Kerala Plus Two Business Studies Chapter Wise Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Nature and Significance of Management
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In order to be successful, an organization must change its goals according to the needs of the environment. Which characteristic of management is highlighted in the statement?
Answer:
Management is dynamic.
Question 2.
Management consists of functions like planning, organizing, directing, controlling, etc. This characteristic of management is called(Management as a group activity, Management as a process, Management as a system of authority, Management as a profession)
Answer:
Management is a process.
Question 3.
Identify the concept of management depicted in the following diagram.
Answer:
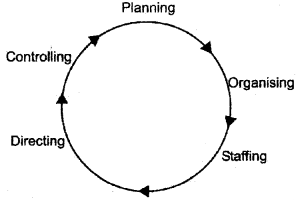
Question 4.
“Management should have systematized body of knowledge and should establish cause and effect relationship” identify the concept of management?
Answer:
Management is a science
Question 5.
“The principles of management are applied to all types of activities.” Which characteristic of management is highlighted by this statement?
Answer:
Management is universal.
Question 6.
Good Managers require continuous practice and personal skills. Identify the Management concept referred in this context
Answer:
Management is a profession
Question 7.
Amina, who is working as the Managing Director of a company, comes under which level of management?
Answer:
Top-level
Question 8.
To meet the objectives of the firm, the Management of BPL limited offers employment to physically challenged persons. Identify the organisational objective it is trying to achieve.
Answer:
It is social objective
Question 9.
Almost all universities conduct several courses on management subject. Numerous research studies are still going on this subject. Identify the concept of management referred to in this context.
Answer:
Management as a discipline.
Question 10.
Find the odd one and state the reason.
Chief Executive, Managing Director, Foreman, General Manager
Answer:
Foreman.
All others are belongs to top-level management
Question 11.
Which level of management establishes policies, plans and objectives?
Answer:
Top-level
Question 12.
The visiting card of a person is given below. Identify the level of management in which he belongs to?
Answer:
providing employment.
Question 13.
The visiting card of a person is given below. Identify the level of management in which he belongs to ?
Answer:
Question 14.
Choose the odd one from among the following persons working at different levels of management.
Answer:
(a) Purchase manager
(b) Production manager
(c) Marketing Manager
(d) Managing director
Answer:
(d) Managing director
Question 15.
Administrative functions are mainly performed by
(a) Top management
(b) Middle management
(c) Operational management
Answer:
(a) Top management
Question 16.
Mr. Arun is working as a supervisor. Identify the level of management he is working.
Answer:
Lower level management
Question 17.
Policy formulation is the function of
(a) Top-level managers
(b) Middle-level managers
(c) Operational managers
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Top-level managers
Question 18.
Which is not a function of management of the following?
(a) planning
(b) staffing
(c) co-operating
(d) controlling
Answer:
(c) co-operating
Question 19.
The following is not an objective of management
(a) earning profits
(b) growth of the organisation
(c) providing employment
(d) policymaking
Answer:
(c) providing employment
Question 20.
Identify the management function integrating the activities of different units of an organisation to achieve the organisational goals.
Answer:
Co-ordination
Question 21.
Which among the following is not an element of co-ordination?
(a) Integration
(b) balancing
(c) proper timing
(d) Direction
Answer:
(d) Direction
Question 22.
Co-ordination is
(a) Function of management
(b) The essence of management
(c) An objective of management
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) The essence of management
Question 23.
Identification and grouping of activities to be undertaken and assigning them to different departments is (Planning, Directing, Organising, Co-ordinating)
Answer:
Organising
Question 24.
Which of the following is correct to the concept of the levels of management?
(a) Board of Directors come under the category of. middle-level management.
(b) Middle-level management plans day-to-day activities.
(c) Lower level management is also known as supervisory management.
(d) Top-level management is accountable to employees.
Answer:
(c) Lower level management is also known as supervisory management.
Question 25.
Which of the following is ‘not’ a function of Middle-level management?
(a) Reporting to top management.
(b) Participate in operational decisions.
(c) Lays down the objectives of the enterprise
(d) Directing the managers at lower levels.
