital market and money market. Treasury bill, Debentures, Certificate of deposit, Bonds, Equity shares, Commercial paper, Trade bill, and Preference shares.
Answer:
- Treasury bill – Money market
- Debentures – Capital market
- Certificate of deposit – Money market
- Bonds – Capital market
- Equity shares – Capital market
- Commercial paper – Money market
- Trade bill – Money market
- Preference shares – Capital market
Question 2.
During late 1990’s trading took place in the trading ring of the stock exchange through direct auction. In the trading, ring brokers assemble together and make a bargain on the price of securities. Therefore, investors felt difficulty in taking the delivery of securities soon after the execution of the transaction.
- Explain the new system emerged to overcome these limitations.
- Explain the merits of the new system.
Answer:
1. Online Trading.
2. Advantages of electronic trading system (Screen based online trading)
On line trading means buying and selling of shares and debentures are done through a computer terminal.
- On line trading ensures transparency in dealing.
- It helps in fixing prices of securities efficiently.
- It increases efficiency of operations by reducing time, cost and risk of errors.
- People from all over the country can buy or sell securities through brokers.
- All trading centres have been brought into one trading platform.
Question 3.
“NSEI” is the largest stock exchange of the country”.
- Do you agree?
- Explain its features.
Answer:
1. National Stock Exchange of India (NSE):
NSE is the most modern stock exchange in India. It was incorporated in 1992 and was recognised as a stock exchange in April 1993. It commenced operations in 1994. NSE has set up a nationwide fully automated screen based trading system.
2. Objectives of NSE:
- Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
- Ensuring equal access to investors all over the country.
- Providing a transparent securities market using electronic trading system.
- Enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements.
- Meeting international benchmarks and standards.
Question 4.
What are the objectives of SEBI?
Answer:
Objectives of SEBI
- To regulate stock exchange and the securities market to promote their orderly functioning.
- To protect the rights and interests of investors and to guide and educate them.
- To prevent trade malpractices.
- To regulate and develop a code of conduct to intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers etc.
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In India, a major portion of money market transaction is conducted by commercial banks like SBI, PNB, etc. Development banks like IFC, IDBI, etc. and special financial institutions like DFHI, UTI, etc. The indigenous banks, moneylenders and chitty funds are also other participants in the market.
- Categorise these money market participants into appropriate heads.
- Identify the submarkets in which these institutions participate for short term dealings.
Answer:
1. Capital market can be divided into organized market and unorganized market.
| Organised Money Market | Unorganised Money Market |
| Commercial Banks | Indigenous Bank |
| Development banks | Moneylenders |
| Special financial institutions | Chitty Funds |
2. The submarkets are called money market, commercial bill market, treasury bill market, commercial paper market, etc.
Question 2.
Listing of securities with a stock exchange involves stringent procedures. Small companies find it difficult to undergo is such formalities. Therefore, when such companies issue shares, there are only a few buyers for them.
- Identify the stock exchange promoted to solve these problem faced by small companies.
- List out the main features and advantages of this stock exchange.
Answer:
1. Over the Counter Exchange of India (OTCEI):
The OTCEI is a company incorporated under the Companies Act 1956. It was set-up to provide smalt and medium companies an access to the capital market.
It is fully computerised, transparent, single window exchange which provides quicker liquidity to securities at a fixed and fair price, liquidity for less traded securities. It is commenced trading in 1992.
2. Objectives of OTCEI
- Provide a trading platform to smaller and less liquid companies.
- Provide online trading facilities to the investors.
- Ensure a transparent system of trading.
- Ensure liquidity to the listed securities.
- Help the investors to exchange the securities at minimum cost.
Question 3.
Shareholders in India were facing a lot of problems in handling the paper-based certification, such as delay in transfer of ownership, forgery and theft of certification, bad delivery, etc. But nowadays there are no such difficulties. Paper forms of shares are not seen.
- What is this paperless security called?
- What are its merits?
Answer:
1. Dematerialisation
2. Dematerialisation:
It is a process by which physical share certificates are converted into an equivalent number of securities to be held in electronic form and credited in the investors’ account. For this, the investor has to open a Demat account with an organisation called a depository.
Question 4.
Explain the steps involved in the Purchase / Sale of securities.
Answer:
Trading Procedure on a Stock Exchanges:
- Selection of a broker.
- Opening Demat account with the Depository Participant (D.P.).
- Placing an order for the purchase or sale of securities with the broker.
- Purchase or sale of securities through on-line.
- Delivery of the contract note to the investor.
- Effecting changes in the Demat account.
- Making payment or receiving of money.
Question 5.
What are the benefits of depository services and Demat Account?
Answer:
Benefits of Depository Services and Demat Account:
- Sale and Purchase of shares and stocks of any company make easy.
- Saves time.
- No paperwork.
- Lower transaction costs.
- Ease in trading.
- Transparency in transactions.
- No counterfeiting of security certificate.
- Physical presence of investor is not required in stock exchange.
Question 6.
“SEBI is the watchdog of the security market”. Do you agree? Comment.
Answer:
Yes.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI):
In order to protect the investors and to promote the development of stock market, the Govt, of India established the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1988. In 1992 it becomes a statutory body under a special law of the Parliament.
SEBI is the supervisory body for regulation and promotion of securities market in the country. Investor protection is the major responsibility of SEBI. It’s head office is at Mumbai.
Question 7.
- What do you mean by dematerialisation?
- What are the benefits of Demat account?
Answer:
1. Dematerialisation:
It is a process by which physical share certificates are converted into an equivalent number of securities to be held in electronic form and credited in the investors’ account. For this, the investor has to open a Demat account with an organisation called a depository.
2. Benefits of Depository Services and Demat Account:
- Sale and Purchase of shares and stocks of any company make easy.
- Saves time.
- No paperwork.
- Lower transaction costs.
- Ease in trading.
- Transparency in transactions.
- No counterfeiting of security certificate.
- Physical presence of investor is not required in stock exchange.
Plus Two Business Studies Financial Markets Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- What is the Secondary market?
- Explain the functions of Secondary Market.
- Distinguish it from the Primary Market.
Answer:
1. Secondary market:
The secondary market is also known as the stock market or Stock exchange. It is a market for the purchase and sale of existing securities. It also provides liquidity and marketability to existing securities
2. Functions of a Stock Exchange:
a. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities:
Stock Exchange provides a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
b. Pricing of Securities:
A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. It is based on the forces of demand and supply.
c. Safety of Transaction:
Stock exchange has its own well-defined rules and regulations. This ensures safety and fair dealings to investors.
d. Contributes to Economic Growth:
Stock exchange provides a platform by which savings are channelised into the most productive investment proposals, which leads to capital formation and economic growth.
e. Providing Scope for Speculation:
Stock exchange provides scope within the provisions of Law for speculation in a restricted and controlled manner.
f. Economic barometer:
A stock exchange serves as a barometer of a country’s economic condition. Price trends in stock exchange indicate whether economy is going through boom or depression.
3. Differences between Primary Market and Secondary Market:
| Primary Market | Secondary Market |
| 1. It deals with new securities. | 1. It deals with existing securities. |
| 2. It promotes capital formation directly. | 2. It promotes capital formation indirectly. |
| 3. Investors can only buy securities. | 3. Investors can buy and sell the securities. |
| 4. Prices of the securities are determined by the management of the company. | 4. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of securities. |
| 5. Companies sell securities directly. | 5. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of securities. |
Question 2.
“In today’s commercial world, the stock exchange performs vital functions”. Explain the functions.
Answer:
Functions of a Stock Exchange:
1. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities:
Stock Exchange provides a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
2. Pricing of Securities:
A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. It is based on the forces of demand and supply.
3. Safety of Transaction:
Stock exchange has its own well-defined rules and regulations. This ensures safety and fair dealings to investors.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
Stock exchange provides a platform by which savings are channelised into the most productive investment proposals, which leads to capital formation and economic growth.
5. Providing Scope for Speculation:
Stock exchange provides scope within the provisions of Law for speculation in a restricted and controlled manner.
6. Economic barometer:
A stock exchange serves as a barometer of a country’s economic condition. Price trends in stock exchange indicate whether economy is going through boom or depression.
Question 3.
Prepare a seminar report on various segments of the money market.
Answer:
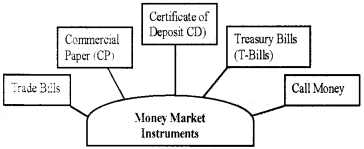
Money Market Instruments:
1. Treasury Bill:
They are issued by the RBI on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short term requirement of funds. They are issued at a discount on the face value of the instruments and repayable at par. They are issued in the form of promissory notes.