Answer:
(c) Lays down the objectives of the enterprise
Question 26.
Mr. Goutham Krishna is the Production Manager of a joint stock company and he is always maintaining a close watch on day-to-day performance of his department. Identify the level of management he belongs to.
Answer:
Middle level management
Question 27.
Management is multidimensional. Which of the following is not a right statement?
(a) Management of machinery
(b) Management of work
(c) Management of people
(d) Management of operation’s
Answer:
(a) Management of machinery
Question 28.
The presence of management can be felt in the way the organisations’ functions. Which characteristics of management is mentioned here?
Answer:
Management is intangible
Question 29.
Which among the following is not an organisational objective of management?
(a) Existence
(b) Profit
(c) Creating employment opportunities
(d) Growth
Answer:
(d) Growth
Question 30.
Select the right pairfrom the following.
(a) Managing Director – Lower level management
(b) Production Manager-Top level management
(c) Foreman – Middle-level management
(d) Purchase Manager – Middle-level management
Answer:
(d) Purchase Manager – Middle-level management
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Two Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In which level of management, the given persons are working?
(a) Supervisor
(b) Department heads
(c) General Manager
(d) Managing Director
Answer:
(a) Lower level
(b) Middle level
(c) Top-level
(d) Top-level
Question 2.
Management is a series of continuous interrelated functions. Comment.
Answer:
Management is a continuous process of planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling. All these functions are interrelated.The success of a business organisation depends on the effective performance of all the managerial functions.
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Three Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mr. N S. Nair has retired as the director of a company.
- At what level of management was he working?
- What functions do you think he was performing at that level?
Answer:
1. He was working in Top-level Management
2. Top Management:
It consists of chairman, the Chief Executive Officer, Board of Directors, Managing Director, etc.
Functions of Top Level Management
- Lays down the objectives of the business
- Prepares strategic plans and policies
- Appoint middle level managers
- Issues necessary instructions to departmental heads.
- To maintain relations with outside agencies like govt., public, trade unions, etc.
- Co-ordinate and control all the departments in the organisation
Question 2.
Complete the following chart.
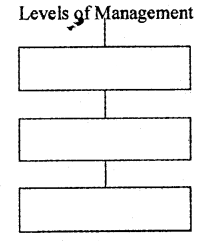
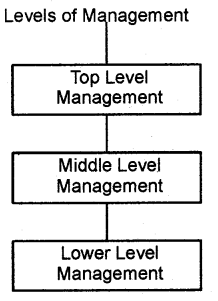
Answer:
Question 3.
“Management is a universal phenomenon.’
- Do you agree with this statement?
- Explain.
Answer:
I agree this statement. Management is universal in character because its principles and techniques are equally applicable in all types of organisation.
Question 4.
What do you mean by efficiency & effectiveness?
Answer:
Efficiency and effectiveness are both commonly used management terms. Efficiency means whatever we produce or perform; it should be done in a perfect way. Efficiency refers to doing things in a right manner. It is defined as the output to input ratio and focuses on getting the maximum output with minimum resources.
Effectiveness has a broader approach, which means the extent to which the actual results have been achieved to fulfill the desired outcome, ie, doing accurate things. Being Effective is about doing the right things while being Efficient is about doing things right.
Difference between Efficiency and Effectiveness:
| Efficiency | Effectiveness |
| 1) Work is to be done in a correct manner | 1) Doing accurate work only |
| 2) Emphasis is on inputs and outputs | 2) Emphasis on means and ends |
| 3) Short-run objective | 3) Long run objective |
| 4) Narrow concept (Introverted) | 4) Wide concept (Extroverted) |
| 5) Aims at strategy implementation | 5) Aims at strategy formulation |
Question 5.
The concept of Management has been interpreted in three different ways. Comment.
Answer:
- Management as a discipline
- Management as a process
- Management as group
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Four Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- Based on authority and responsibility, how the management levels are classified?
- Explain the function of various levels of management.