They are also known as Zero-Coupon Bonds as no interest is paid on such bills. They are highly liquid. The maturity period of these bills may be between 14 to 364 days.
2. Commercial Paper:
Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a maturity period of 15 days to one year. It is sold at a discount and redeemed at par.
3. Call Money:
Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions.
4. Certificate of Deposit:
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are short-term instruments issued by Commercial Banks and Special Financial Institutions (SFIs), which are freely transferable from one party to another. The maturity period of CDs ranges from 91 days to one year.
5. Commercial Bill:
A commercial bill is a Bill of Exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. When goods are sold in credit, the seller draws the bill and the buyer accepts it. The seller can discount the bill before its maturity with the bank. When a trade bill is accepted by a commercial bank it is known as commercial bills.
Question 4.
“Stock exchange is the barometer of the country’s economic health”. Discuss.
Answer:
Functions of a Stock Exchange:
1. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities:
Stock Exchange provides a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
2. Pricing of Securities:
A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. It is based on the forces of demand and supply.
3. Safety of Transaction:
Stock exchange has its own well-defined rules and regulations. This ensures safety and fair dealings to investors.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
Stock exchange provides a platform by which savings are channelised into the most productive investment proposals, which leads to capital formation and economic growth.
5. Providing Scope for Speculation:
Stock exchange provides scope within the provisions of Law for speculation in a restricted and controlled manner.
6. Economic barometer:
A stock exchange serves as a barometer of a country’s economic condition. Price trends in stock exchange indicate whether economy is going through boom or depression.
Question 5.
Prepare an assignment on functions of stock exchange.
Answer:
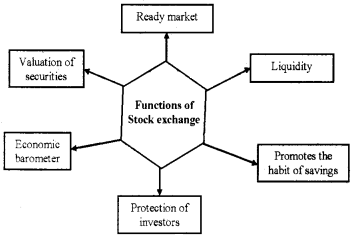
Functions of a Stock Exchange:
1. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities:
Stock Exchange provides a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
2. Pricing of Securities:
A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. It is based on the forces of demand and supply.
3. Safety of Transaction:
Stock exchange has its own well-defined rules and regulations. This ensures safety and fair dealings to investors.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth:
Stock exchange provides a platform by which savings are channelised into the most productive investment proposals, which leads to capital formation and economic growth.
5. Providing Scope for Speculation:
Stock exchange provides scope within the provisions of Law for speculation in a restricted and controlled manner.
6. Economic barometer:
A stock exchange serves as a barometer of a country’s economic condition. Price trends in stock exchange indicate whether economy is going through boom or depression.
Question 6.
RBI is the controller and guide of banks in India. In the field of stock market an institution similar to RBI is there. Can you name it and explain its objectives and functions?
Answer:
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI):
In order to protect the investors and to promote the development of stock market, the Govt, of India established the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1988. In 1992 it becomes a statutory body under a special law of the Parliament.
SEBI is the supervisory body for regulation and promotion of securities market in the country. Investor protection is the major responsibility of SEBI. It’s head office is at Mumbai.
Question 7.
“It is the regulatory and development agency of Indian Capital Market.”
- Identify the agency referred here.
- Explain its functions.
Answer:
1. SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India)
2. Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI):
In order to protect the investors and to promote the development of stock market, the Govt, of India established the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 1988. In 1992 it becomes a statutory body under a special law of the Parliament.
SEBI is the supervisory body for regulation and promotion of securities market in the country. Investor protection is the major responsibility of SEBI. It’s head office is at Mumbai.
Question 8.
- What is Primary Market?
- How it differs from Secondary Market?
Answer:
1. Primary Market:
The primary market is also known as the new issues market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time. A company can raise capital through the primary market in the form of equity shares, preference shares, debentures, loans, and deposits.
Funds raised may be for setting up new projects, expansion, diversification, etc. of existing enterprises. The investors in this market are banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, mutual funds, and individuals.
2. Differences between Primary Market and Secondary Market:
| Primary Market | Secondary Market |
| 1. It deals with new securities. | 1. It deals with existing securities. |
| 2. It promotes capital formation directly. | 2. It promotes capital formation indirectly. |
| 3. Investors can only buy securities. | 3. Investors can buy and sell the securities. |
| 4. Prices of the securities are determined by the management of the company. | 4. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of securities. |
| 5. Companies sell securities directly. | 5. Prices are determined by the demand and supply of securities. |