Answer:
1. Management levels are classified as Top Level Management, Middle-Level Management, and Lower Level Management,
2. Functions of various levels of Management.
There are three levels in the hierarchy of an organisation. They are:
- Top-Level Management
- Middle-Level Management
- Lower-Level Management
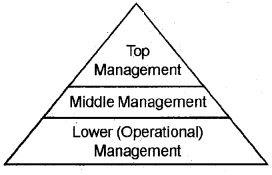
1. Top Management:
It consists of chairman, the Chief Executive Officer, Board of Directors, Managing Director, etc.
Functions of Top Level Management
- Lays down the objectives of the business
- Prepares strategic plans and policies
- Appoint middle-level managers
- Issues necessary instructions to departmental heads.
- To maintain relations with outside agencies like govt., public, trade unions, etc.
- Co-ordinate and control all the departments in the organisation
2. Middle Management:
All the functional epartment heads and branch managers come under the category of middle-level managers. E.g. Production Manager, Sales Manager, Finance manager, etc.,
Functions of Middle-Level Management
- Carry out the plans formulated by the top managers.
- To act as a link between Top Level Management and Lower Level Management.
- Assign necessary duties and responsibilities to the subordinates.
- Motivate them to achieve desired objectives.
- Co-operate with other departments.
- Reporting to top-level management.
3. Lower Management:
This level includes foremen, supervisors, finance and accounts officers, sales officers, etc. This level of managers have direct contact with employees.
Functions of Lower Level Management
- Plan day-to-day production activities.
- Assign workers to different jobs
- Solve the problems of workers
- Provide job training to workers
- Looking after safety of workers.
- Send periodical reports to middle level management.
- Act as a link between management and employees.
Question 2.
Mr. Anand was appointed as a foreman in V. Guard Industries pump division.
- Name the level of Management in which he was appointed.
- What are the various functions he performed there?
Answer:
1. Lower Level Management.
2. Functions of Lower Level Management:
- Plan day-to-day production activities.
- Assign workers to different jobs
- Solve the problems of workers
- Provide job training to workers
- Looking after safety of workers.
- Send periodical reports to middle level management.
- Act as a link between management and employees.
Question 3.
- Name the level of management which has direct contact with operative employees.
- Also mention different functions performed by managers at this level.
Answer:
1. The level of managment which has direct contact with operative employees is lower-level managers.
2. Functions of lower lever management:
- Plan day-to-day production activities.
- Assign workers to different jobs
- Solve the problems of workers
- Provide job training to workers
- Looking after safety of workers.
- Send periodical reports to middle level management.
- Act as a link between management and employees.
Question 4.
Is ‘Management’ a science? Briefly explain.
Answer:
Yes. Management is a science.
Science is a systematised body of knowledge that is based on general truths. The features of science are as follows.
- Science is a systematic body of knowledge.
- Scientific principles are developed through experiments.
- Universal validity and application.
Management can be treated as a science because:
- Management has a systematized body of knowledge.
- Management principles are developed after scientific enquiry, experimentation and observation.
- Management principles are applicable to all types of organizations.
So management is also called science.
Question 5.
“Anything minus management is zero”. Explain the importance of management in light of this statement.
Answer:
Need and Importance of Management
1. Achieving Group Goals:
Efficient management coordinates all the activities for the achievement of organisational goals.
2. Increases Efficiency:
Management helps to reduce costs and increase productivity through better planning, organising, directing, staffing and controlling the activities of the organisation.
3. Creates Dynamic Organisation:
Good management enables the business to adapt and adjust according to the changes in the business environment.
4. Achieving Personal Objectives:
Through motivation and leadership, the management helps individuals to develop team spirit, co-operation and commitment to group success.
5. Development of Society:
Management helps to provide good quality products and services, creates employment opportunities, adopts new technology, etc., for the good of the people and society.
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is your opinion to the statement “management is both an art and a science”?
Answer:
Management can be rightly regarded as both a science and an art. It is a science with a systematised body of knowledge and universal application; It uses certain principles. Management principles are universal. Management is an art because it requires specific skills and experience for the attainment of organisational objectives.
Question 2.
The management function in a circular movement is shown below.
- Re-arrange these management functions in the correct sequence.
- Identify the concept of management depicted by the diagram.
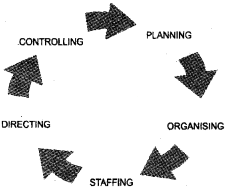
Answer:
1.
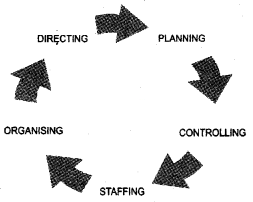
2. Management is a continupus process.
Question 3.
All the functional departmental heads come under this category of management.
- Identify the level of management.
- What are the general functions performed by this level of management?
Answer:
1. Functional departmental heads are middle-level managers.
2. Functions of middle-level managers:
- Plan day-to-day production activities.
- Assign workers to different jobs
- Solve the problems of workers
- Provide job training to workers
- Looking after safety of workers.
- Send periodical reports to middle level management.
- Act as a link between management and employees.
Question 4.
Draw a diagram to show management as a process.
Answer:
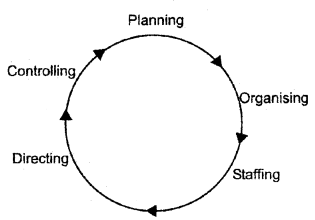
Question 5.
Following are the lists of managerial personnels in an organization. State in which level of management they belong to:
- Foreman
- Departmental management
- General manager
- Supervisor
- Divisional manager
- Chief executive
- Managing director
- Deputy Manager
- Superintendent
- Section Officer
Answer:
- Foreman – Lower level
- Departmental manager – Middle level
- General manager – Top level
- Supervisor – Lower level
- Divisional manager – Middle level
- Chief executive – Top level
- Managing director – Top level
- Deputy manager – Top level
- Superintendent – Lower level
- Section officer – Middle level
Question 6.
In a classroom debate you argue that management is a Profession. What are the points you will raise to substantiate your argument?
Answer:
Management as a Profession :
Profession means an occupation for which specialised knowledge and skills are required. The main features of profession are as follows.
1. Well defined body of knowledge
2. Formal education and training
3. Professional Associations Management is a profession because:
- Management is based on a systematic body of knowledge comprising well-defined principles.
- A manager acquires management skills through formal education and training.
- All professions are affiliated to a professional association which regulates entry and frame code of conduct relating to the profession.
Question 7.
“Co-ordination is the essence of management”. Do you agree? If so why?
Answer:
Co-ordination:
The process by which a manager synchronises the activities of different departments is known as co-ordination. Coordination is the force that binds all the other functions of management.
Importance of Coordination
1. It increases efficiency:
Co-ordination increases organisational efficiency.
2. Key to other functions:
Co-ordination is the key to other managerial functions. Co-ordination makes planning more effective, organisation more well-knit and control more regulative.
3. Functional differentiation:
The process of linking the activities of various departments is accomplished by co-ordination.
4. Unity in diversity:
In an organization, there are large numbers of employees with different ideas, cultures, etc. Coordination brings unity in diversity.
5. Specialisation:
Coordination helps to coordinate the efforts of various specialists in ah organisation.
Question 8.
Mr. Santhosh and Mr. Pradeep are associates with a company. Mr. Santhosh is doing with policy decision in the company and Mr. Pradeep is overseeing the subordinates at work.
- Name the levels of management they engaged in.
- List out the functions of each level?
Answer:
1. Top-level and lower-level management.
2.
a. Top Management:
It consists of chairman, the Chief Executive Officer, Board of Directors, Managing Director, etc.
Functions of Top Level Management
- Lays down the objectives of the business
- Prepares strategic plans and policies
- Appoint middle-level managers
- Issues necessary instructions to departmental heads.
- To maintain relations with outside agencies like govt., public, trade unions, etc.
- Coordinate and control all the departments in the organisation
b. Lower / Supervisory / Operational Management:
This level includes foremen, supervisors, finance and accounts officers, sales officers, etc. This level of managers have direct contact with employees. Functions of Lower Level Management
- Plan day-to-day production activities.
- Assign workers to different jobs
- Solve the problems of workers
- Provide job training to workers
- Looking after safety of workers.
- Send periodical reports to middle-level management.
- Act as a link between management and employees.
Question 9.
Read the following arguments of two students.
Anil: “Management is an ordinary job, which doesn’t require any special knowledge and skill”.
Sunil: Management is a profession, which requires specialised knowledge and skill.”
- Whose argument do you favor?
- Justify your answer.
Answer:
1. Sunil’s argument is correct.
2. Management as a Profession:
Profession means an occupation for which specialised knowledge and skills are required. The main features of profession are as follows.
a. Well defined body of knowledge
b. Formal education and training
c. Professional Associations Management is a profession because:
- Management is based on a systematic body of knowledge comprising well defined principles.
- A manager acquires management skills through formal education and training.
- All professions are affiliated to a professional association which regulates entry and frame code of conduct relating to the profession.
Question 10.
As a commerce student advice your friend about the characteristics and objectives of modern management.
Answer:
a. Characteristics/Nature of Management
1. Management is goal-oriented.
2. Management is universal in character.
3. Management is multidimensional, which include
- Management of works
- Management of people
- Management of operations
4. It is a continuous process.
5. It is a group activity.
6. It is a dynamic function,
7. It is an intangible force.
b. Objectives of Management:
Management fulfills three basic objectives like organisational, social and personal.
1. Organisational Objectives:
Management is responsible for setting and achieving objectives for the organisation.
It includes:
- Survival: Management must strive to ensure the survival of the organisation.
- Profit: Management has to ensure that the organization makes reasonable profit.
- Growth: management must exploit fully the growth potential of the organisation.
Plus Two Business Studies Nature and Significance of Management Eight Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Discuss the functions of management.
Answer:
Functions of Management:
1. Planning:
Planning is the function of determining in advance what is to be done and who is to do it.
2. Organising:
It is the management function of assigning duties, grouping tasks, establishing authority responsibility relationship and allocating resources required to carry out a specific plan.
3. Staffing:
Staffing means finding the right people with the right qualifications to accomplish the goals of the organisation. It involves activities such as recruitment, selection, placement and training of personnel.
4. Directing:
Directing involves leading, supervising, communicating and motivating the employees to perform the tasks assigned to them.
5. Controlling:
It means monitoring organizational performance towards the attainment of organisational goals.
Question 2.
“Management is the function of getting things done, through and with people”. Explain the importance of management in light of this statement.
Answer:
Need and Importance of Management
1. Achieving Group Goals:
Efficient management co-ordinates all the activities for the achievement of organisational goals.
2. Increases Efficiency:
Management helps to reduce costs and increase productivity through better planning, organising, directing, staffing and controlling the activities of the organisation.
3. Creates Dynamic Organisation:
Good management enables the business to adapt and adjust according to the changes in the business environment.
4. Achieving Personal Objectives:
Through motivation and leadership, the management helps individuals to develop team spirit, co-operation and commitment to group success.
5. Development of Society:
Management helps to provide good quality products and services, creates employment opportunities, adopts new technology, etc., for the good of the people and society.
Question 3.
“Co-ordination is the orderly arrangement of group efforts to provide unity of action in the pursuit of a common purpose”. IF\ the light of this statement explain the importance of co-ordination in a business enterprise.
Answer:
Co-ordination:
The process by which a manager synchronises the activities of different departments is known as co-ordination. Coordination is the force that binds all the other functions of management.
Characteristics of Coordination:
- Co-ordination integrates group efforts of different departments
- Co-ordination ensures unity of action
- Co-ordination is a continuous process
- Co-ordination is an all-pervasive function
- Co-ordination is the responsibility of all managers
- Co-ordination is a deliberate function
Importance of Coordination:
1. It increases efficiency:
Co-ordination increases organisational efficiency.
2. Key to other functions:
Co-ordination is the key to other managerial functions. Co-ordination makes planning more effective, organisation more well-knit’ and control more regulative.
3. Functional differentiation:
The process of linking the activities of various departments is accomplished by co-ordination.
4. Unity in diversity:
In an organization, there are large numbers of employees with different ideas, culture, etc. Coordination brings unity in diversity.
5. Specialisation:
Coordination helps to coordinate the efforts of various specialists in ah organisation.
